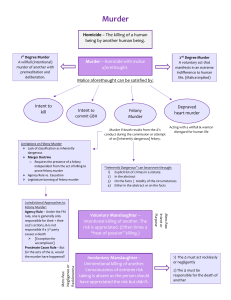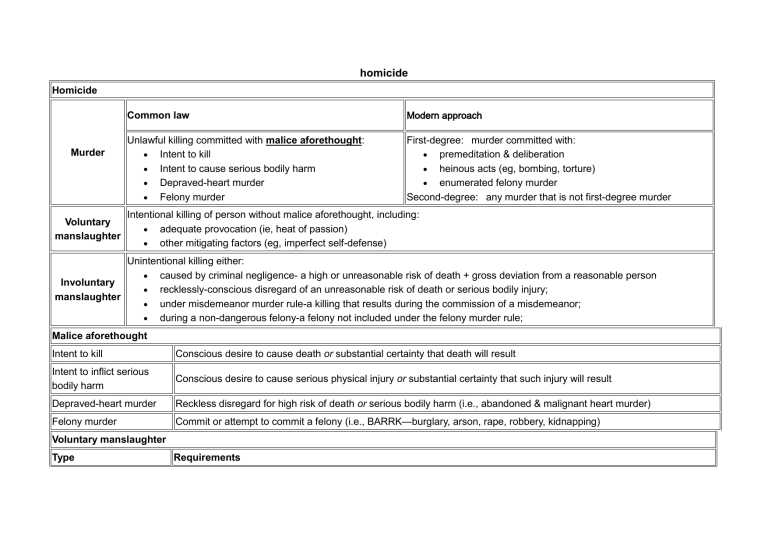
homicide Homicide Murder Voluntary manslaughter Common law Modern approach Unlawful killing committed with malice aforethought: Intent to kill Intent to cause serious bodily harm Depraved-heart murder Felony murder First-degree: murder committed with: premeditation & deliberation heinous acts (eg, bombing, torture) enumerated felony murder Second-degree: any murder that is not first-degree murder Intentional killing of person without malice aforethought, including: adequate provocation (ie, heat of passion) other mitigating factors (eg, imperfect self-defense) Unintentional killing either: caused by criminal negligence- a high or unreasonable risk of death + gross deviation from a reasonable person Involuntary recklessly-conscious disregard of an unreasonable risk of death or serious bodily injury; manslaughter under misdemeanor murder rule-a killing that results during the commission of a misdemeanor; during a non-dangerous felony-a felony not included under the felony murder rule; Malice aforethought Intent to kill Conscious desire to cause death or substantial certainty that death will result Intent to inflict serious bodily harm Conscious desire to cause serious physical injury or substantial certainty that such injury will result Depraved-heart murder Reckless disregard for high risk of death or serious bodily harm (i.e., abandoned & malignant heart murder) Felony murder Commit or attempt to commit a felony (i.e., BARRK—burglary, arson, rape, robbery, kidnapping) Voluntary manslaughter Type Requirements Heat of passion Intentional killing committed: in heat of passion and in response to adequate provocation Imperfect defense Intentional killing committed either: with honest but unreasonable belief that deadly force was necessary to prevent serious bodily injury or death or when defendant started altercation that led to necessary use of deadly force