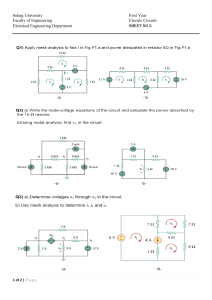
Circuit Analysis Technique ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ KCL KVL NODE ANALYSIS MESH ANALYSIS THEVENIN THEOREM NORTON THEOREM SOURCE TRANSFORMATION SUPERPOSITION FOURIER ANALYSIS LAPLACE TRANSFORMATION ❖ RC CIRCUIT ❖ RL CIRCUIT ❖ RLC CIRCUIT ➢ Circuit variables and elements: Voltage, current, power, energy, independent and dependent sources, resistance. Basic laws: Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s current and voltage laws. Simple resistive circuits: Series and parallel circuits, voltage and current division, Wye-Delta transformation. Techniques of circuit analysis: Nodal and mesh analysis including super node and super mesh. Network theorems: Source transformation, Thevenin’s, Norton’s and Superposition theorems with applications in circuits having independent and dependent sources, maximum power transfer condition and reciprocity theorem. Energy storage elements: Inductors and capacitors, series parallel combination of inductors and capacitors. Responses of RL and RC circuits: Natural and step responses. ➢ Magnetic quantities and variables: Flux, permeability and reluctance, magnetic field strength, magnetic potential, flux density, magnetization curve. Laws in magnetic circuits: Ohm’s law and Ampere’s circuital law. Magnetic circuits: series, parallel and series-parallel circuits.