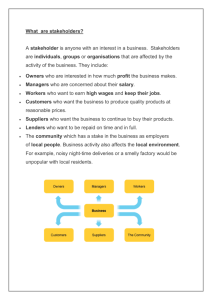
10 principles Scalability It is the capability of a system, network, or process to handle a growing amount of work, or its potential to be enlarged in order to accommodate that growth. Big Ideas A small business is no more effective that the idea upon which is built. The entrepreneur’s vision is more important to the life of the business than anything else. Systems You must recognize that a small business is a system in which all parts contribute to the success or failure of the whole. In this system, everything must work together: from employee to president; from equipment to resources. Sustainability A business must be dynamic-able to thrive through all economic conditions, in all markets, providing meaningful, highly differentiated results to all of its customers. Such as differentiation is key to survival. Growth All businesses need internal growth. A small business is a school in which its employees are students, with the intention, will, and determination to grow. Vision It is meant to exemplify the mission is was intended to fulfill Purpose A small business is a fruit of higher aim in the mind of the person who conceived it Autonomy A business is not part of the owner's life, but is, in fact, its own entity. A small business possesses a life of its own, in the service of God, in whom it finds reason. Profitability A small business is an economic entity, driving an economic reality, creating an economic certainty for the communities in which it thrives. Standards A small business creates a Standard against which all small businesses are measured as either successful, or not. All small businesses should aim to thrive beyond the standards that formerly existed. Tools in evaluating a business 1. SWOT A SWOT analysis is defined as a set of methods used to examine both internal and external factors that affect the performance of a company. This analysis is mostly applied in the initial stages before the company launches any new plans, especially strategic marketing plans. 2. PEST analysis This analysis PEST standing for Political, Economic, Sociological, and Technological is a method used to analyze the outside impacts on the performance of any enterprise. 3. MOST analysis This method is suitable for any company looking for performing internal analysis since it helps the owners sure that they are on the right pattern. The name MOST is an acronym for mission, objectives, strategies, and tactics. 4. Heptalysis This is a model that studies the important factors of a business venture at the beginning of assessment process. This analysis is completed by analyzing 7 fundamental elements which are; market opportunity, product or solution, execution plan, financial engine, human capital, potential return, and margin of safety. 5. De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats This method is mostly suitable when you want some new ideas for your business. Using this analysis during brainstorming process helps you generate different ideas and examine them to figure out the most appropriate one. 6. Catwoe This business analysis used to force businessmen to brainstorm their goals within limited time. There are 6 essential factors: customers, actors, transformation process, world view, owners, and environmental constraints to make this analytical tool, which also make up the acronym for its name. 7. Five whys This analytical tool is usually applied when the company wants to identify the causes of a problem. It provides the owners the general overview about what is really happening to their businesses. 8. MoSCoW A business often chooses this analytical tool when they have numerous tasks to handle and they need to decide which task will receive priority. By listing the tasks and analyzing them, business owners can quickly make decision based on the validity of requirements for each task. 9. SCRS analysis Another useful business analytical tool is SCRS. Using this method, it means that the company will follow the order of the current state and requirements from a business strategy to look for suitable solutions. 10. VPEC-T analysis This analysis allows users to make decision when they have to examine different expectations from several opinions about a system. The name of this tool stands for values, policies, events, content, and trust. Tools in Evaluating a Business It's the Holy Grail for small business owners – finding ways to make efficiency savings in all aspects of their operations. The good news isthere are plenty of tools, tips and techniques available to help them make cost savings and boost productivity. Here are 10 of them. 1. Use technology to speed up workflow- Businesses should be look-ing to innovations in technology to solve day-to-day inconveniences and to increasee efficiency. 2. Shorter meetings fuel efficiency- Hold a brief meeting standing up,every morning, where each person explains what they are going to work on that day to ensure everyone is on the right track and not wasting time on non-urgent tasks. 3. Smart office space pays- Office space can involve a big outlay for SMEs, but it is also an area where some smarter thinking can make a real difference. 4. Advertisement- Advertising keeps your business top of mind so consumers think of it when they require or need a service or product. 5. Small changes, big savings--One way of improving efficiency is for business owners to make small changes to the way they handle their company's expenses.6. Keep a firm grip on cash flow-"Cash is King not profit”. Ensure the right management of your inflow and outflow of cash. 7. Stay connected on the move- The growing trend towards mobileand flexible working means that employees are permanently con-nected and on the go. 8. Use time more efficiently-Being more efficient is more about beingthan doing. It's probably 90% mindset, (Allan, 2013). In addition,“The shorter the amount of time you allow yourself, the more you willget done”. 9. Get the best deal on insurance- Businesses need insurance be-cause it helps cover the costs associated with property damage andliability claims. 10. Don't be lax with the legalIn the hectic process of starting up a business, the founders oftenput off sorting out the legal matters until later, or not at all.