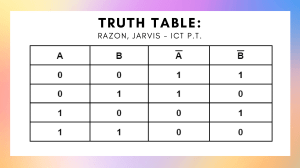
General Physics Hawassa, Ethiopia BY: Mideksa K.(MSc.) August,2021 Chapter Three Fluid PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER Elastic Behavior Elastic Material Elastic Deformation Plastic Materials Stress/stra Mechanical in Energy Tensile Shear Volume Elasticity Moduli Young’s Modulus The ratio of the tensile stress to the tensile strain. Shear Modulus (S) The ratio of shear stress to shear strain. Bulk Modulus Example The ratio of Volume stress to Volume strain. A2.0-m-long,1.0-mm-diameter wire is suspended from the ceiling. Hanging a 4.5 kg mass from the wire stretches the wire’s length by 1.0 mm. What is Young’s modulus for this wire? Can you identify the material? Example 2. The area of cross section of a steel wire (Y = 2.0x1011 N/m2) is 0.1 cm2. Calculate the force required to double its length. Example A load of 2.0 kg is applied to the ends of a wire 4.0 m long, and produces an extension of 0.24 mm. If the diameter of the wire is 2.0 mm, find: the stress on the wire and the strain it produces. Density and Pressure Density Specific Gravity The quantity of mass (m) per unit volume (V) of a body. The ratio of the density of the substance to the density of another substance which is taken as a standard Pressure A normal compressive force exerted by a fluid per unit area. Atmospheric Pressure Gauge Pressure The weight the air exerts on you Example The surface of the water in a storage tank is 30 m above a water faucet in the kitchen of a house, Calculate the difference in water pressure between the faucet and the surface of the water in the tank. Absolute Pressure The pressure measured from zero (0) value Buoyant Force Pascal’s Principle The pressure of a gas or liquid exerts force equally in all directions against the walls of its container. Example The hydraulic lift at a car repair shop is filled with oil. The car rests on a 25-cm-diameter piston. To lift the car, compressed air is used to push down on a 6.0-cm-diameter piston. What does the pressure gauge read when a 1300 kg car is 2.0 m above the compressed-air piston? The buoyancy force is equal to Archimedes’ Principle the weight of the fluid displaced. Example A 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm block of wood with density 700 kg/m3 is held underwater by a string tied to the bottom of the container. What is the tension in the string? Fluid Dynamics Laminar When the particles of fluid move along straight line path or parallel to each other Factors affecting laminar flow are density, compressibility, temperature and viscosity of the fluid. Turbulence Irregular flow characterized by small whirlpool-like regions, Equation of continuity The volume flow rate is constant at all points in a tube. Bernoulli’s Equation For an incompressible , inviscid flow and steady flow, energy per unit volume is constant throughout the flow.” Example Water flows through the pipes shown in Figure .The water’s speed through the lower pipe is 5.0 m/s and a pressure gauge reads 75 kPa. What is the reading of the pressure gauge on the upper pipe? Application of Bernoulli’s Equation Torricelli theorem Airplane Wings and Dynamic Lift