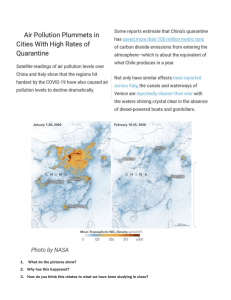
SECTION 2, ANALYSIS INTRODUCTION THE OBJECTIVES OF THIS SECTION • Identifying perspective • Interpreting connection • Making connection • Solving problems GOAL • Identify perspectives and synthesis argument and evidence from a range of source on a given topic • Identify patterns and trends in graphical or numerical data in order to support an argument • Make some links between cause and consequence of an issue at persona, local, and global levels • Recommend an appropriate course of action and explain possible consequences for national or global issue. WHAT IS ANALYSIS? Analysis • Is to look at something in more drtail • May involve understanding different perspectives on a topic or issue or how different causes and consequences are related to one another. • May involve understanding data resented as unmbers or in the form of graphs, charts or tables. KEY POINTS • A cause the reason why something happens. For example, one of the cause of global warming is burning of fossil fuels. • A consequence is the result of something. For example, global warning is the consequence of burning fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas and oil. • An issue is a topic that needs discussion because people have different perspectives about the best way to take action in order to resolve it. • A perspective is a way of looking something, based on evidence. An opinion is what something think and is often unsupported. A viewpoint is the same as an opinion and is someone’s view about something. KEY POINTS • Global is anything relates to the whole world. For example, a global perspectives is a way of looking at a topic that is shared by many people from different countries around the world. • Local is anything relates to a particular place, such as a town or city, a district or region. • National is anything relates to a whole country. • Personal is anything that relates to you as an individual. • Evidence can be in the form of graphs, photos, video clips, audio recordings, and written texts(newspaper/magazine articles, books, leaflet, newsletters, blogs, etc) • Closed questions, such as those requiring ‘yes’ or ‘no’ answers, are easy to analyse, and findings can be presented as a graph. • Open questions often start with ‘why’ and ‘how’ are more difficult to analyse, research findings from open questions are often presented as a summary. • An outcome is a product created as a result of a course of action, for example a leaflet to promote the Paralympics. KEY POINTS