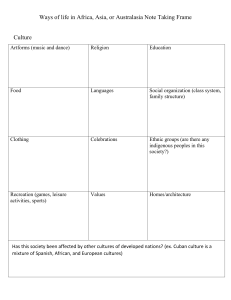
Culture, Identity and Representation Multiculturalism Why do we need multiculturalism? It allows us to have a better understanding of our society, we live in a world where large vast of community have heavily integrated cultures in there society so it's key not just for children but for ourselves to understand cultures. It teaches people about race, cultures, and ethnicity. Multiculturalism in Ecuador Ecuador is a multicultural country, where people of different nationalities and cultures coexist. Indigenous peoples inhabited the country since before the Spanish conquest. Over time, the coexistence of Spanish conquerors with indigenous people produced mestizo descent (Encalada et. Al, 1999, p.2). Currently, miscegenation is a key component for Ecuador and a symbol of national identity (Hidezaku, 2011, p.34). However, the social incorporation of minority groups such as indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants implied a process and a constant struggle that persists to this day. The Ecuadorian Constitution was allowed to recognize in 1998 that indigenous and Afro-Ecuadorians are legally and legitimately differentiated as subjects of cultural and collective rights. In this way, progress was made in the incorporation of rights and guarantees for minorities, which were recognized as an "intrinsic part of the multiethnic and multicultural nation of Ecuador" (Sánchez, 2008, p.90) Is Ecuador a multicultural country? If so why? Which cultures are the most representative? What kind of Greetings do you know? Can it be a problem among people of different cultures? What is Acculturation? Interculturalism Intercultural refers to the plurality of cultures that coexist and share. "To the relationship between cultures." The presence and equitable interaction of diverse cultures and the possibility of generating shared cultural expressions, acquired through dialogue and an attitude of mutual respect ”. Intercultural communication occurs: When individuals influenced by different communities cultures negotiate shared means of interaction ”. Tries to “establish communication bridges in a society. Types of identity: Ascribed identity: • how external people perceive the characteristics of a group. Recognized identity: • what a certain group accepts as its culture. Stages of the intercultural process Encounter: identity, presentation of expectations. Respect: I treat with dignity, I treat like friendly subjects. Listen with respect and free expression of perceptions and beliefs. Horizontal dialogue: Interactions with equal opportunities. Recognition that there is no single truth. Empowerment Building a horizontal "win - win" relationship. Mutual understanding: Understanding of the other (s). Mutual enrichment, attunement and resonance (Capacity and willingness to understand and incorporate what is raised by the other. Empathy. Synergy: Obtaining results that are difficult to obtain from a single perspective and independently. Value of diversity, where one plus one is more than two. Differences In multicultural communities, In cross-cultural communities, In intercultural communities, • we live alongside each other. • It refers to several cultural or ethnic groups living alongside one another but not necessarily engaging with each other. • there is some reaching across boundaries. • It deals with the comparison of different cultures, whereby differences are understood and can bring about individual but not collective change. • there is comprehensive mutuality, reciprocity, and equality. • It focuses on the mutual exchange of ideas and cultural norms and the development of deep relationships. In an intercultural society, no one is left unchanged because everyone learns from one another and grows together.