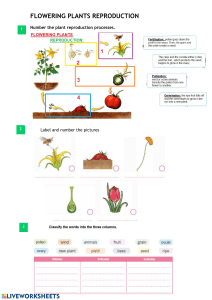
7 E’S LESSON PLAN IN NSCI 110 – STS Lesson: The Roles of Science and Technology in Combating Environmental Problems I. OBJECTIVES Content Standard: Performance Standard: Learning Competencies: II. CONTENT A. References: 1. Curriculum Guide: 2. Teacher’s Guide: 3. Learner’s Material: __________ 4. Textbook: _________ 5. Additional resources from the LR portal: _____________ B. Other Learning Resources: PowerPoint presentation, pictures, activity sheets, video clips III. PROCEDURE TEACHER’S ACTIVITY STUDENTS’ ACTIVITY A. Preliminary Activities 1. Greetings Good morning students. Good morning, ma’am Gintoro. Good morning Classmates. 2. Energizer _____________ _____________ 3. Checking Attendance Is there any absent in the class? Excellent! 4. Setting of Classroom Rules None, ma’am. Before we start our lesson, let us First recall our classroom rules. Who can Give me the first rule? Correct. What are the others? Sit properly. Be quiet. Listen attentively. Participate. B. Developmental Activities 1. Drill Let us have a game. I will show you A series of letters. Arrange them properly To find the hidden words. _____________ C. ELICIT __________________________ _____________ _____________ _____________ D. Engage Let us examine the following Pictures of some organisms we saw Earlier. These are pictures of a starfish and a dog. One of them needs 1 parent to reproduce While the other one needs two parents. Why do you think these happen? Sir, maybe the dog can have Two sexes while the starfish has only One sex. You have a point. What else? (The students will give other answers.) Do these organisms always look the same Like their parents? (The students will give their anwers.) Why do you think these are possible? (The students will give their answers.) E. Explore Now, we will have a trip inside the Classroom. I will group you into five. The classroom has five learning Areas. Each of them offers a different topic That you will observe and examine. Write Your notes as you go on. I will assign each group to a Designated learning area. After 3 minutes, You will proceed to the next learning area Until you finish visiting all learning areas. Before we do that, let us recall The guidelines in doing an activity. What Is the first step? That’s right. What else? Be cooperative. Show respect to your groupmates. Don’t disturb other groups. Follow directions correctly. Let us start the activity. (Designated learning areas for the groups:) Group 1 – Area 1 Group 2 – Area 2 Group 3 – Area 3 Group 4 – Area 4 Group 5 – Area 5 (The students will do the activity.) Learning Area 1: Vegetative Reproduction “Can You Grow Plants from ‘Eyes’?” 1. In this activity, a potato tuber was cut into pieces and was planted. 2. Observe and examine the changes in the tubers. 3. Where did the new plants come from? 4. How many parents did it need to reproduce new plants? 5. What plants reproduce in the same manner? Cite some examples. Learning Area 2: Pollination “Can You Grow Plants from ‘Dust’?” 1. Study the male and female parts of the flower. What qualities do they have? 2. What does the stamen have? What do we call the dust-like particles in it? 3. Touch the pistil. What does it feel like? Why do you think it is sticky? 4. What process spreads pollen to other plants? What organisms aid in this process? 5. How many parents are needed to reproduce? Learning Area 3: Budding “Can One Become Two?” 1. Using a compound microscope, study and examine the slides with yeast cells. 2. Notice that there are smaller cells in the yeast. Those are called buds. It detaches itself from the mother cell and grows into a mature cell. 3. How many parents are needed to reproduce? Learning Area 4: Internal Fertilization “Sperm and Egg Cells” 1. Study the picture. Where does a sperm cell come from? Where does an egg cell come from? 2. How many organisms are needed to reproduce an offspring? 3. Does the offspring only have similarities in just one parent? Support your answer. Learning Are 5: Fragmentation “A New Worm By Cutting?” (Present a video clip about cutting a segmented worm into two parts.) 1. Observe and study the video clip. What organism is it? 2. What happened to the worm when it was cut? 3. What happened to the separated part of the worm? 4. How many parents are needed for the reproduction? 5. Does the offspring have similarities with the parent worm? Support your Answer. F. Explain Let us examine and hear your Observations in the activity. Each group shall have a designated Speaker to present what they’ve observed In a learning area. Each group will only present their Observations in the first learning area that They visited. (The students will present their work.) (The teacher will assist the learners in the Presentation. The teacher will give the Correct scientific term for every needed Observation.) Examples: Pollination Stamen Budding Pistil Pollen Reproduction What have you observed in the Parents of the different offsprings? Do they Have the same number of parents? Why does it happen? That is correct. Does every offspring Looked exactly the same like their parents? Why do you say so? Yes, that is right! G. Elaboration There are two kinds of reproduction. Asexual reproduction needs one parent to Produce an offspring. No, sir. Some organisms needed only one Parent. Others need two parents To reproduce. No, sir. The organisms that need 1 parent, such as the segmented worm, looked alike their parent. On the other hand, the organisms with two parents got traits from both parents. Some examples of asexual Reproduction are vegetative reproduction from Potatoes, budding from the yeast cells and Fragmentation just like what happened to The segmented worm. Offsprings from asexual reproduction Looks the same with the parent organism. Sexual reproduction requires two Parents- a male and a female- to reproduce. Examples of this process are pollination in Plants and internal fertilization in humans. Offsprings from sexual reproduction Gets traits from both parents. To further understand the lesson, let Us have an activity. I will group you now into Three. I will give you an activity card and Follow the directions in it. (The students will do the activity.) Group 1: 1. Make a Venn Diagram about Asexual And Sexual Reproduction. Show their similarities and differences. Group 2: 1. Draw two organisms that undergo Asexual reproduction. Group 3: 1. Draw two organisms that undergo Sexual reproduction. Let us take a look in your Works. Let us recall our lesson today. What are the two kinds of reproduction? Correct! How many parents does An organism need for an asexual and a sexual Reproduction? (The students will present their work.) The two kinds of reproduction are Asexual and sexual. An organism needs one parent for Asexual reproduction while two parents Are needed for sexual reproduction. What can you say about the Similarities of the offsprings to the parent In an asexual and sexual reproduction? Offsprings from asexual reproduction Looked the same with their parent. On The other hand, offsprings from sexual Reproduction gets traits from both Parents. Exactly. H. Evaluate Write AR if the sentences refer to an asexual reproduction and SR for sexual reproduction. ____1. Ginger and sweet potatoes can reproduce by planting their plant tubers in the soil. ____2. The male organism produces sperm cells and the female organism produces an egg cell. ____3. Lisa cut a worm into two pieces. She was shocked when she saw the two pieces move separately and independently. ____4. Male elements of a flower releases pollen to a female element of the flower. ____5. Sponges have smaller parts that can grow and become a different organism. Answers: 1. AR 2. SR 3. AR 4. SR 5. AR I. Extend Read the sentences below. 1. If a starfish loses a body part, it grows itself a new one. The separated part grows into a new independed starfish. Why do you think this happened? 2. To produce desirable gumamelas, the farmer needs to propagate a good variety of the flowers. What method can the farmer use? Support your answer. Prepared by: NIEL M. BAJAO Teacher - I