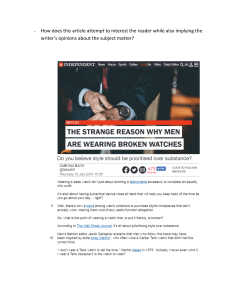
English Language B 4EB1 Paper 1 Topic: Text Analysis (Answering Questions 3, 6 and 7) Section: A Sample Question: Explain how the writer presents his impressions of New York. You should support your answer with close reference to the passage, including brief quotations. A02 understand and analyze how writers use linguistic and structural devices to achieve their effects (Q3 and Q6) (10) A03 explore links and connections between writers' Ideas and perspectives, as well as how these ere conveyed (Q7) (15) What are you required to do in your answer? Comment, Quote, discuss Effects. You will comment on the 1. Content 2. Language/style, and 3. The structure of the passage. You will quote words/phrases/clauses/sentence to support your comment and discuss e effects. [See page 110-111 of the student book] How will you organize your points/findings coherently in your answer? The next point is how you will write the answer. Will you just use the following components of the checklist and comment on various parts of the passage/text randomly? No, you should not. Solution: Make Genre, Audience and "Purpose of the text/passage the goal or main focus of your discussion/answer. In other words. discuss how the writer has used some of the following components to adopt a genre, address the Audience, and achieve the Purpose. The word 'how' Includes Ideas or content points, form and the use of language/style - and language or style Involves almost everything of English Language. To comment, what will you look for in the passage? Here Is your checklist with its various components: • Content: Fact, Opinion, Examples, Sufficient/Insufficient, Data, Relevant/Irrelevant, subject matter, etc. • Theme or subject matter: something universal, something local, geographical, social, environmental, psychological, about science and technology, about the sports world, etc. • Setting of Place/Time: Tense, Sequence of events • Genre, Audience, Purpose (Genre or some non-fiction texts: Personal Account, Personal Anecdote, Biography or Autobiography, Obituaries, Speeches, Newspaper or Magazine Articles, Travel Writing, Diaries or Letters, Reviews, etc.) [See page 58 of the Student Book] (Purpose: to entertain/ Inform/ create awareness/ persuade/ thrill/ excite/ protest remember/ pay tribute/ clarify/ advertise/ advocate, etc.) [See page 87 of the Student Book] [See page 89 of the Student Book for Effects. Also see page 100 -101] • Voice, Point of view, perspective, or tone (Apathetic, affectionate, apologetic. blunt, ambivalent, cynical, disdainful, humorous, Impartial, grave, optimistic, patronizing, sympathizing, etc.) • What does a reader or a character of the text feel? Some words expressing different feelings: Afraid, Agitated, Alarmed. Amazed, Amused, Annoyed, Anxious, Appreciative, Ashamed, Awkward, Baffled, Bored, Confused, Contented. Demoralized, Displeased, Dispassionate, dissatisfied, Distressed, Disturbed, Embarrassed, Enraged, Enthusiastic. Frantic. Friendly, Frightened, Frustrated, Grateful, Hateful. Helpful, Hesitant, Hopeless, Humble, Humiliated, Impatient, Insecure, Nervous, Offended, Oppressed, Optimistic, Overwhelmed, Proud. Regretful. Relieved, Resentful, Shocked, Suspicious, Terrified, Threatened, Thrilled. Uncertain, Uncomfortable, etc. • Figures of Speech: Alliteration, Simile, Metaphor. Oxymoron, Pun, Hyperbole, Analogy, Paradox, Irony, Onomatopoeia, personification, Climax, etc. [See page 63 of the Student Book] • Image/ Imagery (Which words/phrases/techniques are building it up?) • Words or parts of Speech: Examine how some Nouns/ Pronouns/ Adjectives/ Verbs/ Adverbs/ Conjunctions/ Prepositions, Interjection/ Determiners are functioning. • Sentence types: Simple, Complex, Compound, Affirmative, Negative, Imperative, Interrogative, Rhetorical Question, Exclamatory, Short, Long, Lucid, etc. [See page 89 of the Student Book] • Sentence Purpose: Sentences can convey explanation, understanding, discussion, Information, advice, opinions, guidance, instruction, suggestions, entertainment, amusement, Inspiration, hop e, praise, pleading, bargaining, opinions, persuasion, warning, terror, etc. [See page 40 of the Student Book] • Types of the writing: descriptive, narrative, persuasive, discursive, argumentative Descriptive: involves place, adjectives, adverbs, direction: dimensions, number, sensory words, concrete or abstract things, condition of things. temperature, feelings etc. So, these are few components of descriptive language. Narrative: involves passage of TIME. events/actions, voice, tone, perspective, rise of action. climax, characters, plot, etc. • Direct speech (Has it been used? What is the effect? In what way? • Language: formaI, informal, emotive, chatty, colloquial • Use of Positive/ Negative language • Why a particular information Is used • Structure: Title/Subtitle, Heading/Subheading, Paragraphing, Beginning/Introduction, Middle/Developing paragraphs, End/Conclusion, Repetition, Small/Big, Length of something. English Language B 4EB1 Paper 1 Topic: Text Analysis (Answering Questions 3, 6 and 7) Section: A What language can you use to introduce an EXPLANATION? This suggests that, This infers that, This implies that, This insinuates (suggests indirectly) that, This shows that, etc. What kind of language can you use to QUOTE or to give EVIDENCE? The evidence that supports this is “Quote”, This is ·evident when “ ”, This is illustrated by “ “, This is demonstrated by “ “ etc. What language can you use to discuss the EFFECTS? The use of descriptive language creates a sense of….. Repetition of…..creates a sense of….. The use of typical language/behavior/attitude…..makes the reader/article/writing….. The writer is surprised/shocked/moved/amused by the…..and this is expressed by “ “. At the start of the extract, the writer uses…..to….. For example, it says “ ”, This makes the audience think/feel/imagine….. The writer uses…..which creates the effect of…..on the read er….. Examples of FLUENT QUOTING: In the third paragraph, the writer conveys a powerful sense of the crowd's behavior through his lexical choice. He describes them as “very still” and how a “deep, low, happy sigh” emanated from them. He likens the scene to one at the theatre, and says how the crowd were pleased they were going to get “their bit of fun” when he finally shoots the elephant. The writer goes on to describe the “devilish roar of glee” that the crowd makes when he fires the first shot. The adjective 'devilish' suggests something primitive and almost evil in their Joy, and that he does not share the crowd's delight . The noun 'roar' suggests he sees the crowd as almost being like a wild beast which is unpredictable and dangerous, and fears them. What will you· write about the EFFECTS? Repetition In threes or lists of points: adds detail to the text, makes the text more persuasive by using a technique often used In speeches and advertising, makes the subject seem more complex or Interesting Alliteration: catches the reader's Interest visually and aurally makes the text more like poetry or advertising, makes the text more Memorable Emotive vocabulary: makes the subject more emotional, provokes a response in the reader (makes us agree/disagree /happy/ unhappy) Formal or informal vocabulary: (did not" vs "didn't) Formal: makes the text feel more authoritative/powerful / convincing Informal: makes the text appeal to us because it's speaking to us, on our level, conversational Hyperbole(Overstatement): makes the point more powerful, helps us to visualize and remember the idea Metaphor/simile: makes the subject more vivid, helps us to visualize the idea, uses a technique often used in advertising and storytelling Pun(wordplay): makes the text memorable/amusing I quirky/noticeable, appeals to the reader by making us think we are clever for noticing the pun Addressing the reader directly ("you"): makes the reader feel involved, gets the reader to empathize with the writer or someone in the text, encourages our emotional reaction, makes the text more memorable Adjectives and adverbs: adds detail to the text which helps us to visualize what is being described, uses the senses to make the text more vivid, paints a picture in our minds which will help us to remember the text Short/long sentences: creates rhythm in the text which makes it more interesting to read short sentences give clarity and authority, long sentences may make it more formal or more conversational, overall effect will be to hold our Interest better Use of statements/commands/questions: adds interest to the text by not using one tone of voice, this will keep us reading and help us to remember the text, commands may provoke a response from us ("Stop talking and listen") and establish a link between writer and reader, questions ("Why should you visit Ibiza?") draws us into the text. Use of dialogue: helps bring the text to life by adding human voices, grabs our interest by personalizing the subject, adds visual interest on the page by being different from ordinary paragraphs [See page 89 and 103, of the Student Book.] The main points of comparison in the answer of Question 7: • The audience for each text • The purpose of each text and how the writers achieve this • The subject or theme of each text and how this is presented - but the response should not focus only on the content • The techniques the writers have used, for example vocabulary, imagery, rhetorical devices, sentence length and complexity, • paragraph length, structuring or organization of Ideas • The writer's Ideas and perspectives or point of views • Which text is more effective (Unless asked, this is not a must-do) Advice: • While reading for details and scanning, you must underline/tick your findings (words/phrases/clauses/...). You may write small comments beside them. It will help you in many ways. • Do not summarize the passage or just repeat its content points in your language. Your task wants you to COMMENT. • Do not write disconnected points or in note form. Make it a coherent writing and use Sentence Linkers to give it the quality of a continuous writing. • Better to use Simple Present and Present Perfect Tenses in situations like these: "In Text 1, the tone is….." "The writer has used many adjectives to…..He/ She has demonstrated this in….." • Your quotations need to be small (words/phrases). Do not quote a big sentence, instead, use dots in the middle. • Do not write everything in only one paragraph