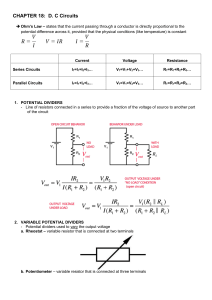
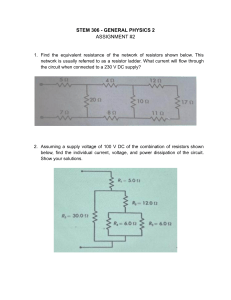
Detailed Lesson Plan INDUSTRIAL ARTS – ELECTRONIC PRODUCT ASSEMBLY AND SERVICING NC II School : Cotmon National High School Teacher : Grade Level : Grade 12 Learning Area : TVL-EPAS Teaching Date and Time : December 5, 2017 7:30 – 9:20 and 1:00 – 3:00 Quarter : 3RD I – OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate an understanding of the underlying principles in testing electronic components based on manufacturer’s specifications and testing criteria B. Performance Standard The learners shall be able to test electronic components based on manufacturer’s specifications and testing criteria C. Lesson/Learning Competency /LC code/Objectives LESSON 7: TESTING ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS (TEC) LO 1. Determine criteria for testing electronics components TLE_IAEPAS9-12TCEC-IIId-e-22 At the end of the session, the students should be able to: 1. Determine how electronic components works 2. Understand the importance of electronic components 3. Select electronic components and give its function II – CONTENT Basic electronic components and how it’s working III – LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages IA-EPAS NC II CURRICULUM GUIDE p. 17 B. Other Learning Resources Power Point Presentation http://leaprobots.com/basic-electronic-components-and-how-its-working/ IV - PROCEDURES A. Preparatory Activities 1. Daily routine/Prayer 2. Checking of attendance 3. Reviewing previous lesson B. Developmental Activities Teacher’s Activity 1 – Motivation What are the two types of electronic components? Passive components are those Do Not have gain or Directionality while Active components are those that have gain or directionality Student’s Activity The two types of electronic components are 1)Passive components and 2).Active components. What are the examples of passive components? How about active components? Resistors, capacitors, Inductors Diode, Transistors, SCR 2 – Presentation Electronic components are specified by their parameters. A parameter is some property of the component that has a numerical value, and describes one feature of the component's performance. The values of a given component's parameters are found in the manufacturer's data sheet and are usually called the "specs" (specifications). Let us review first the basic components and how it works. Resistors: In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Capacitors: A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Capacitors come in several different varieties, the two most common being ceramic disk and electrolytic. The amount of capacitance of a given capacitor is usually measured in microfarads, abbreviated μF. Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. Diodes: A diode is active device that lets current flow in only one direction. A diode has two terminals, called the anode and the cathode. Current will flow through the diode only when positive voltage is applied to the anode and negative voltage to the cathode. If these voltages are reversed, current will not flow. Light-Emitting Diodes: A light-emitting diode (LED) is a two-lead semiconductor light source. It is a p–n junction diode, which emits light when activated. When a suitable voltage is applied to the leads, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is called electroluminescence, and the color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy band gap of the semiconductor. Transistors: A transistor is a three-terminal active device in which a voltage applied to one of the terminals (called the base) can control current that flows across the other two terminals (called the collector and the emitter). The transistor is one of the most important devices in electronics. It is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. Integrated Circuits: An integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or “chip”) of semiconductor material, normally silicon. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip resulted in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, cheaper, and faster than those constructed of discrete electronic components. ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC’s components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) because of their small size and close proximity 3 – Application Ask student to select electronic components and give its function. 4 – Evaluation 1. Compare passive and active electronic components. 2. Give the function of the following components: A. Resistor B. Capacitor C. Diode D. LED E. Transistor F. IC V – REMARKS VI – REFLECTION A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation. ___________ B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% ____ C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. Of learners who have caught up with the lesson. _______ D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation. _________ E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? ________________________________________________________ F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? ________________________________________________________ G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? ___________________________________________ Prepared by: .l