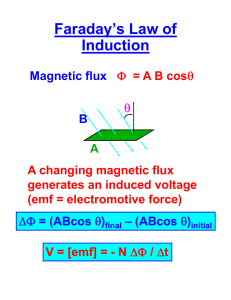
GRADE 11 DAILY LESSON LOG School Teacher Teaching Week DAY 1 Date Section April 25, 2023 (Tue) I. 12-STEM Aguinaldo J. Santos National High School Mary Ann I. Santos FIRST DAY 2 Time Date Section 10:40-11:40 OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards B. Performance Standards C. Learning Competencies /Objectives Unlocking of students difficulties. Mastered the top 10 least learned competencies. April 26, 2023 (Wed) 12-STEM Time 10:40-11:40 Grade Level Learning Area Quarter DAY 3 Date Section 12 General Physics 2 Fourth DAY 4 Time Date Section Time April 27, 2023 (Thurs) 10:40-11:40 12-STEM 10:40-11:40 12-STEM April 28, 2023 (Fri) 1. Use theoretical and, when feasible, experimental approaches to solve multiconcept, richcontext problems using concepts from electromagnetic waves, optics, relativity, and atomic and nuclear theory Identify the factors that affect the magnitude of the induced emf and the magnitude and direction of the induced current (Faraday’s Law) 1. Use theoretical and, when feasible, experimental approaches to solve multiconcept, richcontext problems using concepts from electromagnetic waves, optics, relativity, and atomic and nuclear theory Compare and contrast electrostatic electric field and non electrostatic/induced electric field 1. Use theoretical and, when feasible, experimental approaches to solve multiconcept, richcontext problems using concepts from electromagnetic waves, optics, relativity, and atomic and nuclear theory a. Determine the factors that affect the magnitude of the induced emf and the magnitude and direction of the induced current (Faraday’s Law) b. Perform a simple activityFaraday’s experiment. c. Appreciate the uses of generators or motors. 1. Distinguish the differences between electrostatic and nonelectrostatic electric field, 2. Create a concept map on the similarities and differences of electrostatic and nonelectrostatic electric field, 3. Develop awareness on the importance of electric field on electrostatic and nonelectrostatic. 1. Describe induced electric field, magnetic field, current and Lenz’ Law 2. Illustrate the direction of the induced electric field, magnetic field and current on conducting/non conducting loop using Lenz’ law 3. Realize the importance of knowing the direction of the induced electric field, and magnetic field General Physics 2 Activity Sheet Quarter 4 – MELC 3 Week 1 Force on Current Carrying Wires General Physics 2 Activity Sheet Quarter 4 – MELC 4 Week 1 Magnetic Field Vector at Any Point Along the Axis of Circular Current Loop Calculate the induced emf in a closed loop due to a time-varying magnetic flux using Faraday’s Law Write the LC code for each II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. 1. 2. References Teacher’s Guide pages Learner’s Materials pages General Physics 2 Activity Sheet Quarter 4 – MELC 1 Week 1- Field Due to an Infinitely Long Straight Uniformly Charged Wire 3. 4. 5. Textbook pages Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) portal Other Learning Resources IV.PROCEDURES A. Reviewing the previous lesson or presenting the new lesson Enumerate the top 10 least learned items. 3,9,17,18,20,15,19,21,45,11 What are the contributions of Andre Mari Ampere and Alessandro Volta in the study of electricity? Ask the students about the following What is charges? Present a video presentation Discussion follows Differences between positive and negative charge?. B. Establishing the purpose of the lesson C. Presenting examples/instances of the new lesson Picture Analysis: Picture about electrostatic electric field and nonelectrostatic /induced electric field Guide Question: 1.What the picture all about? 2 What is the negatively and positively charges? Let the learners watch a PHET simulation. The teacher will give the following guide questions: 1 What are the materials used in the experiment? 2.What can you say about direction of the current as poles of magnet move? 3. How can you describe the strength of magnetic flux at different number of turns of wire? 4. How can you describe Faraday’s Law? Video Analysis: Video about electrostatic electric field and nonelectrostatic /induced electric field Guide question: 1.What the video all about? 2.What is the behavior of negatively and positively charges on electrostatic electric field and nonelectrostatic /induced electric field? Let the students to describe what is being shown in the given diagram D. E. Discussing new concepts and practicing skill # 1 Discuss with the students the least learned items. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skill #2 Let the students experience the same experiment done by Faraday. Divide the class into three groups. Distribute the materials needed and explain some precautionary measures. Presentation of output by group. Let each group give /cite their feedbacks to one another. F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment) How induced-current can be produced? G. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living When do we use generators? Do you know how it works? H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson I. Evaluating Learning What are the factors that affect the magnitude of the induced emf and the magnitude and direction of the induced current (Faraday’s Law)? ESSAY: Suppose you are holding a circular ring of wire in front of you and a) suddenly thrust a magnet, south pole first, away from you toward the center of the circle. Is a current induced in the wire? b) Is a current induced when the magnet is held steady within the ring? c) Is a current induced when you withdraw the magnet? For each yes answer, specify the direction. Explain your answers. Give a short test to the students. RUBRICS: (5 points) Exceptional – student responses far exceed what is expected (4 points) Excellent – information is factually accurate and offers extra supporting facts. (3 points) Good – The student somewhat responds beyond the basic level of the Concept Map: Similarities and differences between electrostatic electric field and nonelectrostatic /induced electric field DISCUSS THE Lenz’s Law: emf appears and current flows that creates a magnetic field that opposes the change – in this case an decrease – hence the negative sign in Faraday’s Law. Oral Discussion: What is the similarities and differences between electrostatic electric field and nonelectrostatic /induced electric field Think and Pair Activity 1.negative charge nonelectrostatic 2. positive charge nonelectrostatic 3. negative charge electrostatic 4.positive charge electrostatic What is the importance of nonelectrostatic electric field and electrostatic electric field in electricity and magnetism? Let them to discuss the Lenz’s Law. Let them to illustrate the induced electric field, magnetic field and current (Provided worksheet) Explain the maglev train in the application of magnetic induction Answering sample problem Ask the students to complete the table below: Electrostatic Nonelectrostatic electric field electric field Using the formula 𝐵𝑧 = ( 𝜇𝑜 𝐼𝑦 2 2(𝑧 2+𝑦 2) 3 2 ) complete the table below by predicting the effect of one variable to another variable while keeping other variables constant. question to provide supporting details and or interpretation. (2 points) Fair – student responses, although somewhat correct, are lacking in relevant details and supporting examples and or interpretation. (1 point) Not Mastered - student responses are largely incorrect. J. Additional activities for application or remediation V.REMARKS < VI.REFLECTION Sections A.) No.of learners who earned 80% on the formative assessment B.)No.of learners who require additional activities for remediation. C.)Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson. D.)No. of learners who continue to require. E.)Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F.)What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G.)What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: Checked by: MARY ANN I. SANTOS Teacher III ISABELITA S. CANOZA Assistant Principal II Approved by: JAYPEE DS. ARMENION Principal I