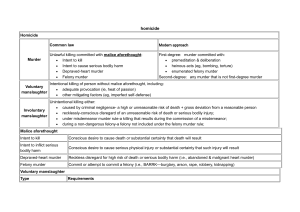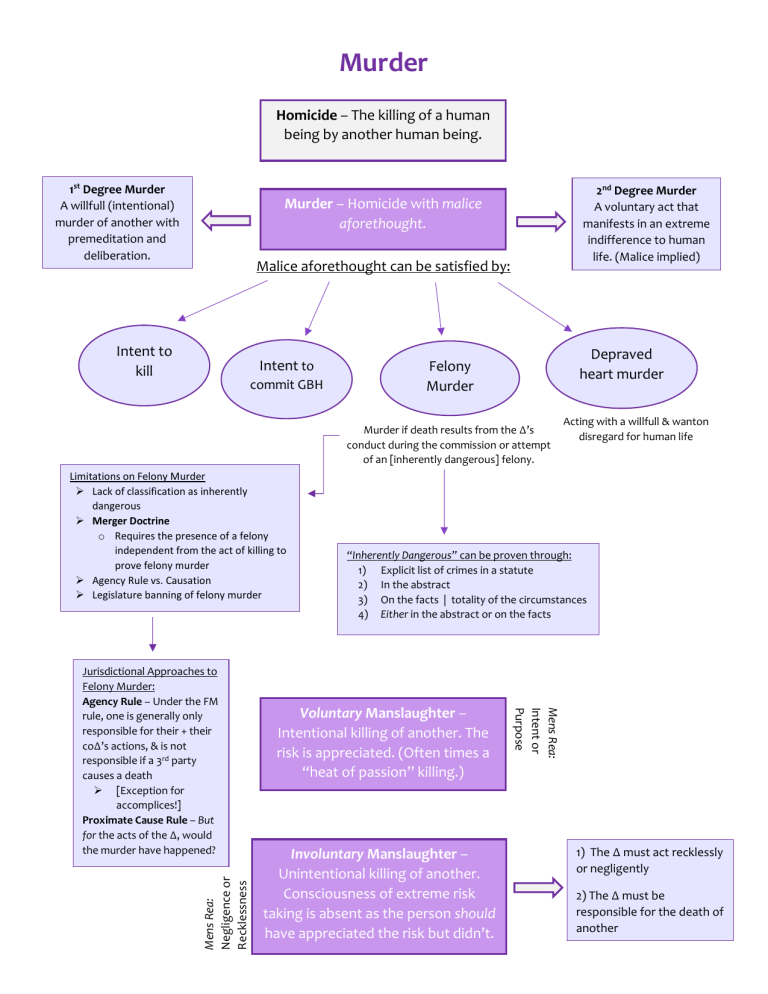
Murder Homicide – The killing of a human being by another human being. 1st Degree Murder A willfull (intentional) murder of another with premeditation and deliberation. 2nd Degree Murder A voluntary act that manifests in an extreme indifference to human life. (Malice implied) Murder – Homicide with malice aforethought. Malice aforethought can be satisfied by: Intent to kill Intent to commit GBH Depraved heart murder Felony Murder Murder if death results from the ∆’s conduct during the commission or attempt of an [inherently dangerous] felony. Limitations on Felony Murder Lack of classification as inherently dangerous Merger Doctrine o Requires the presence of a felony independent from the act of killing to prove felony murder Agency Rule vs. Causation Legislature banning of felony murder Mens Rea: Negligence or Recklessness “Inherently Dangerous” can be proven through: 1) Explicit list of crimes in a statute 2) In the abstract 3) On the facts | totality of the circumstances 4) Either in the abstract or on the facts Voluntary Manslaughter – Intentional killing of another. The risk is appreciated. (Often times a “heat of passion” killing.) Involuntary Manslaughter – Unintentional killing of another. Consciousness of extreme risk taking is absent as the person should have appreciated the risk but didn’t. Mens Rea: Intent or Purpose Jurisdictional Approaches to Felony Murder: Agency Rule – Under the FM rule, one is generally only responsible for their + their co∆’s actions, & is not responsible if a 3rd party causes a death [Exception for accomplices!] Proximate Cause Rule – But for the acts of the ∆, would the murder have happened? Acting with a willfull & wanton disregard for human life 1) The ∆ must act recklessly or negligently 2) The ∆ must be responsible for the death of another