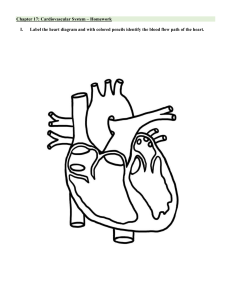
BME 312 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Seminar 2 – Components of ECG Dr. NG Hsiao Piau Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 What we will cover: Recap on ECG Recording of ECG Block diagram of ECG Frequently encountered problems 2 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Recap on ECG 3 of 24 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Recap on ECG The contraction of the numerous muscle cells at one time creates a mass electrical signal – ECG signal This signal can be detected by electrodes placed on the surface of the patient’s chest 4 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Recap on ECG 5 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Recap on ECG 6 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Recap on ECG 7 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 8 of 24 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 9 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 10 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 11 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 12 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Placing electrodes on the limbs: 13 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording VI VII VIII 14 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 15 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 16 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording ECG signals from Leads I, II, and III Limb Leads I, II, and III 17 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 18 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording aVR lead - an augmented unipolar limb lead in which the positive electrode is on the right arm 19 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording aVL lead - an augmented unipolar limb lead in which the positive electrode is on the left arm 20 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording aVF lead - an augmented unipolar limb lead in which the positive electrode is on the left leg 21 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 22 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Vector diagram of standard and augmented leads 23 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Vector diagram of standard and augmented leads 24 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Leads in the transverse plane 25 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Leads in the transverse plane 26 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Leads in the transverse plane 27 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Measurement of V1,V2, …, V6 28 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 29 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording Wilson’s central terminal (a reference terminal) 30 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 31 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 32 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 33 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 ECG Signal Recording 34 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Reflection Questions 1. DIn ECG measurement,VII is the voltage between __________. 2. The following circuit measures _______. 3. Is it true that the potential at Wilson’s central terminal is 0 voltage? 35 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 36 of 24 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 37 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 38 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 39 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Example 40 of 68 Amplifier has a gain of 25 in the dc-coupled stage High-pass filter feeds a noninverting amplifier stage that has a gain of 32 Total gain = 25x32 = 800 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Frequency filters Typical ECG signal frequency band 41 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 42 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 43 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 44 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Deducing the circuit: 45 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 46 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 47 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 48 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Driven right leg circuit 49 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 50 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 51 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 52 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 53 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 54 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Defibrillator protection • If the patient is connected to a defibrillator, a very high pulse may pass through the ECG • Defibrillator protection circuit can make use of diodes • Diodes will breakdown when a high voltage is present 55 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG ECG machine 56 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Typical surface electrodes 57 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG 58 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Block Diagram of ECG Holter Monitor (Suitable for long time monitoring) Portable tape recorder Records electrical activity of heart 59 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Reflection Questions 1. What is the purpose of ECG lead fall-off alarm system? 2. What is the purpose of driven right leg circuit? 3. If DC couple stage of preamplifier of ECG device has a gain of 20 and non-inverting stage has a gain of 10, what is the total gain? 60 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Frequently Encountered Problems 61 of 24 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Frequently Encountered Problems Noisy or Poor Quality ECG Traces Cannot be used for evaluation May be caused by: Patient or cable movement Shivering or seizures Electrical 50 Hz interference Distortions Make ECG trace interpretation difficult 62 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Frequently Encountered Problems 63 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Frequently Encountered Problems Frequency distortion 64 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Frequently Encountered Problems Saturation or cut-off distortion 65 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Frequently Encountered Problems 66 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Reflection Questions 1. Discuss some of the potential causes of poor quality ECG traces. 2. What is a potential problem that can be caused by improper adjustment of amplifier in ECG? 67 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014 Questions & Answers 68 of 68 Biomedical Instrumentation and Systems Effective: Sept 2014