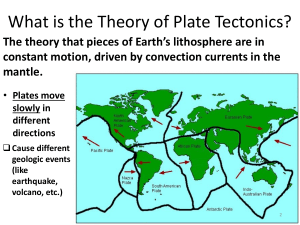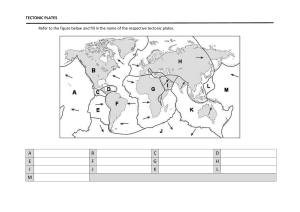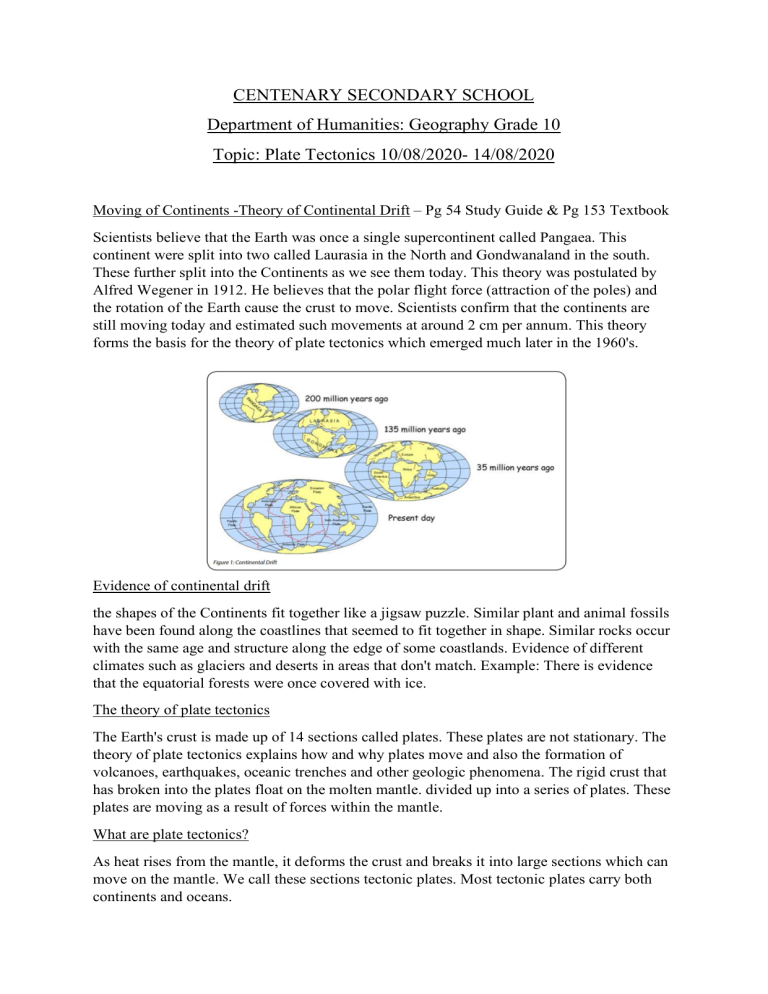
CENTENARY SECONDARY SCHOOL Department of Humanities: Geography Grade 10 Topic: Plate Tectonics 10/08/2020- 14/08/2020 Moving of Continents -Theory of Continental Drift – Pg 54 Study Guide & Pg 153 Textbook Scientists believe that the Earth was once a single supercontinent called Pangaea. This continent were split into two called Laurasia in the North and Gondwanaland in the south. These further split into the Continents as we see them today. This theory was postulated by Alfred Wegener in 1912. He believes that the polar flight force (attraction of the poles) and the rotation of the Earth cause the crust to move. Scientists confirm that the continents are still moving today and estimated such movements at around 2 cm per annum. This theory forms the basis for the theory of plate tectonics which emerged much later in the 1960's. Evidence of continental drift the shapes of the Continents fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. Similar plant and animal fossils have been found along the coastlines that seemed to fit together in shape. Similar rocks occur with the same age and structure along the edge of some coastlands. Evidence of different climates such as glaciers and deserts in areas that don't match. Example: There is evidence that the equatorial forests were once covered with ice. The theory of plate tectonics The Earth's crust is made up of 14 sections called plates. These plates are not stationary. The theory of plate tectonics explains how and why plates move and also the formation of volcanoes, earthquakes, oceanic trenches and other geologic phenomena. The rigid crust that has broken into the plates float on the molten mantle. divided up into a series of plates. These plates are moving as a result of forces within the mantle. What are plate tectonics? As heat rises from the mantle, it deforms the crust and breaks it into large sections which can move on the mantle. We call these sections tectonic plates. Most tectonic plates carry both continents and oceans. The mechanics of plate movements. Heat inside at provides the energy for the mechanics which causes the plates to move. Heat rises from the core and spreads through the mantle in convection currents. These currents form convection cells, so heat is constantly moving towards the crust. At the top of each convection cell, the convection current moves sideways and eventually downwards to complete the cell. It may be difficult to believe that the hard, rigid tectonic plates that make up the Earth’s crust are moving. But below the crust, the mantle has a plastic consistency. In other words it is not rigid, and so it can move flow. Geologists describe the upper layer of the mantle, immediately below the plate, as a soft layer of slush. The tectonic plates can just slowly on this slush. Figure 2: Movement of plate tectonics Complete the following activity and return to school when picking up the next worksheet: Activity 8 found in the Textbook on Pg 153 or Activity 2.4 found in the study guide on Pg 66