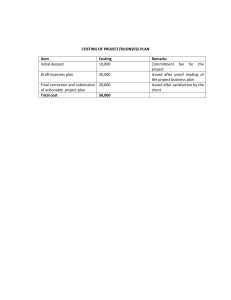
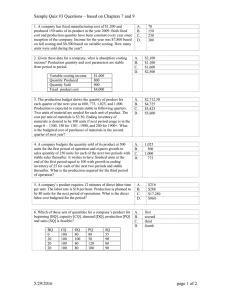
CPAR CPA REVIEW SCHOOL OF THE PHILIPPINES Manila MANAGEMENT ADVISORY SERVICES APRIL 28 AND MAY 1, 2021 Final Pre-board Examination Instructions: Choose the BEST answer for each of the following items. 1. A company is using a constant growth dividend discount model to forecast the value of a share of common stock. Inherent in such company’s assumptions is the idea that a. compounding growth is linear. b. dividends will grow at a rate faster than the presumed discount rate. c. stock price will grow at the same rate as the dividend. d. stock price will grow at the same amount as the dividend. 2. ABC Company wants to buy shares of XYZ Company in two years. ABC Company uses a constant growth dividend discount model with a presumed dividend growth rate of 5%. If ABC’s discount rate is 10% and XYZ’s current year dividend is P20, what is the approximate price ABC Company will pay? a. P400 c. P441 b. P420 d. P463 3. In equipment replacement decisions, which one of the following does not affect the decision-making process? a. current disposal price of the old equipment b. original fair market value of the old equipment c. cost of the new equipment d. operating costs of the new equipment 4. In considering the payback period for three projects, X Corporation gathered the following data about cash flows: Which of the projects will achieve payback within three years? a. Projects A, B, and C b. Projects B and C c. Project B only d. Projects A and C 5. If a product required a great deal of electricity to produce, and crude oil prices increased, which of the following costs most likely increased? a. Direct materials c. Prime costs b. Direct labor d. Conversion costs 6. Listed below are selected line items from the cost of quality report for a company for last month. Category Rework Equipment maintenance Product testing Product repair Amount P 725 1,154 786 695 What is the company’s total prevention and appraisal cost for last month? a. P 786 c. P1,849 b. P1,154 d. P1,940 7. A corporation had sales of P2,000,000, a profit margin of 11%, and assets of P2,500,000. The company decided to reduce its debt ratio to 0.40 from 0.50 by selling new common stock and using the proceeds to repay principal on some outstanding long-term debt. After the refinancing, what is the company’s return on equity? a. 3.5 percent c. 14.7 percent b. 5.3 percent d. 22.9 percent 8. The coefficient of determination, r2, in a multiple regression equation is the a. percentage of variation in the independent variables explained by the variation in the dependent variable. b. percentage of variation in the dependent variables explained by the variation in the independent variable. c. measure of the proximity of actual data points to the estimated data points. d. coefficient of the independent variable divided by the standard error of regression coefficient. 9. Which of the following is correct if there is an increase in the resources available within an economy? a. More goods and services will be produced in the economy. b. The economy will be capable of producing more goods and services. c. The standard of living in the economy will rise. d. The technological efficiency of the economy will improve. 10. Assume an economy is at the peak of the business cycle. Which of the following policy combinations is the most effective way to dampen the economy and prevent inflation? a. Increase government spending, reduce taxes, increase money supply, and reduce interest rates. b. c. d. Reduce government spending, increase taxes, increase money supply, and increase interest rates. Reduce government spending, increase taxes, reduce money supply, and increase interest rates. Reduce government spending, reduce taxes, reduce money supply, and reduce interest rates. 11. The benefits of a just-in-time system for raw materials usually include: a. elimination of non-value adding operations. b. increase in the number of suppliers, thereby ensuring competitive bidding. c. maximization of the standard delivery quantity, thereby lessening the paperwork for each delivery. d. decrease in the number of deliveries required to maintain production. 12. Controllers ordinarily are not responsible for a. preparation of tax returns. b. reporting to government. c. protection of assets. d. investor relations. 13. The professional certification program most suited for one interested in a career in management accounting leads to which of the following designations? a. Certified Computing Professional (CCP) b. Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) c. Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) d. Certified Management Accountant (CMA) 14. The IMA Statement of Ethical Professional Practice includes an integrity standard. It requires an IMA member to a. refrain from conduct that prejudices the ability to perform duties ethically. b. report any relevant information that could influence users of financial statements, c. disclose confidential information when authorized by his or her firm or required under the law. d. refuse gifts from anyone. 15. Following are a company’s production costs for the month just ended: Direct materials Direct labor Factory overhead P100,000 90,000 4,000 What amount of costs should be traced to specific products in the production process? a. b. P194,000 P190,000 c. d. P100,000 P 90,000 16. A company has fixed costs of P100,000 and breakeven sales of P800,000. What is the projected profit at P1,200,000 sales? a. P 50,000 c. P200,000 b. P150,000 d. P400,000 17. A company is concerned about its operating performance last year, as summarized below: Revenues (P12.50 per unit) Variable costs Operating loss P300,000 180,000 (40,000) How many additional units should have been sold in order for the company to breakeven last year? a. 32,000 c. 16,000 b. 24,000 d. 8,000 18. A company is contemplating marketing a new product. Fixed costs will be P800,000 for production of 75,000 units or less, and P1,200,000 if production exceeds 75,000 units. The variable cost ratio is 60% for the first 75,000 units. Variable costs will decrease to 50% of sales for units in excess of 75,000. If the product is expected to sell for P25 per unit, how many units must the company sell to breakeven? a. 120,000 c. 96,000 b. 111,000 d. 80,000 ITEMS 19 TO 21 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: A wholesale distributing company has budgeted its before-tax profit to be P643,500 for Year 3. The company is preparing its annual budget for Year 4 and has accumulated the following data: Projected sales Variable costs as a percent of sales: Cost of merchandise Sales commissions Shipping expenses Annual fixed operating costs: Selling expenses Administrative expenses 19. P6,000,000 30% 5% 10% P 772,200 1,801,800 If the wholesale distributing company wants to earn the same beforetax operating income in Year 4 as budgeted for Year 3, the projected sales would not be P6,000,000 but would have to be: a. P4,950,000 c. P5,850,000 b. P5,362,500 d. P7,150,000 20. Using the original P6 million projection, the wholesale distributing company’s margin of safety in terms of revenues for Year 4 would be a. P 82,500 c. P 280,000 b. P150,000 d. P1,320,000 21. Using the original P6 million projection, the wholesale distributing company’s degree of operating leverage for Year 4 would be a. 8.06 times c. 4.54 times b. 2.33 times d. 1.82 times 22. The following is a summarized income statement for a company’s profit center for the month just ended: Contribution margin P70,000 Period costs: Manager’s salary P20,000 Facility depreciation 8,000 Corporate expense allocation 5,000 33,000 Profit center income P37,000 Which of the following amounts would most likely be subject to the control of the profit center’s manager? a. P70,000 c. P37,000 b. P50,000 d. P33,000 ITEMS 23 TO 25 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: A corporation is a highly automated manufacturing firm. The vice president of finance has decided that traditional standards are inappropriate for performance measures in an automated environment. Labor is insignificant in terms of the total cost of production and tends to be fixed, material quality is considered more important than minimizing material cost, and customer satisfaction is the number one priority. As a result, delivery performance measures have been chosen to evaluate performance. The following information is considered typical of the time involved to complete orders of 50 units. Wait time from order being placed to start of production Wait time from start of production to completion Inspection time Process time Move time 23. What is the manufacturing cycle efficiency for this order? a. 40% c. 80% b. 32% d. 61.5% 5 7 2 8 3 hours hours hours hours hours 24. What is the delivery cycle efficiency for this order? a. 40% c. 80% b. 32% d. 61.5% 25. What is the velocity for this order? a. 0.16 c. 2.5 b. 0.40 d. 6.25 26. A computer service center had the following operating statistics for the month: Sales Operating income Net profit after taxes Total assets Shareholders’ equity Cost of capital P450,000 25,000 8,000 500,000 200,000 6% Based on the given information, which one of the following statements is true? The computer service center has a a. return on investment of 4%. b. residual income of P(5,000). c. return on investment of 1.6%. d. residual income of P(22,000). ITEMS 27 AND 28 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: A company reported these data at year end: Pre-tax operating income Current assets Long-term assets Current liabilities Long-term liabilities P4,000,000 4,000,000 16,000,000 2,000,000 5,000,000 The long-term debt has an interest rate of 8%,and its fair value equaled its book value at year-end. The fair value of the equity capital is P2 million greater than its book value. The company’s income tax rate is 25%, and its cost of equity capital is 10%. 27. What is the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) to be used in the economic value added (EVA) calculation? a. 8.0% c. 9% b. 8.89% d. 10% 28. The economic value added (EVA) is a. P1,380,000 c. P1,830,000 b. P1.620,000 d. P3,000,000 29. An appropriate transfer price between two divisions of a manufacturer can be determined from the following data: FABRICATING DIVISION: Market price of subassembly Variable cost of subassembly Excess capacity in units P50 P20 0 ASSEMBLING DIVISION: Number of units needed 500 If the Fabricating Division would consider to sell the needed subassembly to the Assembling Division, the minimum transfer price for this sale is: a. P20 c. P50 b. P70 d. P35 ITEMS 30 TO 32 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: A company purchased a new machine to stamp the company logo on its products. The cost of the machine was P250,000, and it has an estimated useful life of 5 years with an expected salvage value at the end of its useful life of P50,000. The company uses the straight-line depreciation method. The new machine is expected to save P125,000 annually in operating costs. The company’s tax rate is 40%, and it uses a 10% discount rate to evaluate capital expenditures. 30. What is the traditional payback period for the new stamping machine? a. 2.00 years c. 2.75 years b. 2.63 years d. 2.94 years 31. What is the accounting rate of return based on the average investment in the new stamping machine? a. 20.4% c. 40.8% b. 34.0% d. 51.0% 32. What is the profitability index of the new stamping machine? a. 1.504 c. 0.665 b. 1.380 d. 2.507 33. An auditor used regression analysis to evaluate the relationship between utility costs and machine hours. The following information was developed using a computer software program: Intercept Regression coefficient Correlation coefficient Standard error of estimate Number 0f observations 2,050 0.825 0.800 200 36 What is the expected utility cost if the company’s 10 machines will be used 2,400 hours next month? a. P4,050 c. P3,970 b. P4,030 d. P3,830 34. A firm must decide the mix of production of Product X and Product Y. There are only two resources used in the two products, resources A and B. Data related to the two products are given as follows: Resource A Resource B Unit profit Product X 3 2 P8 Product Y 7 1 P6 What is the appropriate objective function to maximize profit? a. 3x + 7y c. 8x +6y b. 2x + y d. 5x + 8y 35. Sustainability reporting a. is about communicating how the company manages its long term value creation by taking an integrated approach to both traditional risks and the wider sustainability risks. b. intends to show how the company integrates environmental and social thinking into business. c. is about communicating publicly how the company assesses which environmental or social issues are most important, how these issues are managed, and how the company is performing against each of these key issues. d. pulls together information that sits in separate reporting strands to explain how the firm creates value. ITEMS 36 TO 39 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: LOS ANGELES CORP. manufactures a cleaning solvent. The company employs both skilled and unskilled workers. Skilled workers class C are paid P12 per hour, while unskilled workers class D are paid P7 per hour. To produce one 55-gallon drum of solvent requires 4 hours of skilled labor and 2 hours of unskilled labor. The solvent requires 2 different materials: A and B. The standard and actual material information is given below: Standard: Material A: Material B: 30.25 gallons @ P1.25 per gallon 24.75 gallons @ P2.00 per gallon Actual: Material A: Material B: Skilled labor hours: Unskilled labor hours: 10,716 gallons purchased and used @ P1.50 per gallon 17,484 gallons purchased and used @ P1.90 per gallon 1,950 @ P11.90 per hour 1,300 @ P7.15 per hour During the current month LOS ANGELES CORP. manufactured 500 55-gallon drums. (Round all answers to the nearest whole peso.) 36. What is the total material mix variance? A. P3,596 F C. P4,864 F B. P3,596 U D. P4,864 U 37. What is the total material yield variance? A. P1,111 U C. P2,670 U B. P1,111 F D. P2,670 F 38. What is the labor mix variance? A. P1,083 U B. P2,588 U C. P1,083 F D. P2,588 F 39. What is the labor yield variance? A. P2,583 U B. P2,583 F C. D. P1,138 F P1,138 U ITEMS 40 TO 42 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: BENGUET CORP. provided the following information in relation to its operating activities which started only this year. Units sold @ P20 per unit Units produced during the period Direct materials Direct labor Factory overhead Office expense Selling expense 40. Unit Variable Cost P8.00 5.00 2.00 4.00 30,000 25,000 Fixed Cost P100,000.00 What is the total period cost under variable costing? A. P240,000 C. P260,000 P40,000.00 B. P140,000 D. P160,000 41. What is the total period cost under throughput costing? A. P450,000 C. P415,000 B. P470,000 D. P400,000 42. What is the total amount of fixed cost presented in the income statement under absorption costing? A. P 40,000 C. P140,000 B. P123,333 D. P120,000 43. In relation to variable and absorption costing, which of the following statements is correct? A. Fixed overhead volume and spending variance do not exist under variable costing. B. Even if sales are constant but production is fluctuating, net income under variable costing also fluctuates. C. Variable costing income statement classifies cost that is useful for CVP analysis while absorption costing income statements classifies cost in accordance with PFRS. D. Both A and C. 44. In relation to comprehensive budgeting, which of the following statements is incorrect? A. The budget committee DO NOT PREPARE and DEVELOP BUDGETS. They only approve it because the preparation of budgets rests with individual managers. B. Rolling budget is a budget that is revised on a regular (continuous) basis. C. The information on budgeted balance sheet does not contain information for the current budget only but rather it has cumulative information like a usual balance sheet of a set of financial statements. D. None from the statements is incorrect. 45. Which of the following budgets are usually prepared first? A. Direct labor budget C. Purchases budget B. Cash budget D. Production budget NUMBERS 46 TO 49 ARED ON THE FOLLOWING: At the end of 2019, RAICHU CORP., beach volleyball merchandiser, provided the following information regarding its statement of financial position (balance sheet): Assets Cash Receivables Inventory Plant, net Total Equities P 40,000 Accounts payable 50,000 30,000 Stockholders’ equity 60,000 P 180,000 Total P 45,000 135,000 P 170,000 RAICHU has recently completed its 2020 sales forecasting and generated the following sales information for the next 4 months: January February March April P120,000 80,000 150,000 100,000 Additional information: • RAICHU has a gross profit rate of 40% and applied constantly to all of its sales. • RAICHU’s total sales comprise of 80% credit sales and 20% cash sales. • RAICHU maintains inventory at 60% of the coming month’s budgeted sales requirements. • RAICHU collects 70% of its sales in the month of sale, 30% in the following month. • RAICHU pays for its purchases 40% in the month of purchase, 60% in the following month. • The company has a total monthly fixed costs of P15,000, P5,000 of which is the depreciation of the company’s plant. All cash fixed costs are paid in the month they are incurred. • On the month of February, property taxes amounting to P60,000 are to be paid. • At the end of the first quarter, quarterly dividends amounting to P70,000 are to be paid. • Due to a high capital expenditure requirements for 2020, RAICHU is planning to issue additional shares of 10,000, with a par value of P2, at P3 per share on March 15, 2020. 46. How much is the total purchases of the first quarter of 2020? A. P 72,000 C. P216,000 B. P212,400 D. P118,800 47. What is the cash balance at the end of February 2020? A. 45,720 C. 56,200 B. 97,880 D. None of the above 48. What are the total assets at the end of the first quarter of 2020? A. P181,500 C. P192,400 B. P165,320 D. P173,200 49. What is the total shareholder’s equity as of the end of the first quarter of 2020? A. P100,000 C. P120,000 B. P150,000 D. P130,000 NUMBERS 50 AND 51 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: CHARMANDER INC. manufactures and sells ski shirts and gears. For the year 2020, the following sales forecasts are made: January 120,000 February 100,000 March 110,000 CHARMANDER wants to maintain a finished goods inventory of 40% of the next month’s sales requirements. In addition, CHARMANDER is maintaining raw materials inventory of 30% of the next month’s needs. The following standard amounts per unit were predetermined for the year 2020: Direct materials (2.5 feet @ P2.00) Direct labor (1.50 hours @ P2.50) Factory overhead (1.50 hours @ P1.50) P5.00 3.75 2.25 The budgeted variable selling and administrative expense is P2.10 per unit. The budgeted fixed selling and administrative expense is P30,000 per quarter, which includes depreciation of P3,000 per month. 50. What are the total manufacturing costs for the month of January? A. P1,220,000 C. P1,320,000 B. P1,232,000 D. P1,332,000 51. What is the total amount of operating expense for the month of January? A. P245,200 C. P262,000 B. P282,000 D. P259,000 52. Which of the following costs is relevant in a scrap or rework decision on a defective product? Variable Manufacturing Cost Applied Fixed Rework Cost A. Yes No B. No Yes C. Yes Yes D. No No 53. In relation to opportunity cost, which of the statements below is incorrect? S1: S2: S3: A. B. 54. Opportunity cost is recorded in the accounts of an organization whether the company is using variable or full costing. If a potential benefit was not given up since there is no other alternative, opportunity cost is zero. Opportunity costs are costs irrevocably incurred by past actions. S1 and S2 S2 and S3 D. E. S1 and S3 S3 only A make or buy cost analysis involves all of the following considerations except (M2) A. comparison of incremental revenue with incremental costs. B. consideration of opportunity costs. C. comparison of relevant internal costs with the cost to purchase externally. D. evaluation of an external supplier. NUMBERS 55 AND 56 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: YUGI CORP. manufactures three types of playing cards. Because of a recent lack of skilled wood machine operators, the corporation has had a shortage of available direct labor hours. The following per unit data relates to the three products of the corporation: Sales price Variable costs Labor hours required Regular P30 20 1 Standard P80 56 3 Deluxe P90 45 5 YUGI only has 9,000 labor hours available next month. 55. Assuming that YUGI has no limit as to the production of any products, what is the total contribution margin YUGI has to report on its CVP income statement? A. P90,000 C. P86,400 B. 56. P80,400 D. P78,200 Assuming that YUGI can only sell 1,200 units of each product, what is the total contribution margin YUGI has to report on its CVP income statement? A. P90,000 C. P86,400 B. P80,400 D. P78,200 57. EXODIA CORP. is considering dropping its MAGIC CARD toy due to continuing losses. Revenue and cost data on the toy for the past year follow: Sales of 15,000 units Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Net operating loss P150,000 120,000 30,000 40,000 (P10,000) If the toy were discontinued, then EXODIA could avoid P8,000 per year in fixed costs. if the MAGIC CARD toy is dropped, the production and sale of other EXODIA toys would increase so as to generate a P16,000 increase in the contribution margin received from these other toys. At what selling price per MAGIC CARD should EXODIA be indifferent (on economic grounds) between dropping the MAGIC CARD or continuing its production and sale? (All other conditions remain the same, including annual sales of 15,000 units of the MAGIC CARD toy.) A. P8.33 C. P9.60 B. P9.25 D. P10.70 NUMBERS 58 AND 59 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: The next year’s budgeted sales of BALMOND CORP is P1,000,000, 90% would be credit sales. The current credit term of the company is 30 days which is also its average collection period. The company estimates that a proposed relaxation of credit standards would increase credit sales by 30% and increase the average collection period form 30 days to 45 days. However, bad debts losses on the incremental sales would be 3%. The following information relates to BALMOND CORP.: Selling price Variable cost per unit Carrying cost Fixed costs Assume 360 days a year and a tax rate of 30%. P50 30 10% P250,000 58. What is the incremental carrying cost resulting from relaxation of the credit policy? A. P 4,275 C. P 3,700 B. P 4,750 D. P 5,675 59. What would be the effect of those changes in net income? A. P 66,605 increase C. P 66,937.50 increase B. p 65,975 increase D. P 108,062.50 decrease 60. A company using very tight standards in a standard cost system should expect that A. No incentive bonus will be paid B. Most variances will be unfavorable C. Employees will be strongly motivated to attain the standard D. Costs will be controlled better than if lower standards were used NUMBERS 61 TO 64 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: Information about PRODUCT X of KAGURA CORP is as follows: Annual sales Ordering cost Carrying cost per year 500,000 units P1,125 per order P500 per unit Currently, every order or KAGURA from its supplier has a lot size of 1,000 units. Delivery of the supplier is not that stable. The usual delivery takes three days, however at times, the lead time has gone as high as eight days. KAGURA uses 200-day work per year. 61. What is economic order quantity? A. 1,000 units B. 667 units C. D. 1,500 units 800 units 62. Currently what is the total carrying cost of KAGURA? A. P6,500,000 C. P375,000 B. P250,000 D. P500,000 63. At economic order quantity, what is the total cost related to its inventories? A. P750,000 C. P7,062,500 B. P500,000 D. P7,000,000 64. What is reorder point? A. 12,500 units B. 20,000 units 65. EOQ I. II. III. A. C. D. 7,500 units 5,000 units is unaffected by: The increase of safety stock. The increase in the variable costs of placing and receiving an order. The change of inventory valuation (e.g. FIFO to Average Method). I and II D. I, II and III B. II and III C. I and III 66. In relation to relevant costing, determine the incorrect statement. A. Opportunity cost is a relevant cost but unrecorded on the books of accounts. B. Avoidable cost is a cost that cannot be incurred if an activity is suspended, thus, relevant cost. C. If there is no market limitation in a product mix decision, the whole scarce resource shall be allocated to the product with the highest contribution margin per scarce resource in order to maximize net benefits. D. In an accept or reject a special order decision, if the company has an excess capacity but not enough to cater the special order, lost units from regular sales is equal to the number of units of the special order. 67. Before each transaction takes place, FREYA COMPANY’s current ratio is greater than 1 to 1 and its acid-test ratio is less than 1 to 1. Which of the following transactions can improve both ratios? I. Bought inventory for cash (use perpetual inventory system) II. Sell merchandise for cash A. I only C. Both I and II B. II only D. Neither I nor II NUMBERS 68 AND 69 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING: HAYABUSA INC. produces two types of samurai swords, NORMAL AND TOP-OF-THE-LINE types. Currently, overhead are allocated to the two products on a single cost pool on the basis of direct labor hours. Reports about competitors’ products show signs of poor cost data. With these, HAYABUSA’s management is considering to switch to activitybased costing. ABC revealed that there are 3 significant cost pools for overhead and they are as follows: Cost Pool Quality control Machine set-ups Others Amount P300,000 400,000 100,000 Appropriate cost driver Number of inspections Number of set-ups Direct labor hours Information about HAYABUSA’s two products are as follows: Production Direct labor hours Direct labor cost per hour Direct material cost Set-ups Inspections NORMAL 10,000 units 40,000 hrs. 3 50,000 80 100 TOP-OF-THE-LINE 5,000 units 10,000 hrs. 3 60,000 120 400 HAYABUSA determines selling prices by adding 40% to a product's total cost. 68. What are the selling prices of NORMAL and TOP-OF-THE-LINE products, respectively under the existing system? A. P81.00;P50.00 C. P64.00;P32.00 B. P113.40;P70.00 D. P89.60;P44.80 69. What are the selling prices of NORMAL and TOP-OF-THE-LINE products, respectively under the ABC system? A. B. 70. P30.00;P100.00 P65.80;P165.20 C. D. P42.00;P140.00 Answer not given PHARSA COMPANY’s next year annual cash requirement is 4 Million. The cash requirement is needed uniformly throughout the year. PHARSA’s strategy to obtain the necessary cash is to periodically sell its marketable securities and other short term investments, currently earning at 10% per annum. In converting those securities, the company will incur P20 per transaction. If PHARSA’s goal is to minimize its total cost in relation to the above strategy, what is its total cost? A. P40,000 C. P4,000 B. P20,000 D. P2,000 - END -