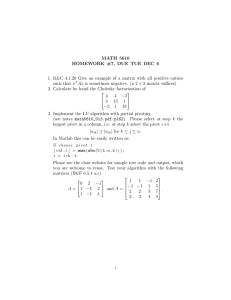
Sources of Innovation 1. Knowledge Push - use ideas based on own research or others to create new ventures. 2. Need Pull - necessity is the mother of invention; innovation as response to a need for change. 3. Shocks to the System - events which changed the world forcing innovation to new directions. 4. Making Process Better - social need providing the pull for new products, processes, and services. 5. Crisis-driven Innovation - urgency of a need or the extent of demand. 6. Challenge of Undeserved Markets - differences among potential users; disruptive. 7. Emerging Markets - developing solutions to meet needs of a potential market. 8. Mass Customization - meet demands for variety and increasing customization. A. Distribution - packaging, schedule, location B. Assembly - standardized components C. Fabrication - manufactured to order D. Design - products do not exist until customer order initiated 9. Users as Innovators - users themselves become source of ideas. 10. Using the crowd - various people in the crowd as source of perspectives. 11. Extreme Users - users in the toughest environments satisfy their need through innovation. 12. Prototyping - boundary object; idea passed around with more ideas becomes a shared project. A. Stepping stone in our thought processs B. Allows plurality C. Allows learning D. Suggests further possibilities 13. Watching others and learning from them - benchmarking; structured comparisons with others. 14. Recombinant Innovation - transferring or combining old ideas in new contexts. 15. Design-led Innovation - design process seeking to give meaning, shape and form to products. 16. Regulation - stimulus given by changes in rules and regulations. 17. Futures and Forecasting - through imagining and exploring alternative trajectories. 18. Accidents - unexpected events as a source of discovery in innovation. Managing Innovation Within Firms - Innovation is increasingly viewed as an organizational activity. Dilemma in Innovation Management Efficiency Gains - Creativity Gains stable and controlled environments - loose and flexible environment stable routines - room for creativity to try out new ideas 1. Exploitation - efficiency, increasing productivity, control, certainty, variance reduction. 2. Exploration - search, discovery, autonomy, innovations, embracing variation. 3. Ambidexterity - both with other competencies, systems, incentives, processes, culture. *In low technology sectors - dominance of incremental innovation; scarcity of disruptive innovation. Dynamic Capabilities - capacity of an organization to purposefully create, extend or modify its resource base. Low Output Uncertainty High Managing Uncertainty Pearson’s Uncertainty Map 3. Applications Engineering 4. Combining market opportunities with technical capabilities Low 1. Exploratory/Blue Sky Research 2. Development Engineering Process Uncertainty High Organizational Characteristics that facilitate the Innovation Process 1. Innovation Stimulus - leadership, people management, knowledge management, creativity management 2. Innovation Capacity - technology management, R&D management 3. Innovation Performance - product innovation, process innovation Classification of Industrial Firms 1. Supplier-dominated Firms - housebuilding firms,agricultural firms, retail firms 2. Science-based Firms/Technology-intensive Firms - manipulation of science and technology; pharmaceuticals, electronics, computing 3. Scale-intensive Firms - manufacturing sector; engineering, design,manufacturing 4. Specialist Equipment Suppliers Organizational Structures and Innovation 1. Formalization - organic vs mechanistic organizational structure 2. Complexity - number of professional groups or diversity of specialists within the organization 3. Centralization - location of power within an organization 4. Organizational Size - economic and organizational resources; number of employees, scale of operation IT Systems and their Impact on Innovation - ERP Systems - software used to manage day-to-day business activities. Innovation Management Tools and Methods 1. Knowledge and Technology Management 2. Market Intelligence 3. Cooperation and Networking 4. Human Resource and Management 5. Interface Management 6. Creativity Development 7. Process Improvement 8. Innovation Project Management 9. Design and Product Development 10. Business Creation Innovation Audit - to uncover areas of strength and weakness and to see how to improve the firm’s performance Developing New Products and Services Development of New Products Process 1. Concept Generation - identifying opportunities A. Market Pull B. Technology Push 2. Project Assessment and Selection - screening and choosing projects that satisfy certain criteria A. Costs a) Actual Cost b) Opportunity Cost B. Filtering a) Aggregate Product Plan i. Ensure that resources are applied to appropriate types and mix of projects ii. Develop a capacity plan to balance resource and demand iii. Analyze the effect of proposed projects on capabilities to ensure meeting of future demand b) Development Funnel/Stage-gate System - identify, screen, review and converge development projects as they move from idea to commercialization; formal framework for filtering based on explicit criteria 3. Product Development - translating selected concepts to physical products A. All activities necessary to take the chosen concept and deliver a product for commercialization 4. Product Commercialization - testing, launching, marketing new product A. Customer Co-development, test marketing and use of alpha, beta and gamma test B. Identify factors that influence directly the process of new product development Agile Development - setting up a core self-managed team, drawing on different functions and with a clear and stretching target Lean Start-up - low waste approach Core Elements 1. Build-Measure-Learn - design hypothesis to test an idea and adjust project based on feedback 2. Minimum Variable Product - simple prototype to generate data 3. Validated Learning - data that provide useful information and help learning about the venture 4. Innovation Accounting - using data to ensure resources are being well spent 5. Pivoting - test idea out on customers and adapt accordingly to feedback A. Zoom-in Pivot - single feature in product becomes entire product B. Zoom -out Pivot - whole product becomes a single feature in something much larger C. Customer Segment Pivot - product was right but customer segment isn’t D. Customer Need Pivot - validated learning highlights a more important customer need or problem E. Platform Pivot - single separate application converge to become a platform F. Business Architecture Pivot - essentially changing the underling business model G. Value Capture Pivot - changes involve rethinking marketing strategy, cost structure, product and so on H. Engine of Growth Pivot - start-up model is rethought; viral, sticky, paid growth I. Channel Pivot - different routes to reach the market are explored J. Technology Pivot - alternative new technologies are used but the rest of the business model remain the same 6. Single Unit Flow - working in small batches and completing tasks on those rather than working in high volume 7. Line Stop/Andon Cord - ability to stop production when an error occurs 8. Continuous Improvement - keep reviewing and improving the core product and the process delivering it 9. Kanban - system of stock management associated with JIT production 10. Five Whys - tool that helps find the root causes of problems and directs action towards solving the those problems rather than treating symptoms Best Criteria for Success 1. Product Advantage - delivering unique benefits to users 2. Market Knowledge - detailed market studies and business/financial analysis; competitive analysis 3. Clear Product Definition - defining target markets , clear concept definition and benefits to be delivered, clear and complete; use of priority list agreed before development begins 4. Risk Assessment - appropriately addressing risk with respect to the market and the firm’s capabilities 5. Project Organization - use of cross-functional, multidisciplinary teams carrying responsibility for the project from beginning to end 6. Project Resource - sufficient financial and material resources and human skills must be available 7. Proficiency for Execution - quality of technological and production activities and all pre-commercialization business analyses and test marketing 8. Top Management Support - management must be able to create an atmosphere of trust, coordination and control from concept to launch Factors influencing product success/failure -Commitment of Senior Management -Clear and Stable Vision -Improvisation -Information Exchange -Collaboration under Pressure Developing New Services *Great care needs to be taken when making any generalization about the service sectors. Fundamental Difference between Manufacturing and Service Operations 1. Tangibility - goods are tangible whereas service are mostly not 2. Simultaneity - time between production and consumption of goods allow room for distribution, storage and sales while service are produced and almost immediately consumed 3. Perceptions of Performance and Quality - more important in services; difference between expectations and perceived performance 4. Tangible Aspects - appearance of facilities, equipment and staff 5. Responsiveness - prompt service and willingness to help 6. Competence - ability to perform service dependably 7. Assurance - knowledge and courtesy of staff and ability to convey trust and confidence 8. Empathy - provision of caring, individual attention 9. Storage - services cannot usually be stored A. Capacity Management - ability to hold stocks of services matching supply and demand a) Pricing - help smooth fluctuations in demand; discounts at off-peak times b) Outsourcing or employing part-time workers c) Queueing 10. Customer Contact - customers have low to no contact with the operations which produced goods whereas services demand high levels of contacts between operations and ultimate customer 11. Location - service location is often more important than operations that produced goods Diffusion on Innovation Diffusion - consumer willingness to embrace change Adoption - considered to be the decision to acquire something Implementation and Utilization - imply some action and adaptation Processes on Diffusion -Diffusion of an innovation is typically described by an S-shaped (logistic) curve Innovators - Early Adopters - Late Majority - Laggards 1. Demand-side Factors - direct contact with adopters with different perceptions of benefits and risk 2. Supply-side Factors - relative advantage of an innovation, availability of information, barriers to adoption, feedback between developers and users Characteristics of an Innovation 1. Relative Advantage - degree to which innovation is perceived as better than the product it supersedes or competing products 2. Compatibility - degree to which innovation is perceived to be consistent with the existing values, experience and needs of potential adopters 3. Complexity - degree to which innovation is perceived as being difficult to understand or use 4. Trialability - degree to which innovation can be experimented with on a limited basis 5. Observability - degree to which the results of innovation are visible to others Innovation Networks 4 Major Arguments pushing for Greater Levels of Networking in Innovation 1. Collective Efficiency - way of getting access to different resources through a shared exchange process 2. Collective Learning - facilitate a shared leaning process in which partners exchange experiences, challenge models and practices, bring new insights and ideas and support share experimentation 3. Collective Risk-Taking - permits higher levels of risk to be considered than any single participant might be prepared to undertake 4. Intersection of Different Knowledge Sets - opens up the participating organization to new stimuli and experiences Network - complex interconnected group or system; involves using that arrangement to accomplish particular tasks Why Networks? 1. Benefits of Cospecialization, sharing of joint infrastructure and standards and other network externalities outweigh the costs of network governance and maintenance 2. Mutual knowledge and social bonds develop through repeated dealings, increasing trust and reducing transaction costs. 3. Firms may be able to access the resources of a wide rage of other organizations through direct and indirect relationships Emergent Properties - the potential for the whole to be greater than the sum of its parts Learning Networks - shared learning can help deal with some of the barriers to learning which individual firms might face 1. There is potential for challenge and structured critical reflection from different perspectives. (Shared Learning) 2. Reduce perceived and actual costs and risks in trying new things. (Shared Experimentation) 3. Provide support and open new lines of inquiry and exploration. (Shared Experiences) 4. Explicate the system principles and seeing the pattern. (Shared Learning) 5. Provides an environment for surfacing assumptions an exploring mental models outside normal experience of individual organizations. (Shared Learning) Breakthrough Technology Collaborations - reduced risk and increased resource focused on a learning and experimental process Mobilizing Networking - happens in an informal way when people get together and share ideas as a by-product of their social and work interactions Types of Innovation Networks 1. Entrepreneur-based - bringing different complementary resources together to help take an opportunity forward. 2. Internal Project Teams - like entrepreneur network but inside an established organization 3. Internal Entrepreneur Networks - aimed at tapping into employee ideas 4. Communities of Practice - involve players inside and across different organizations bounded by a shared concern with a particular aspect or area of knowledge 5. Spatial Clusters - formed because players are close to each other (geographical closeness or proximity) 6. Sectoral Networks - formed because players share a common sector and often have the purpose of shared innovation to preserve competitiveness 7. New Product or Process Development Consortium - sharing knowledge and perspectives to create and market a new product or process concept 8. New Technology Development Consortium - sharing and learning around newly emerging technologies 9. Emerging Standards - exploring and establishing standards around innovative technologies 10. Supply Chain Learning - developing and sharing innovative good practice and possibly shared product development across value chain 11. Learning Networks - groups of individuals and organizations who converge to earn about new approaches and leverage their shared learning experience 12. Recombinant Innovation Networks - cross-sectoral groupings that allow for networking across boundaries and the transfer of ideas 13. Managed Open Innovation Networks - “not all smart people work for us” amplify access to ideas and resources 14. User Networks - connect to user as a source of innovation input rather than simply as passive markets 15. Innovation Markets - broadcast innovation needs and connect to potential solutions in a market place 16. Crowdfunding and new resource approaches - mobilization of crowd not as sources of ideas but of resources and judgment Networking at the Start Up Harder Benefits - leads to customers, investors, partners, suppliers, employees, and technical and market knowledge/information Softer Benefits - credibility/legitimacy, advice and problem solving, confidence and reassurance, motivation/inspiration, relaxation/interests Networking on the Inside - giant jigsaw puzzle which only a small number of the pieces have so far been fitted together; knowledge management Networking on the Outside - creating and combining different knowledge sets; open innovation Networking into the Unknown - identifying relevant new partners and learning how to work with them 1. Finding Prospective Partners a) Geographical b) Technological c) Institutional 2. Forming Relationships with Prospective Partners a) Ideological b) Demographic c) Ethnic Challenges of Innovations Networks 1. Set Up Stage a) Providing momentum for bringing network together and clearly defining its purpose b) Driven by a shared perception of opportunity 2. Operating Stage a) Network Boundary Management - how membership is defined and maintained b) Decision-making - how decisions get taken at the network level c) Conflict Resolution - how conflicts are resolved effectively d) Information Processing - how information flows among members and is managed e) Motivation - how members are motivated to join/remain within the network f) Risk/Benefit Sharing - how risks and rewards are allocated across member g) Coordination - how the operations are integrated and coordinated 3. Closing Stage - case for sustaining the networking activities for as long as members see benefits; periodic review and retargeting