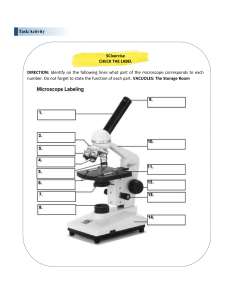
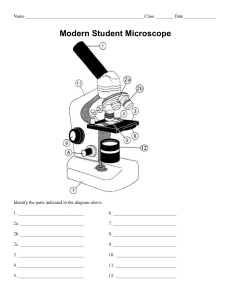
LAB_Chapter 4_Microscope and Staining Name:___________________________________________Period:_____________Date:___________ Activity 1_ Observe the microscope and label it. Activity 2_ Types of bacteria baccili Cocci Spirillum Describe Draw Activity 2_Identify these microorganisms Organism Type Description Pro/Eukaryotes Important characteristics Anabaena bacteria Coprinus mushroom Fungus Aspergillus condiophores fungus Dinoflagellates algae Euglena plant-animal Oscillatoria bacteria filamentous cyanobacterium Drawing Paramecium unicellular eukaryote Bacterial nucleoplasm Saccharomyces budding cells (yeast) fungus Penicillum ascomycetous fungi Spirogyra algea mixed diatoms type of plankton called phytoplankton, (fungus) Saprolegnia Rhizophus sporangia (fungus) Stemonitis mold-fungi Physarum plasmodium mold-fungi Amoeba Proteus (Eukaryote) Polysiphonia sporophyte (filamentous red algae) Focus monocious conceptacle (plant) Activity 3_ Preparing and fixing slides Aim Of The Experiment To study and demonstrate mitosis use of microscope by preparing the slides of microscopically small objects. Materials Required Compound microscope Water Filter paper Coverslip Glass Slide Forceps Procedure Of The Experiment Collect objects provided by your teacher at each station table. Make slide. Observe under the microscope and complete the following table. Object Description Drawing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. POST LAB QUESTIONS 1. The total magnification achieved by the microscope is calculated by _____ the magnification of the objective and the ocular lens. 2. What is the purpose of adding a drop of mineral oil to the slide? 3. Which of the following is an INCORRECT association? 4. Which of the following prepared specimens contained rod-shaped cells? 5. What microscope component should be adjusted to regulate the amount of light entering the condenser in order to ensure the best contrast which changing from one objective lens to another? 6. After you position the specimen over the opening in the stage and rotate one of the low power lenses into position, what step should be completed next? 7. Which cell are larger: Human blood cells or Bacillus subtilis. 8. What is the recommended procedures when returning the microscope to the cabinet?