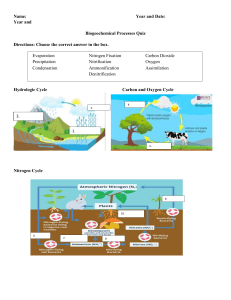
lOMoARcPSD|21129033 Unit 1 The Living World 2019 AP Environmental Science (High School - USA) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Cuiwei Xu (cuiweixu70@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|21129033 Unit 1 The Living World Predator-an animal that naturally hunt others for survived Prey- an animal that is hunted and killed Symbioses-interaction between two different organisms living close physical association typically to the advantage of both. What is competition? The activity or condition of competing How does competition sometimes lead to resource partitioning? It is a way to avoid competition for resources, it happens when species divide a niche. Biodiversity- the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem Biome- a large naturally occurring community of flora and fauna occupying a major habitat Nitrification- the transformation of ammonia to nitrate biological oxidation Denitrification-nitrate being reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen by bacteria Assimilation- process by which plants and animals incorporate the NO3- and ammonia formed through nitrogen fixation and nitrification. Nitrogen Fixation- which molecular nitrogen in the air is converted into ammonia or related nitrogenous compounds in soil Ammonification- the organically bound nitrogen of microbial, plant, and animal biomass is recycled after their death. Biotic:any living component that affects another organism or shapes the ecosystem. Examples: Grass Mouse Deer Abiotic:non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Examples: Wind Water Soil Downloaded by Cuiwei Xu (cuiweixu70@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|21129033 First law of Thermodynamics Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, energy can only be transferred or changed from one to another. Second Law of Thermodynamics When energy changes from one form to another, or matter moves freely, entropy, in a closed system increases Gpp Gross primary productivity the rate at which solar energy is captured in sugar molecules during photosynthesis NPP Net primary productivity, minus the rate of energy loss to metabolism and maintenance Downloaded by Cuiwei Xu (cuiweixu70@gmail.com)