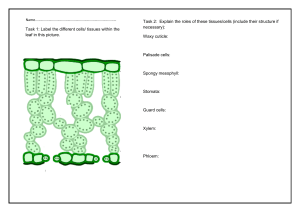
Chapter 01 Organisation of Plant Tissues and Growth 1.1 Organisation of Plant Tissues 1.1.1 Two types of plant tissue and their main functions ➀ ➁ ➂ 2 types of plant tissues: (i) Meristematic tissues ➻ tissues that actively dividing through mitosis (ii) ➻ matured tissues that have experienced or are experiencing Permanent tissues differentiation 3 types of permanent tissues: (i) Epidermal tissues (ii) Ground tissues (iii) Vascular tissues Epidermal tissues ➻ the outermost surface of stems, leaves and roots of young plant Cuticle ➻ epidermal cell walls that exposed to the air Characteristics of cuticle • Epidermal cell wall that has a waxy and waterproof layer Function of cuticle © Reduces loss of water through evaporation © Protects the leaf from mechanical injuries and pathogens Modified epidermal cells and their functions Å Guard cells – To control the opening and closing of the stoma Å Root hair cells – To increase the surface area of the root to absorb more water and mineral salts 1 Typed by LBO@2023 ➃ Ground tissues (i) Parenchyma tissues (ii) Collenchyma tissues (iii) Sclerenchyma tissues Types of Ground Tissues Living Cells / Dead Cells Parenchyma tissues Collenchyma tissues Simplest living cells & do not undergo differentiation Living cells & flexible when matured Dead cells when they are matured Have cell wall thicker than parenchyma tissue but thinner than sclerenchyma Have the thickest cell wall among the ground tissues Cell wall is thickened by cellulose Cell wall is not uniformly thickened with pectin & hemicellulose Cell wall is uniformly thickened by lignin 1. Stores food 2. Undergo photosynthesis 3. Gives support and shape to herbaceous plants Gives mechanical support to the young plants, herbaceous plant & non-woody plants Gives mechanical support to the mature plants Thickness of Cell Have the thinnest cell Wall wall among the ground tissues Cell Wall Thickening Function ➄ Sclerenchyma tissues Vascular tissues (i) Xylem tissue (ii) Phloem tissue Xylem tissue is made up of xylem vessels & tracheid Characteristics of xylem tissues • Dead cells & no cytoplasm Adaptations of xylem tissues P1 - The cell wall of xylem is thickening with lignin E1 – To provide mechanical support to the plant P2 - Xylem vessels that are elongated, hollow and connected to each other from its root to the leaves E2 - To transport water and mineral salt to all parts of a plant 2 Typed by LBO@2023 Phloem tissue is made up of companion cells & sieve tubes Characteristics of sieve tubes Sieve tubes are living cells & has cytoplasm & no any organelles (nucleus & ribosome) as they decompose at maturity stage Sieve tubes arranged from end to end forming elongated and continuous tube structures Function of phloem Þ To transport sugars produced from the photosynthesis from the leaves to storage organs such as roots, fruits and tubers 3 Typed by LBO@2023