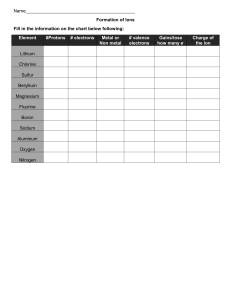
Name KEY Date Pd Chemistry – Unit 6 Worksheet 1 When Metal-Non-Metal (ionic) compounds are dissolved, the metal particles tend to form positively charged ions (cations) as evidenced by their attraction to a negative electrode, while non-metal particles tend to form negatively charged ions (anions) and migrate to a positively charged electrode. We will now examine the patterns that exist for the ratios in which these elements combine in order to determine the charges of the ions they form. 1. Write the formula, draw a particle diagram for each compound, and name it. The ratio of ions in each compound is given. When naming ionic compounds, we simply write the name of the first (the metal) element and then the second (non-metal) element, but change the ending to –ide. See the completed names below. Note that no prefixes are used. Atoms involved formula 1 calcium 1 oxygen 2 lithium 1 oxygen CaO 2 aluminum 3 sulfur 1 beryllium 1 sulfur Al2S3 BeS Li2O particle diagram name calcium oxide Atoms involved formula 2 boron 3 oxygen lithium oxide aluminum sulfide 1 magnesium 1 oxygen B2O3 2 sodium 1 sulfur MgO beryllium sulfide 3 sodium 1 nitrogen Na2S Na3N particle diagram name Atoms involved formula boron oxide 1 magnesium 2 chlorine magnesium oxide 1 lithium 1 fluorine MgCl2 sodium sulfide 1 beryllium 2 bromine LiF 1 aluminum 3 bromine BeBr2 AlBr3 beryllium bromide aluminum bromide sodium nitride 1 sodium 1 fluorine NaF particle diagram name magnesium choride lithium fluoride ©Modeling Instruction – AMTA 2013 1 sodium fluoride U6 ws1 v4.0 Atoms involved formula 1 sodium 1 chlorine 1 calcium 2 bromine NaCl 1 aluminum 3 chlorine CaBr2 3 potassium 1 phosphorus 3 magnesium 2 phosphorus AlCl3 K3P Mg3P2 aluminum chloride potassium phosphide magnesium phosphide particle diagram name sodium chloride calcium bromide 2. Write each formula from Question 1 in the boxes corresponding to its elements. For example, the compound formed from sodium and sulfur have been written in the box for sodium and in the box for sulfur. Now add the rest. Hydrogen 1 Helium 2 H Lithium 3 He Beryllium 4 Boron 5 Li Li2O LiF Be BeS BeBr2 B B2O3 Sodium 11 Magnesium 12 Aluminum 13 Na Na2S Na3N NaF NaCl Potassium 19 K K3P Carbon 6 C Silicon 14 Mg MgO MgCl2 Mg3P2 Al Al2S3 AlBr3 AlCl3 Si Calcium 20 Gallium 31 Germanium 32 Ca CaO CaBr2 ©Modeling Instruction – AMTA 2013 Ga Ge 2 Nitrogen 7 N Na3N Phosphorus 15 P K3P Mg3P2 Arsenic 33 As Oxygen 8 Fluorine 9 Neon 10 Chlorine 17 Al2S3 BeS Cl MgCl2 NaCl AlCl3 Argon 18 Selenium 34 Bromine 35 Krypton 36 O CaO Li2O B2O3 MgO Sulfur 16 S Na2S Se F LiF NaF Br BeBr2 AlBr3 CaBr2 U6 ws1 v4.0 Ne Ar Kr 3. What patterns do you find in the formulas of the compounds formed in the table in #2? Elements in groups 1A and 7A combine in a 1:1 ratio, 2A and 7A in a 1:2 ratio, 3A and 7A in a 1:3 ratio. Elements in 2A and 6A combine in a 1:1 ratio, 3A and 6A in a 2:3 ratio. Based on these patterns, predict the formulas of the compounds formed by the ions below. Ratio of ions in compound Atoms ___ potassium ___ calcium ___ gallium ___ magnesium involved ___ oxygen ___ sulfur ___ oxygen ___ fluorine Ga2O3 MgF2 formula K2O CaS 4. How does a neutral atom become a positive ion? a negative ion? A neutral atom must lose electrons to become a positive ion. It must gain electrons to become negative. 5. Do the elements in group 1A behave more like top or bottom tape? How about the elements in group 7A? How so? Metals tend to lose electrons making them (+) charge, like the top tape. Elements in group 7A are non-metals and would gain electrons. This makes them like the bottom tape. 6. Make whatever generalizations you can about the charge of the ions formed by elements in columns 1A, 2A, 3A and 7A based on the ratio of atoms in each of the compounds they form. Group I forms +1 ions, group 2A forms +2 ions, group 6A forms -1 ions and group 7A forms -1 ions. “But what if group 2A were +1”. Then that group 7A would have to have a charge of -1/2, and that fractional charge is unlikely. 7. Using the fact that compounds are also neutral, account for the fact that the ions combine in the ratios you have listed in the table in #2. Provide a couple of specific examples to support your explanation. Ions combine is such a way as to form compounds that are electrically neutral. Two =1 Li ions combine with one -2 oxide ion to form lithium oxide, Li2O. The Al+3 ion combines with 3 Cl-1 ions to form the neutral AlCl3 ©Modeling Instruction – AMTA 2013 3 U6 ws1 v4.0