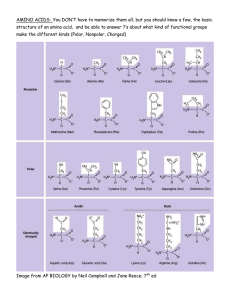
1a. Cell Theory - The cell theory states that all biological organisms are composed of cells; cells are the unit of life and all life come from preexisting life. The cell theory is so established today that it forms one of the unifying principles of biology. 1.b Features of a living cell Those characteristics are cellular organization, reproduction, metabolism, homeostasis, heredity, response to stimuli, growth and development, and adaptation through evolution. 2a. Organelle Function Nucleus DNA Storage Mitochondrion Energy production Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) Lipid production; Detoxification Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell Golgi apparatus Protein modification and export Shipping department 2b. Cells make up the smallest level of a living organism such as yourself and other living things. The cellular level of an organism is where the metabolic processes occur that keep the organism alive. That is why the cell is called the fundamental unit of life. 4ai Essential amino acids- Essential amino acids cannot be made by the body. As a result, they must come from food. The 9 essential amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Ii Non essential amino acids- Nonessential amino acids include: alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. Conditional amino acids are usually not essential, except in times of illness and stress. 4b. “A zwitterion is a molecule that has both positive and negative regions of charge.” In the solid state, amino acids exist as dipolar ions called zwitterions. While discussing whether a substance is zwitterionic or not, the pH range in which the information is required must be specified (because a sufficiently alkaline solution will change the zwitterion to an anion, and a sufficiently acid solution will change it to a cation). 5a. Amino Acids- Amino acids, often referred to as the building blocks of proteins, are compounds that play many critical roles in your body. You need them for vital processes such as building proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters. Amino acids are concentrated in proteinrich foods such as meat, fish, and soybeans. Some people also take certain amino acids in supplement form as a natural way to boost athletic performance or improve mood. They’re categorized as essential, conditionally essential, or nonessential depending on several factors. 5b. 6a. Lipids - any of a class of organic compounds that are fatty acids or their derivatives and are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include many natural oils, waxes, and steroids. 6b. The Functions of Lipids in the Body Storing Energy. The excess energy from the food we eat is digested and incorporated into adipose tissue, or fatty tissue. Regulating and Signaling. Insulating and Protecting. Aiding Digestion and Increasing Bioavailability. 7a. Fatty Acids-a carboxylic acid consisting of a hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxyl group, especially any of those occurring as esters in fats and oils. 7b. The three primary types of lipids are phospholipids , sterols, and triglycerides . 8a.heteropolysaccharide component sugars functions distribution hyaluronic acid D-glucuronic acid and Nacetyl-D-glucosamine lubricant, shock absorber, water binding connective tissue, skin chondroitin-4-sulfate* D-glucuronic acid and Nacetyl-D-galactosamine-4O-sulfate calcium accumulation, cartilage and bone formation cartilage heparin* D-glucuronic acid, Liduronic acid, N-sulfo-Dglucosamine anticoagulant mast cells, blood gamma globulin* N-acetyl-hexosamine, Dmannose, D-galactose antibody blood blood group substance* D-glucosamine, Dgalactosamine, L-fucose, D-galactose blood group specificity cell surfaces, especially red blood cells 9i. All amino acids except for glycine are stereoisomers. This means that there are mirror images of their structure. It is just like how we have left hands and right hands. These are labeled L (left-handed) and D (right-handed) to distinguish the mirror images. ii. Epimer in stereochemistry specifies one of a pair of stereoisomers. At stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. A molecule may contain numerous stereocenters leading to several stereocenters. iii. Pyranose is a collective term for saccharides that have a chemical structure that includes a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. There may be other carbons external to the ring.