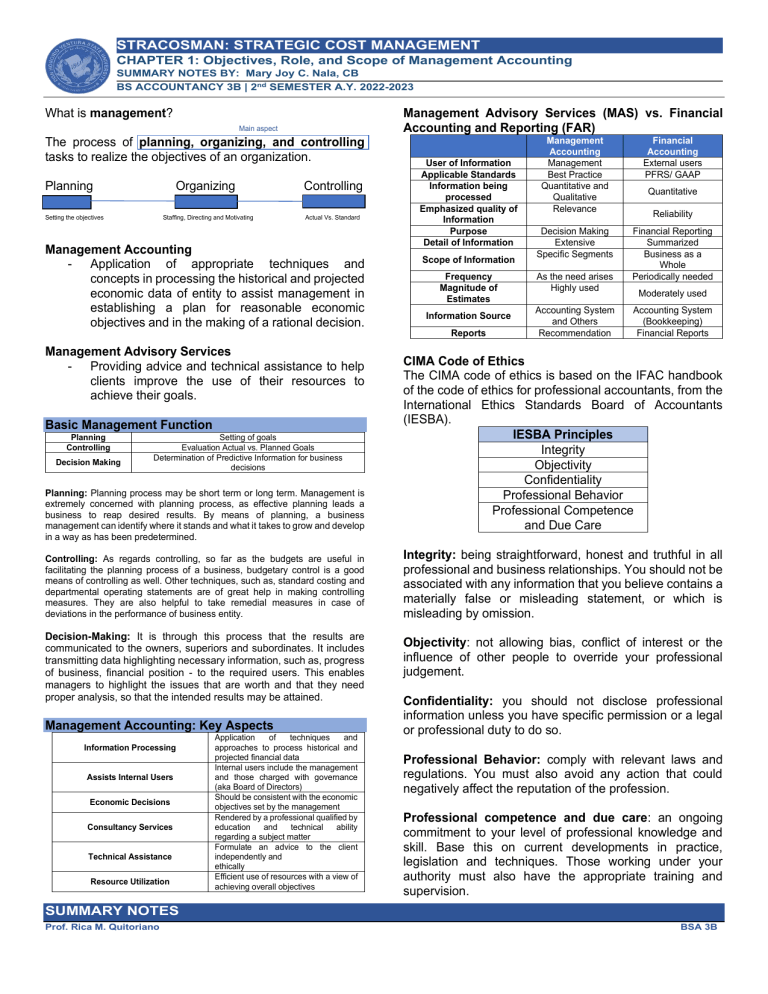
STRACOSMAN: STRATEGIC COST MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1: Objectives, Role, and Scope of Management Accounting SUMMARY NOTES BY: Mary Joy C. Nala, CB BS ACCOUNTANCY 3B | 2nd SEMESTER A.Y. 2022-2023 What is management? Main aspect The process of planning, organizing, and controlling tasks to realize the objectives of an organization. Planning Organizing Setting the objectives Staffing, Directing and Motivating Controlling Actual Vs. Standard Management Accounting - Application of appropriate techniques and concepts in processing the historical and projected economic data of entity to assist management in establishing a plan for reasonable economic objectives and in the making of a rational decision. Management Advisory Services - Providing advice and technical assistance to help clients improve the use of their resources to achieve their goals. Basic Management Function Planning Controlling Decision Making Setting of goals Evaluation Actual vs. Planned Goals Determination of Predictive Information for business decisions Planning: Planning process may be short term or long term. Management is extremely concerned with planning process, as effective planning leads a business to reap desired results. By means of planning, a business management can identify where it stands and what it takes to grow and develop in a way as has been predetermined. Controlling: As regards controlling, so far as the budgets are useful in facilitating the planning process of a business, budgetary control is a good means of controlling as well. Other techniques, such as, standard costing and departmental operating statements are of great help in making controlling measures. They are also helpful to take remedial measures in case of deviations in the performance of business entity. Decision-Making: It is through this process that the results are communicated to the owners, superiors and subordinates. It includes transmitting data highlighting necessary information, such as, progress of business, financial position - to the required users. This enables managers to highlight the issues that are worth and that they need proper analysis, so that the intended results may be attained. Management Accounting: Key Aspects Information Processing Assists Internal Users Economic Decisions Consultancy Services Technical Assistance Resource Utilization Application of techniques and approaches to process historical and projected financial data Internal users include the management and those charged with governance (aka Board of Directors) Should be consistent with the economic objectives set by the management Rendered by a professional qualified by education and technical ability regarding a subject matter Formulate an advice to the client independently and ethically Efficient use of resources with a view of achieving overall objectives Management Advisory Services (MAS) vs. Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR) User of Information Applicable Standards Information being processed Emphasized quality of Information Purpose Detail of Information Scope of Information Frequency Magnitude of Estimates Information Source Reports Management Accounting Management Best Practice Quantitative and Qualitative Relevance Financial Accounting External users PFRS/ GAAP Decision Making Extensive Specific Segments Financial Reporting Summarized Business as a Whole Periodically needed As the need arises Highly used Accounting System and Others Recommendation Quantitative Reliability Moderately used Accounting System (Bookkeeping) Financial Reports CIMA Code of Ethics The CIMA code of ethics is based on the IFAC handbook of the code of ethics for professional accountants, from the International Ethics Standards Board of Accountants (IESBA). IESBA Principles Integrity Objectivity Confidentiality Professional Behavior Professional Competence and Due Care Integrity: being straightforward, honest and truthful in all professional and business relationships. You should not be associated with any information that you believe contains a materially false or misleading statement, or which is misleading by omission. Objectivity: not allowing bias, conflict of interest or the influence of other people to override your professional judgement. Confidentiality: you should not disclose professional information unless you have specific permission or a legal or professional duty to do so. Professional Behavior: comply with relevant laws and regulations. You must also avoid any action that could negatively affect the reputation of the profession. Professional competence and due care: an ongoing commitment to your level of professional knowledge and skill. Base this on current developments in practice, legislation and techniques. Those working under your authority must also have the appropriate training and supervision. SUMMARY NOTES Prof. Rica M. Quitoriano BSA 3B STRACOSMAN: STRATEGIC COST MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1: Objectives, Role, and Scope of Management Accounting SUMMARY NOTES BY: Mary Joy C. Nala, CB BS ACCOUNTANCY 3B | 2nd SEMESTER A.Y. 2022-2023 Roles and Activities of Controller and Treasurer • Controllership Function is the established science of control which promotes the efficient use of an entity’s resources in accordance with its planned objectives. • • • Traditional management and it focuses on the areas of planning and controlling Deals with records, systems and processes to attain the objectives of internal controls and therefore, good managing. Treasury Function, on the other hand, involves the management of money and financial risk in a business. • Deals with money, cash or wealth of an organization. Controllership Functions 1. Planning and Control 2. Reporting 3. Evaluation 4. Government Relations 5. Protection of Assets 6. Economic Appraisal 7. Tax Planning and Administration 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Treasury Functions Capital Financing/Provision for Capital Investor Relations Short-Term Borrowings Banking Relations and Custodians Credit and Collection Investments Insurance objective of ascertaining, reducing and controlling costs. (Cost accounting subject starts from graduation level) Management accounting is the most recently developed branch of accounting. It is concerned with generating accounting information relating to funds, costs, profits, etc., as it enables the management in decision making. We may say that management accounting addresses the needs of a single user group, i.e., management. The accounting system is part of the organization’s management information system (MIS). The cost accounting system, which accumulates data about the costs of producing goods and services, is part of the organization’s overall accounting system. It accumulates cost information for both management accounting and financial accounting. MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING USERS OF REPORT PURPOSE Distinction among Management Accounting, Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting TYPES OF REPORTS Basis Objective Financial Accounting Record transaction and determine financial position and profit or loss. Nature Concerned with historical data Principle Followed Governed by GAAP Data Used Data Qualitative Aspects are not recorded Cost Accounting Management Accounting Ascertainment, allocation, accumulation and accounting for cost To assist the management in decision-making and policy formulation Concerned with both past and present recorded (historical in nature) Certain principles followed for recording costs Deals with projection of data for the future (futuristic nature) Only quantitative aspect used recorded No set principles are followed in it BASIS OF REPORTS STANDARDS OF PRESENTATION REPORTING ENTITY Uses both quantitative and qualitative concepts PERIOD COVERED Financial Accounting is that branch of accounting which records financial transactions and events, summarizes and interprets them before communicating the results to the users. It determines profit earned or loss incurred during an accounting period and the financial position as on the date when accounting period ends. The end product of financial accounting I the profit & loss account for the period ended and the Balance Sheet as on the last day of accounting period. Internal users: officers and managers To provide internal users with information that may be used by managers in carrying out the functions of planning, controlling, decision-making, and performance evaluation. Different types of reports, such as budgets, financial projections, cost analyses, etc., depending on the specific needs of management. Reports are based on a combination of historical, estimated, and projected data. In preparing reports, the management of a company can set rules to produce information most relevant to its specific needs. Focus of reports is on the company’s value chain, such as a business segment, product-line, supplier, or customer. Reports may cover any time period – year, quarter, month, week, day, etc. Reports may be required as frequently as needed. FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING External users: stockholders, creditors, concerned government agencies. To provide external users with information about the organization’s financial position and results of operations. Primarily financial statements and the accompanying notes to such statements. Reports are based almost exclusively on historical data. Reports are prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and other pronouncements of authoritative accounting bodies. Financial reports relate to the business as a whole. Reports usually cover a year, quarter, or month. Cost Accounting is a branch of accounting is concerned with ascertaining cost of products, operations, processes or activities. It is that branch of accounting which deals with recording costs with the SUMMARY NOTES Prof. Rica M. Quitoriano BSA 3B