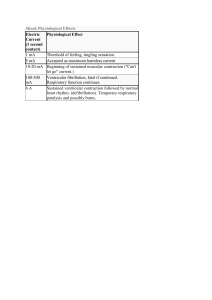
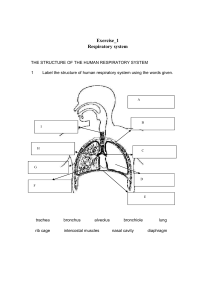
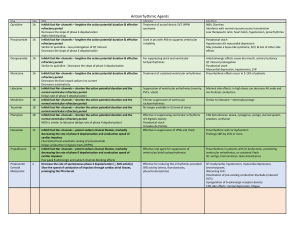
Learning objectives Tuesday, March 22, 2022 11:42 PM 1. Describe and observe the sounds that a normal heart makes. • S1 is AV node closing, after QRS, ventricular systole, lub • S2 is semilunar valve closing, after t wave, ventricular diastole, dub 2. Describe the relationship between the first and second heart sounds and the phases of the cardiac cycle. 3. Record and analyze heart physiology data via ECG and PCG. • Small first hump is P wave: atrial depolarization • QRS: Q is dip, R is spike, S is dip, ventricle depolarization and atrial repolarization • Last hump is T wave, ventricle repolarization 4. Define systolic and diastolic blood pressure. • Systolic is max bp, top number, ventricular contraction (depolarization, systole) • Diastolic is min bp, bottom number, ventricular relaxation (repolarization, diastole) 5. To accurately determine a subject’s blood pressure with a sphygmomanometer. 6. To manually determine a subject’s pulse. 7. To describe changes in pulse and blood pressure that occur with a change in position. • Bp drops when standing after laying down bc gravity slows venous return 8. List and describe the major components of whole blood including their relative abundance. • Plasma, leukocytes (least), erythrocytes (2nd most, large volume), platelets (most, small volume) 9. List and describe the normal components of plasma • 92% water, 7% proteins, 1% other 10. Identify (via figures or virtual microscope), classify and characterize each of the types and subtypes of the formed elements: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. 11. Associate the relative abundance of white blood cells to common disease states. • HIV, low lymphocytes • Mononuclosis, abnormally shaped lymphocytes • Bacterial infection, neutrophil 12. List and describe common blood types along with the clinical importance of this information. • A: antigen A, antibody B • B: antigen B, antibody A • AB: antigen A and B, no anibody • O: no antigens, a and B antibodies • Rh+: d present • Rh-: d absent 13. Conduct blood typing on synthetic blood samples. 14. Identify major respiratory system structures on a model, diagram, or dissected material. 15. Identify major features of tracheal or lung tissue on a microscope slide and describe their functions. 16. Explain how pressure gradients account for flow of air into and out of the lungs and how those gradients are produced • Inspiration: intra-alveolar volume < atmospheric volume, respiratory structure volume increase, pressure decrease • Expiration: intra alveolar volume > atmospheric volume, respiratory structure volue decrease, pressure increase 17. Define the components of, and perform, common clinical measurements of respiratory rate, pulmonary volume, and pulmonary capacity. 18. Describe how common activities affect respiratory rate.