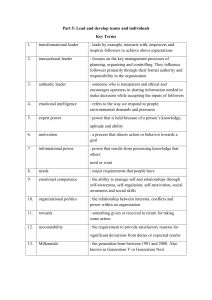
UNIVERSITY OF ZAMBIA SCHOOL OF NURSING SCIENCES PROGRAME: MASTER OF SCIENCE IN CLINICAL NURSING COURSE: LEADERSHIP, MANAGEMENT AND GOVERNANCE PRACTICE COURSE CODE: NRS 5175 LECTURERS: DR. D. CHANDA, MS. P. SINKAMBA, MR. K. LYAMBAI INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT: 1 NAME: DICKSON LUNGU COMPUTERS NUMBER: A leadership style is a leader's method of providing direction, implementing plans, and motivating people. (Kotter 2001). Leaders are characterized as individuals who have differential influence over the setting of goals, logistics for coordination, monitoring of effort, and rewards and punishment of group members. This paper discusses the leadership styles that the author has experienced at the 3 different facilities that he has worked. One of the key reasons why certain leadership styles are blocked with positive outcomes for employees and organizations is the extent to which they build follower trust in leaders. Trust in the leader has been linked to a range of leadership styles and evidence suggests that when followers trust their leaders they are more willing and able to go the extra mile to help their colleagues and organization. Trust also enables them to feel safe to speak up and share their ideas. In contrast, when a leader does not inspire trust, a follower’s performance may suffer as they must spend time and energy watching their backs.( Legwood 2021) LEADERSHIP STYLES AUTOCRATIC: Autocratic leadership is a management style wherein one person controls all the decisions and takes very little inputs from other group members. Autocratic leaders make choices or decisions based on their own beliefs and do not involve others for their suggestion or advice. ( Kotter 2001). An authoritarian leadership style is descried as being as "leaders behavior that asserts absolute authority and control over subordinates and demands unquestionable obedience from subordinates.(Cheng B.S 2004) Such a leader has full control of the team, leaving low autonomy within the group. The group is expected to complete the tasks under very close supervision, while unlimited authority is self-bestowed by the leader. Subordinates' responses to the orders given are either punished or rewarded. A way that those that have authoritarian leadership behaviors tend to lean more on "...unilateral decision-making through the leader and strive to maintain the distance between the leader and his or her followers. (Cheng 2004) Advantages of automatic leadership style: Ensures faster decision making: an autocratic leadership style is considered ideal in emergencies situation as the leader makes all decisions without taking into account the opinion of staff. Moreover, mistakes are not tolerated within the blame put on individuals. Ensures easy communication: Communication in the workplace is sharing information from one person to another. As the leader clearly defines goals, expectations, and other information to employees, it helps in simplifying and enhancing workplace communication. An autocratic leader often sends direct information to the employees, ensuring accuracy in information. Disadvantages of autocratic leadership style Results in mismanagement: An autocratic leader typically supervises small details of the work their team members are performing, resulting in micromanagement. Lacks creativity: It can sometimes be challenging for a single person to develop creative ideas, compared to people who work as a team. Restricting ideas leads to predictable work patterns that don't foster a culture of creativity in the workplace. Low satisfaction: Because of one-way communication and lack of recognition employees do not get the answers to the questions they deserve. They are bound to follow whatever the leaders ask them. ( Cheng B.S 2004) DEMOCRATIC LEADERSHIP STYLE: The democratic leadership style, or participative management, actively involves the people being led. Democratic leaders often seek feedback and input from subordinates. They encourage conversation and participation in the decision-making process. (Kotter 2001). Democratic leadership attempts to manage with democratic principles, such as selfdetermination, inclusiveness, equal participation and deliberation. The following three features characterize democratic leadership: Distribution of responsibility - A manager that leads democratically will distribute responsibility among his group to facilitate participation in decision making. Empowering group members - Leaders must empower their members so that the members can accomplish their responsibilities. Empowerment includes providing training and education necessary for delegated task completion. Aiding group decision-making process - A major role of a democratic leader is to ensure democratic deliberation in making group decisions. This means that a leader should act as a facilitator and mediator between group members and ensure that a psychologically healthy and respectful environment is maintained.(kotter 2001) Advantages of democratic leadership style: Emphasizing a people-first culture: As we mentioned earlier, a democratic management style can improve your culture of employee engagement, commitment, and job satisfaction. Strengthening workplace relationships: This leadership style also leads to deeper relationships. Specifically between the democratic leader and their team members. Upskilling teams: Also, democratic leaders allow the team to think through problems and decisions. This teaches their teams important skills. Like problem-solving and critical thinking. Supporting employees to manage up: Over time, these team members are in a better position to take on bigger responsibilities and operate more independently. Ultimately, developing new leaders. (Kotter 2014) LAISSEZ-FAIRE LEADERSHIP STYLE: The laissez-faire leadership style is where all the rights and power to make decisions is fully given to the followers.(Kevin 2013). Laissez-faire leaders allow followers to have complete freedom to make decisions concerning the completion of their work. It allows followers a self-rule, while at the same time offering guidance and support when requested. The laissez-faire leader using guided freedom provides the followers with all materials necessary to accomplish their goals, but does not directly participate in decision making unless the followers request their assistance. This is an effective style to use when: Followers are highly skilled, experienced, and educated. Followers have pride in their work and the drive to do it successfully on their own. Followers are experts, in situations where followers have more knowledge than the group leader. Followers are trustworthy and experienced.( Kevin 2013) TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP STYLE: Transformational leadership is a theory of leadership where a leader works with teams or followers beyond their immediate self-interests to identify needed change, creating a vision to guide the change through influence, inspiration, and executing the change in tandem with committed members of a group; This change in self-interests elevates the follower's levels of maturity and ideals, as well as their concerns for the achievement.(Bass & Riggio, 2014) As transformational leaders work with their employees to implement effective change, they rely on things like communication, charisma, adaptability and empathetic support. Transformational leaders listen to employees’ concerns and needs so they can provide adequate support. They operate from the understanding that what motivates one person may not motivate someone else. As a result, they’re able to adapt their management styles to accommodate various individuals on their team.Transformational leaders are able to articulate a unified vision that encourages team members to exceed expectations. They understand that the most motivated employees are the ones who have a strong sense of purpose. These leaders are not afraid to challenge employees. They remain optimistic about future goals and are skilled at giving meaning to the tasks at hand. Transformational leaders model ethical behavior. Their moral conduct earns a necessary level of respect and trust. This can help leaders steer decision-making that works to improve the entire organization. (Bass & Riggio 2014) SITUATIONAL LEADERSHIP STYLES: Situational Leadership means adapting your leadership style to each unique situation or task to meet the needs of the team or team members. Directing: This leadership style is mostly a one-way street with little input from the follower or employee. This should be used when one needs detailed guidance on a specific task. Take them through, step-by-step, what needs to get done, how it should be done, and when it needs to be completed.( Hersey & Blanchard 1985) Coaching: This leadership style is more effective when your followers need a lot of guidance but are highly motivated. In other words, this is primarily for people who want and need to learn. The leader might say, “Here’s what I’d like you to do. What do you think?” ( Hersey & Blanchard 1985) Supporting: This is for followers with the skills to complete the task but who may lack the confidence to do it on their own. This style features below-average amounts of direction. You might hear your leader say, “Here’s the task. How do you think it should be done? Let’s talk about it. How can I help you on this one?” ( Hersey & Blanchard 1985). Delegating: This leadership style is ideal for followers and employees who score high in motivation, ability, and confidence. These types of people know what to do, how to do it and can do it independently. For example, the leader might delegate an assignment and say, “If I can help, just ask. If not, you’re on your own.” (Hersey & Blanchard 1985). Advantages of situation leadership styles. Leaders are able to use whichever leadership style they believe is best in a given situation.This type of leadership style is fairly simple, as all that is needed is the ability to assess a situation and adjust to it. Situational leadership can create a more comfortable environment for employees as the leadership style implemented will typically match their needs. This type of leadership accounts for the various levels of development in employees and helps to address each employee's skill level and needs. Disadvantages of Situational leadership could cause confusion within an organization, as a situational leader may constantly change their approach to address each team or individual's needs. Situational leadership tends to only focus on short term goals and as a result, may overlook long term goals..(Hersey & Blanchard ,1969) REFRENCES Kotter, John P., 1947- (2001). What leaders really do. Harvard Business School Pub. Corp. ISBN 157851-382-0. OCLC 57299317 Legood, A., van der Werff, L., Lee, A., & Den Hartog, D. (2021). A meta-analysis of the role of trust in the leadership-performance relationship. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 30(1), 1-22. Chira, Robert (2016). International Logistics Management. p. 412. ISBN 978-1524632090 Cheng, B. S., Chou, L. F., Wu, T. Y., Huang, M. P., & Farh, J. L. (2004). Paternalistic leadership and subordinate responses: Establishing a leadership model in Chinese organizations. Asian Journal of Social Psychology, 7(1), 89–117. Kevin Wren (2013). Social Influences. Routledge. p. 75. ISBN 978-1-134-66357-6. Bass, B. M., & Riggio, R. E. (2014). Transformational leadership. Routledge. Hersey, P. and Blanchard, K. H. (1969). Management of Organizational Behavior – Utilizing Human Resources. New Jersey/Prentice Hall.