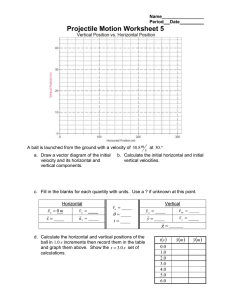
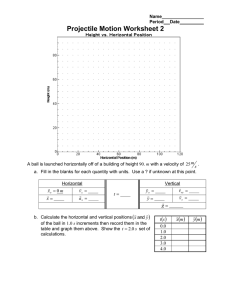
Departamento de Engenharia Física da FEUP Física I / L.EIC - Test, 20-04-2023 DURATION: 1h 00min LKGAH COMPLETE NAME (CAPITAL LETTERS): Smartwatches and smartphone are forbidden. Electronic calculator is not allowed. The test has 10 multiple-choice questions. Mark for a correct answer is +2.0, and for wrong answer is -0.4 There is only one correct option. Multiple answers to a given question are not evaluated. Otherwise indicated, SI units are used. Consider g =10 ms−2 . Other values: cos 60◦ = sin 30◦ = 1/2; sin 60 1. A stone is thrown vertically up to a maximum height of 5 m. Assuming there is no air resistance, the initial speed of the stone is: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (c) (d) (e) √ = cos 30◦ = 3/2. 3. Consider a mass moving horizontally along the xx axis, where its accelaration a varies with its speed v , as a(t) = 2v(t). If the mass is initially at x = 0 with a speed v0 , the equation of its motion x(t) is given by: 2 m/s. 4 m/s. 6 m/s. 8 m/s. 10 m/s. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2. The initial vector velocity of a projectile has an angle of 60◦ above the horizontal. If the initial speed is 10 m/s, which of the sentences below is true when the projectile reaches its maximum height? (a) (b) ◦ x(t) = v0 t + at2 /2. x(t) = tv(t). v0 x(t) = (e2t − 1). 2 x(t) = v0 t(et − 1). x(t) = v0 t(et − 1)/2. 4. In a 2-D motion, the velocity of a given body is desribed by ~v (t) = 2tı̂ + 4̂. If the initial position of this body is ~r0 = ı̂, which of the following expressions relates the horizontal position x with the vertical one y at a given time t? The speed is 10 m/s. The speed is 5 m/s. √ (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) The speed is 5 3 m/s. The horizontal component of the velocity is zero. The horizontal component of the velocity is 5 m/s. 1 x = 1 − y2 . x = 1 + y2 . x = 1 + y 2 /4. x = 1 + y 2 /8. x = 1 + y 2 /16. 2/1 5. A particle with a mass m = 2 Kg, moves without friction along the xx axis. If the potential energy of this particle is given by Ep (x) = −3x3 + x4 J, what will be its speed when x = 1 m, if its mechanical energy is 7 J? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 0 m/s. 1 m/s. 2 m/s. 3 m/s. 10 m/s. F⃗2 m 6. A particle, initially at rest, is released from an incline from a height of 10 cm. Assume there is no frictional force between the particle and the surface of the ramp. When the particle reaches the bottom, it continues to move horizontally during 1 m and then stops. Under these conditions, what is the coecient of kinetic friction between the particle and the horizontal surface? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 8. A heavy block with m = 600 kg, standing on ice, is pulled by two ropes making an angle of 60◦ (see gure). The magnitude of the constant force applied to each rope is 1 N. If the block is initially at rest, what will be its speed after moving 2 m? F⃗1 x (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 0.1 m/s. 0.5 m/s. 2 m/s. 10 m/s. 15 m/s. 9. A block with a mass m1 is on an incline (α = 30◦ ) and is attached by a massless string to other block with a mass m2 (see gure). The fricitional force between block m1 and the surface is negligible. What is the relation between the two masses if the two blocks do not move? 0.9. 0.1. 0.25. 0. 0.7. 7. Consider two blocks (seee gure) with masses m1 and m2 . There is a frictional force only between block m2 and the horizontal surface, where µe and µc correspond respectively to the static and kinetic coecients of friction. When a force F~ is applied to block m1 , the two blocks move together. The accelaration of block 2 is given by: F~ 60◦ m1 m2 (a) 2(µe m1 g+F ) . 3m2 (b) F −µc m2 g m1 +m2 . (c) F −µc m1 g . m2 (d) F m2 . (e) F m1 +m2 . x m1 m2 α (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) √ m2 = m1 / 2. m2 = 2m1 . m2 = m1 /3. m2 = m1 /4. m2 = m1 /2. 10. Under the conditions of the previous problem, consider now that the masses are equal: m1 =m2 . If block 2 is initially at rest, what would be its speed after falling down 20 cm? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2 m/s. 1 m/s. 0.5 m/s. 0.1 m/s. 0 m/s. 1/1 Answer Key for Exam A 1. (e) 6. (b) 2. (b) 7. (b) 3. (c) 8. (a) 4. (e) 9. (e) 5. (d) 10. (b)