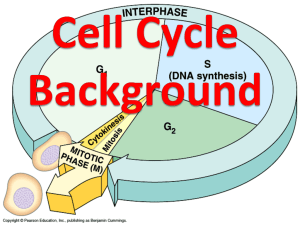
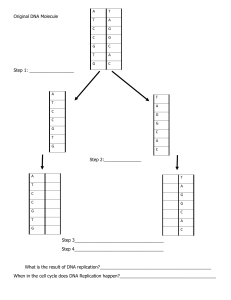
Cell cycle and cell reproduction Part 1 ○ Life cycle: the sequence of growth and development stages that an organism goes through during its life. ○ DNA is a double stranded molecule made of four different subunits of nucleotides ( A ,T, C, G). ○ Chromosomes is a long continuous thread of DNA . ○ Each body cell has 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs. ○ Cells must receive a full set of DNA (no more, no less) to work properly. ○ The scientist Rudolf Virchow in 1858 : each cell arise from a previous cell ○ The cell cycle as a process by which a parent cell grows, duplicates itself and divides to produce new cells. ○ There's 2 portions of the cell cycle : interphase which include a number of stages and mitotic stage when mitosis and cytokinesis occur ○ Cell grows continuously in interphase which consist of three phases Interphase ○ Interphase is the stage during which the cell grows, develops into a mature, functional cell, duplicates the DNA in its nucleus, and prepares for division. ○ Interphase is divided into three stages: Gap 1(G1), synthesis (S), and Gap 2 (G2). ○ Gap 1(G1): growing, carrying out normal cellular functions, and preparing to replicate DNA, (before DNA replication , gap between M phase and S phase ) (Growth) ○ Synthesis (S): copying DNA to prepare for division(DNA synthesis, DNA replication ) ○ Gap 2 (G2): preparing for the division of nucleus (gap between S and M phase , after DNA replication ) (Growth) - Interphase prepares the cell to divide (G1, S, G2) - During interphase, the DNA is duplicated. - Not a part of mitosis - During interphase the chromosomes formed of one chromatin is doubled into two chromatids by a process called duplication or replication.