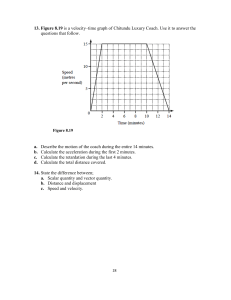
Force and Motion PREPARED BY: TYPE YOUR NAME HERE S7FE - IIIa - 1 Describe the motion of an object in terms of distance or displacement, speed or velocity, and acceleration Force and Motion Standards Students will investigate the relationship between force, mass, and the motion of objects. a. Determine the relationship between velocity and acceleration. b. Demonstrate the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object in terms of gravity, inertia, and friction. Essential Question: What is the relationship between velocity and acceleration? Supporting Questions: How can motion of an object be determined by a graph? Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Goals: To investigate what is needed to describe motion completely. To compare and contrast speed and velocity. To learn about acceleration. An object is in motion if it changes position relative to a reference point. Objects that we call stationary— such as a tree, a sign, or a building—make good reference points. The passenger can use a tree as a reference point to decide if the train is moving. A tree makes a good reference point because it is stationary from the passenger’s point of view. Describing Motion Whether or not an object is in motion depends on the reference point you choose. DISTANCE VERSUS DISPLACEMENT The word “quantity” is used to describe a large amount or number of something while the word “unit” is also used to describe a number of things. “Quantity” is used when referring to an indefinite number while “unit” is used when referring to a definite number of things. QUANTITY UNIT DISTANCE Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to "how much ground an object has covered" during its motion. Distance here will be = 4m + 3m + 5m = 12 m Distance here will be = 4m + 3m + 5m = 12 m Distance is the total movement of an object without any regard to direction. We can define distance as to how much ground an object has covered despite its starting or ending point. Distance is the actual path length travelled by an object in the given interval of time during the motion. It is a positive scalar quantity. Displacement Displacement is defined as the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity and has a direction and magnitude. It is represented as an arrow that points from the starting position to the final position. For example- If an object moves from A position to B, then the object’s position changes. This change in position of an object is known as Displacement. Displacement is the difference between the final and initial positions of the object in a given interval of time. It can also be defined as the shortest distance between these two positions of the object and its direction is from the initial to final position of the object, during the given interval of time. It is a vector quantity. Pytagorean Theorem PYTAGOREAN THEOREM Assume your school is located 2 km away from your home. In the morning you are going to school and in the evening you come back home. In this entire trip what is the distance travelled and the displacement covered? DISTANCE= 4km DISPLACEMENT= 0 John walks from the point A to B to C. What does the distance he travel? What is the displacement? DISTANCE= 7m DISPLACEMENT= 5m DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance When an object moves, it goes from point A to point B – that is the DISTANCE it traveled. (SI unit is the meter) Distance is how much ground an object has covered during its motion. B A Distance Distance (d) – how far an object travels. Does not depend on direction. Imagine an ant crawling along a ruler. What distance did the ant travel? 0 cm 1d = 3 cm2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Distance Distance does not depend on direction. Here’s our intrepid ant explorer again. Now what distance did the ant travel? 1 2 3 4 5 0 cm d = 3 cm Does his direction change the answer? 6 7 8 9 10 Distance Distance does not depend on direction. Let’s follow the ant again. 0 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 What distance did the ant walk this time? d = 7 cm 10 Displacement Displacement (d) – difference between an object’s final position and its starting position. Does depend on direction. Displacement = final position – initial position d = dfinal – dinitial In order to define displacement, we need directions. Examples of directions: + and – N, S, E, W Angles Displacement vs. Distance Example The ant walked 3 cm. Example The An of distance: of displacement: ant walked 3 cm EAST. object’s distance traveled and its displacement aren’t always the same! Displacement Let’s revisit our ant, and this time we’ll find his displacement. - + Distance: 3 cm 0 Displacement: 1 2 +3 cm 3 4 5 cm The positive gives the ant a direction! 6 7 8 9 10 Displacement Find the ant’s displacement again. Remember, displacement has direction! - + 0 Distance: 1 3 32cm cm Displacement: -3 cm 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Displacement Find the distance and displacement of the ant. - + Distance: 7 cm Displacement: +3 cm 1 2 3 0 cm 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Displacement vs. Distance An athlete runs around a track that is 100 meters long three times, then stops. What is the athlete’s distance and displacement? Distance = 300 m Displacement = 0 m Why? DISPLACEMENT DISTANCE IS VECTOR IS A SCALAR Speed Speed (s) – Rate at which an object is moving. speed = distance / time s = d/t Like distance, speed does not depend on direction. Speed A car drives 100 meters in 5 seconds. 1s 2 3 4 5 100 m What is the car’s average speed? s = d/t s = (100 m) / (5 s) = 20 m/s SPEEDOMETER Speed A rocket is traveling at 10 m/s. How long does it take the rocket to travel 30 m? Speed A racecar is traveling at 85.0 m/s. How far does the car travel in 30.0 s? Velocity Velocity (v) – speed with direction. velocity v = displacement / time = d / t Has magnitude and direction! Magnitude – a measure that has a value What is the velocity of a rocket that travels 8000m in 13s travelling to the south? QUIZ TIME 1. A car travels at uniform velocity a distance of 100 m in 4 seconds. What is the speed of the car? 2. If a sprinter runs 100 m in 10 seconds, what is his average velocity? 3. What is the velocity of a rocket that travels 8000m in 13s travelling to the south? 4 . How long will it take if you travel with an average speed of 100m/s? 5. A boy walks at a speed of 4 kmph. How much time does he take to walk a distance of 20 km? 6. A cyclist covers a distance of 15 miles in 2 hours. Calculate his speed. 7. Victor covers 210 km by car at a speed of 70 km/hr. find the time taken to cover this distance. 8. A plane’s average speed between two cities is 600km/hr. If the trip takes 2.5hr/ how far does the plane fly? Speed Calculating Speed: If you know the distance an object travels in a certain amount of time, you can calculate the speed of the object. What is instantaneous speed? Instantaneous speed is the velocity of an object at a certain time. Speed = Distance/time Average speed = Total distance/Total time Velocity Because velocity depends on direction as well as speed, the velocity of an object can change even if the speed of the object remains constant. The speed of this car might be constant, but its velocity is not constant because the direction of motion is always changing. Velocity Velocity is a description of an object’s speed and direction. As the sailboat’s direction changes, its velocity also changes, even if its speed stays the same. If the sailboat slows down at the same time that it changes direction, how will its velocity be changed? Speed v. Velocity How are speed and velocity similar? They both measure how fast something is moving 1. 2. How are speed and velocity different? Velocity includes the direction of motion and speed does not (the car is moving 5mph East) Is velocity more like distance or displacement? Why? Displacement, because it includes direction. 3. Graphing Speed D I S T Speed increasing Object begins moving at a different speed A N Object is stopped C E TIME The steepness of a line on a graph is called slope. The steeper the slope is, the greater the speed. A constant slope represents motion at constant speed. Using the points shown, the rise is 400 meters and the run is 2 minutes. To find the slope, you divide 400 meters by 2 minutes. The slope is 200 meters per minute. Formula for Calculating Speed Speed = Distance time Problem Solving: Calculating Speed What is the speed of a sailboat that is traveling 120 meters in 60 seconds? Step 1: Decide what the problem is asking? A boat traveled 120 meters in 60 seconds. What was the speed of the boat? Step 2: What is the formula to calculate speed? Speed = Distance/Time Step 3: Solve the problem using the formula: Speed = 120 meters 60 seconds = 2 m/s So, the boat was traveling at 2 m/s Now you try: What is the speed of a car that is traveling 150 miles in 3 hours? Answer: Step 1: What are the facts in the problem? A car is traveling 150 miles in 3 hours. Step 2: What is the formula to solve the problem? Speed = Distance/Time Step 3: Solve the problem. Speed = 150 miles 3 hours Speed = 50 miles/hr. So, the car is traveling 50 miles/hr. Acceleration Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. Acceleration can result from a change in speed (increase or decrease), a change in direction (back, forth, up, down left, right), or changes in both. The pitcher throws. The ball speeds toward the batter. Off the bat it goes. It’s going, going, gone! A home run! Before landing, the ball went through several changes in motion. It sped up in the pitcher’s hand, and lost speed as it traveled toward the batter. The ball stopped when it hit the bat, changed direction, sped up again, and eventually slowed down. Most examples of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. Understanding Acceleration 1. As the ball falls from the girl’s hand, how does its speed change? 2. What happens to the speed of the ball as it rises from the ground back to her hand? 3. At what point does the ball have zero velocity? When it stops and has no direction. 4. How does the velocity of the ball change when it bounces on the floor? You can feel acceleration! If you’re moving at 500mph east without turbulence, there is no acceleration. But if the plane hits an air pocket and drops 500 feet in 2 seconds, there is a large change in acceleration and you will feel that! It does not matter whether you speed up or slow down; it is still considered a change in acceleration. In science, acceleration refers to increasing speed, decreasing speed, or changing direction. A car that begins to move from a stopped position or speeds up to pass another car is accelerating. A car decelerates when it stops at a red light. A water skier decelerates when the boat stops pulling. A softball accelerates when it changes direction as it is hit. Calculating Acceleration Acceleration = Change in velocity Total time So…Acceleration = (Final speed – Initial speed) Time Calculating Acceleration As a roller-coaster car starts down a slope, its speed is 4 m/s. But 3 seconds later, at the bottom, its speed is 22 m/s. What is its average acceleration? What information have you been given? Initial speed = 4 m/s Final Speed = 22 m/s Time = 3 s Calculating Acceleration What quantity are you trying to calculate? The average acceleration of the roller-coaster car. What formula contains the given quantities and the unknown quantity? Acceleration = (Final speed – Initial speed)/Time Perform the calculation. Acceleration = (22 m/s – 4 m/s)/3 s = 18 m/s/3 s Acceleration = 6 m/s2 The roller-coaster car’s average acceleration is 6 m/s2. Graphing acceleration S P E Object accelerates Object decelerates E D Object moves at constant speed Time Now You Try: A roller coasters velocity at the top of the hill is 10 m/s. Two seconds later it reaches the bottom of the hill with a velocity of 26 m/s. What is the acceleration of the coaster? Since the slope is increasing, you can conclude that the speed is also increasing. You are accelerating. Distance-VersusTime Graph The curved line on this distance-versus-time graph tells you that the cyclist is accelerating. Acceleration Problems A roller coaster is moving at 25 m/s at the bottom of a hill. Three seconds later it reaches the top of the hill moving at 10 m/s. What was the acceleration of the coaster? Initial Speed = 25 m/s Final Speed = 10 m/s Time = 3 seconds Remember (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time is acceleration. (10 m/s – 25 m/s) ÷ 3 s = -15 m/s ÷ 3 s = -5 m/s2 This roller coaster is decelerating. A car’s velocity changes from 0 m/s to 30 m/s in 10 seconds. Calculate acceleration. Final speed = 30 m/s Initial speed = 0 m/s Time = 10 s Remember (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time is acceleration. (30 m/s – 0 m/s) ÷ 10 s = 30 m/s ÷ 10 s = 3 m/s2 A satellite’s original velocity is 10,000 m/s. After 60 seconds it s going 5,000 m/s. What is the acceleration? Remember (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time is acceleration. Final speed (velocity) = 5000 m/s Initial speed (velocity) = 10,000 m/s Time = 60 seconds (5000 m/s – 10,000 m/s) ÷ 60 s = -5000 m/s ÷ 60 s = -83.33 m/s2 **This satellite is decelerating. If a speeding train hits the brakes and it takes the train 39 seconds to go from 54.8 m/s to 12 m/s what is the acceleration? Remember (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time is acceleration. Final speed= 12 m/s Initial speed= 54.8 m/s Time = 39 s 12 m/s – 54.8 m/s ÷ 39 s = -42.8 m/s ÷ 39 s = -1.097 m/s2 This train is decelerating. Content, images, text, etc. used belong to the rightful owner. No copyright infringement intended.