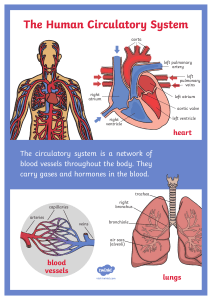
3ºESO BIOLOGÍA-GEOLOGÍA PROFESOR: PABLOALCARAZ NOTES UNIT 4: NUTRITION: CIRCULATORY AND RESPIRATORYSYSTEMSCHAPTER 1 : INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT & BLOOD INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT It is the liquid environment that surrounds all body cells and with which they exchangesubstances: nutrients and waste. Different parts: 1) INTERSTITIAL PLASMA: fluid in between the cells of every tissue. Pass nutrients intocells andreceive their waste products. This is constantly rennovated by: 2) BLOOD. Carry and pass nutrients + fluid into the interstitial plasma and removes wastesubstances from it. Nutrients don’t run out for cells and toxic waste molecules don’t accumulate(their concentration stay constant). Composition and functions: → Blood plasma: liquid, 90% water, 10% disolved substances (minerals, all nutrients,waste products, hormones...). Transport waste. → Blood cells: solid. Types: - Red blood cells (The most abundant. Transport oxygen attachedto their haemoglobin protein, as well carbon dioxide). - White blood cells (The least abundant. Defend against infectionand deasease (destroy phatogens). - Plateletes (coagulate blood to stop bleeding). Blood moves through the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM, connecting the other 3 systems involvedinnutrition: digestive, respiratory and excretory. CHAPTER 2: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (BLOOD CIRCULATION) 2.2. BLOOD VESSELS Blood flows within these tubes/ducts. (bloodstream = torrente sanguíneo). Arteries Capillaries Take blood out fro the heart. Reach and connect w body tissues. Veins Take blood back totheheart. a Thick and elastic muscularwalls. Microscopic vessels. Very thin walls, (single-celled). Thin walls with valves(toprevent fromcoming back. It only travelsdirection). Branch into smaller Small branches calledvenules Allow molecules tooutside and vessels:arterioles. (exchange). pass join to formveins. inone Each organ has an artery coming and a vein leaving it. 3ºESO BIOLOGÍA-GEOLOGÍA PROFESOR: PABLOALCARAZ 2.2. THE HEART Pumps blood (=bombear) Organ with thick wall of muscle tissue Hollow (=hueco) Divided in 2 halves not connected (right & left) Each half with 2 chambers: atrium (upper), ventricle (lower) Parts and blood vessels: *(write them in an schematic drawing) Pulmonary veins (4 veins) Left atrium (pl. atria) Vena cava (2 veins) Right atrium Right “atrium→ventricle” valve Left “atrium→ventricle” valve Left ventricle Right ventricle Right “ventricle→artery” valve (= Semilunar valve) Left “ventricle→artery” valve (= semilunarvalve) Pulmonary artery THE HEARTBEAT (= latido Aorta artery cardiaco) Continuous movement of the heart pumping Heart frecuency (= frecuencia card.) = nº heartbeats/minute (average when resting: 70beats/min)Contraction-relaxation phases: Both right and↓ 1st) Atrial systole 2nd) Ventricular systol 3rd) Diastole left Atria contract relax “atrium→ventricle” valves open close Ventricles “ventricle→artery” contract valves Blood move open a ventricles ventricles (pulmonar & relax close veins (cava &pulmo arteri →atria aorta) (collect/suckblood) Blood pressure (=tensión arterial): blood presses with more force the walls of arteries, soas bloodgoes through them there is a wave of tension on their flexible walls = pulse (=pulso). 2.3. BLOOD CIRCUITS. Circulation is: 1) DOUBLE: to complete the whole round blood passes twice through the heart , each timegoingout and back through a different circuit: *(draw it in your schema) General circuit (larger) Pulmonary circuit (smaller) Right ventricle → pulmonary art. → arterioles → left ventricle →aorta art. →arterioles → → capillaries (exchage with alveoli air: give CO2 , → capillaries (exchage with all bodyorganstake O2) → venules → pulmonary veins → left tissues-cells: give nutrients &O2, takewaste& atrium CO2) → venules →cava v. →right atrium 2) COMPLETE: oxygenated and deoxygenated blood do not mix. 3) CLOSED: blood/cells don’t go out from vessels. Only blood plasma is filtered out to intercellularmatrix. 3ºESO BIOLOGÍA-GEOLOGÍA PROFESOR: PABLOALCARAZ CHAPTER 3: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM - It is part of both immune system + circulatory system but with different vessels. - Transports lymph (=linfa): transparent liquid with lymphatic plasma + lymphocytes (whitebloodcells). - Not moved by the heart (no pump). - It is NOT a closed system: thin lymphatic vessels are closed at one end (=ciegos) andhaveonlyone way of transport: from tissues/intestitial plasma → lymphatic vessels →blood inveins. - It has 2 lymphatic organs (thymus & spleen = timo y bazo) and lymph nodes (=gánglios linfáticos)all around like in the armpit=axila, groin=ingles and neck. They produce lymphocytes &cleantheblood. - FUNTION: 1) Maintain the liquid equilibrium/balance of the internal environment (collect, cleanandreturn excess plasma from tissues to blood). 2) Helps to defend the body from infection. CHAPTER 4: EXCRETORY SYSTEM It is the group of organs that eliminate waste products, produced by cell activity, out fromthebody. WASTE PRODUCTS (toxic if accumulated): - Carbon dioxide (from cell respiration with which we obatin energy). - Urea (from protein destruction) - Uric acid (from nucleic acid destruction) - Toxic substances (from alcohol, drugs, medicines...) ORGANS 1) Respiratory system: Removes CO2 from the blood. 2) Liver: removes (or stores away) some of the extra cholesterol, other toxins substances (fromalcohol, medicines) and the bilirrubin (from hemoglobin/red blood cells destruction). 3) Sweat glands: Keep the skin cool and also realease waste substances. 4) URINARY SYSTEM (aparato urinario): excretion through urine. Organs: kidneys &urinarytract↓ KIDNEYS We have two. Structure: - Cortex (corteza): external part. - Medulla: internal part. - Pelvis: cavity (funnel) which collects urine from nephrons. - NEPRHONS (nefronas): small tubes that filter blood to form urine (=liquid with water, mineral salts, urea and uric acid). Over a million per kidney. Located alongcortexand medulla. 3ºESO BIOLOGÍA-GEOLOGÍA PROFESOR: PABLOALCARAZ NEPHRON PARTS & URINE FORMATION: *(write them in an schematic drawing) → Capsule: rounded “tube” + contains a folded capillary (glomérulo). 1st STEP: FILTRATION. Water, mineral salts, other usefull molecules (vitamins, glucose...) and waste molecules (urea, uric acid) pass from the capillary blood into the capsule tube. → Twisted tubule (túbulo): long twisted tube. In the middle part it has a loop(asa). 2nd STEP: REABSORPTION. Moving along the tubule muchof the filtered substances return to blood in the capillaries aroundit: all the useful molecules and most of the water and mineral salts (not all, to keep its equilibrium back in the inner environment). But ureaanduric acid don’t reabsorb. it continues in the urinary tract, forming 1ml of urine every 125ml of filtered blood. Tubules end in collecting ducts: bigger tubes that collect urine frommany nephronsand channel it into the pelvis. 3rd STEP: COLLECTION. URINARY TRACT *(draw it in your schema) - Ureters: two narrow tubes. Connect the two kidneys to the bladder. - Bladder: elastic sac. Accumulates urine. When full, there is an involuntarily contractionreflex(ofits smooth muscle) that propells urine towards the urethra. But it can be controlledvoluntarily. - Urethra: tube that carries urine out of the body. It has an involuntarily sphincter (esfínter, músculo) that only opens after the previous reflex. Only in men it’s a shared duct with thereproductive system, and it is longer than in women.