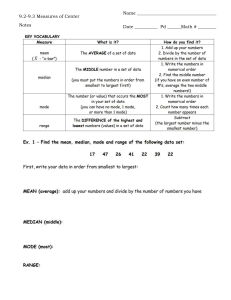
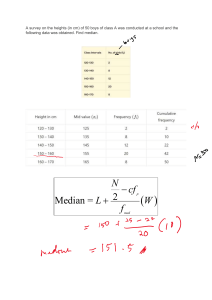
Median The median is the middle value in a set of quantities. It separates an ordered set of data into two equal parts. Half of the quantities found above the median and the other half is found below it. In finding the median of grouped data, we use the formula: where 𝑥̃ = median 𝑋𝑙𝑏 = the lower boundary of true lower limit of the median class N = total frequency 𝑐𝑓𝑏 = cumulative frequency before the median class 𝑓𝑚 = frequency of the median class 𝑖 = size of the class interval To compute the median (𝑥̃) of grouped data, we proceed as follows: 1. Compute the cumulative frequencies by adding the frequencies to the cumulative frequencies. 2. Determine one-half of the total number of cases:N/2. 3. Get the cf of the class immediate below the median class. 4. Determine the frequency (fm) of the median class. 5. Find the class interval in which the median class falls and determine the exact lower limit of this interval. 6. Apply the formula by substituting the given values. Class Interval 47 - 52 41 – 46 35 – 40 29 – 34 23 - 28 17 – 22 11 – 16 5 – 10 i = 6 True Limits Frequency <cf 46.6 – 52.5 40.5 – 46.5 34.5 – 40.5 28.5 – 34.5 22.5 – 28.5 16.5 – 22.5 10.5 – 16.5 4.5 – 10.5 1 0 4 2 9 9 4 1 N = 30 30 29 29 25 23 14 5 1 N = N/2 = cf b = fm = i = Xlb = Use the formula in finding the mean The ages of the residents along Fortaliza street in Hingatungan, Silago, Southern Leyte is given below. Find the median age. Ages 63 - 69 56 – 62 49 – 55 42 – 48 35 – 41 28 – 34 21 – 27 14 – 20 7 – 13 Frequency 3 11 18 26 21 15 12 7 2 Assignment Direction: Using 10 as the size of class interval, make a frequency distribution of the scores obtained by 50 students in a college entrance test. Find the Median. 80 90 100 70 90 110 80 100 120 80 100 100 100 60 80 80 100 100 120 80 90 90 90 70 80 70 100 100 120 100