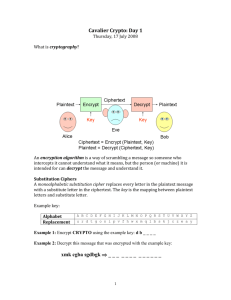
VIGENERE CIPHER
•
The Vigenère Cipher, which uses a keyword to encrypt and decrypt text, is implemented in the
code.
•
The code has two operations: encrypt and decrypt.
•
A plaintext message and a key are entered into the encrypt function, which shifts each letter in
the plaintext by a quantity defined by the corresponding letter in the key to produce the
encrypted message.
•
The decrypt function accepts an encrypted message and a key as inputs and, by reversing the
shift used during encryption, produces the original plaintext message.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class VigenereCipher {
// Method to encrypt plaintext
public static String encrypt(String plainText, String key) {
StringBuilder encryptedMessage = new StringBuilder();
int plainTextIndex = 0;
for (char character : plainText.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(character)) {
int base = Character.isLowerCase(character) ? 'a' : 'A';
int shiftValue = (key.charAt(plainTextIndex % key.length()) base + 26) % 26;
encryptedMessage.append((char) ((character - base +
shiftValue) % 26 + base));
plainTextIndex++;
} else {
encryptedMessage.append(character);
}
}
return encryptedMessage.toString();
}
// Method to decrypt encrypted text
public static String decrypt(String encryptedText, String key) {
StringBuilder decryptedMessage = new StringBuilder();
int encryptedTextIndex = 0;
for (char character : encryptedText.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(character)) {
int base = Character.isLowerCase(character) ? 'a' : 'A';
int shiftValue = (key.charAt(encryptedTextIndex %
key.length()) - base + 26) % 26;
decryptedMessage.append((char) ((character - base shiftValue + 26) % 26 + base));
encryptedTextIndex++;
} else {
decryptedMessage.append(character);
}
}
return decryptedMessage.toString();
}
•
The main function of the code accepts user input for the plaintext message and key before
calling the encrypt and decrypt functions to display the encrypted and decrypted messages,
respectively.
•
The modulo operator is used in the code to ensure that the shift value is always within the range
of letters in the alphabet.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner inputScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter plaintext: ");
String plainText = inputScanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter key: ");
String key = inputScanner.nextLine();
inputScanner.close();
String encryptedText = encrypt(plainText, key);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedText);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decrypt(encryptedText, key));
}
}
OUTPUT: