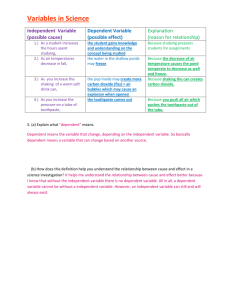
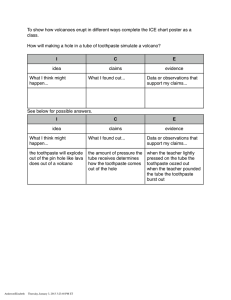
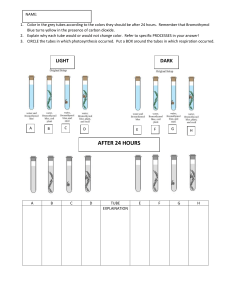
Design for Sustainability Assignment Redesigning a Product Submitted by – Sl. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Name Anson Kodiyan John Aayush Vardia Samdarshi Pratik Prakash Kadam Harshit Singhal Kaustav Ganguly Vijay Singh Rathore Dashrath Rajpurohit Swati Nayak Soumyadeep Biswas Student ID 2241288 2241280 2241279 2241278 2241277 2241276 2241275 2241274 2241273 2241272 Step 1: Product Selection Product Selected: Toothpaste tube Step 2: Product Dossier In 5000 BC, two millennia before they invented the tooth stick, the Egyptians used paste to clean their teeth. The ancient Greeks and Romans eventually created toothpaste recipes of their own, with the people of India and China following suit around 500 BC. The Greeks and Romans took the scrubbing up a level and added crushed bones and oyster shells to their toothpaste. And if you think bone toothpaste sounds bad, spare a thought for the Romans who used urine to whiten their teeth! Toothpaste as we know it today came about in the early 1800s. At this point, it still came in powder form, but it contained more contemporary ingredients like soap, with chalk, ground charcoal or betel nut for abrasion. By the late 1800s, Colgate had released the first liquid toothpaste product in a jar, followed by the modern-day tube in the 1890s. The total number of toothpaste tubes manufactured in a year is 20 Billion globally and it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.7 % from 2021 to 2027. The product is mainly distributed to the consumer market through channels. The supermarket/hyper market segment is estimated to lead the market due to the easy availability of a large number of brands in one place at a lower cost. Initially the tooth paste tubes were manufactured from Aluminium, later it was changed to laminated ones. Standard toothpaste tubes are generally made from a mix of plastics inserted around a thin layer of aluminium. Separating the materials is what makes these tubes difficult to recycle. The extraction of bauxite from which aluminium is made is also detrimental to environment, as the melting process is much more energy intensive. The combination of plastic and aluminium in the waste, presents a technical challenge to recycle them. Most toothpaste tubes are made of Aluminium and plastic and are not easily recycled, as many municipalities do not have the proper equipment. As we know, plastic is a product of oil and the process of both creating and recycling it causes a surge of CO2 into the air. The manufacturing of toothpaste tube is, therefore, very unfriendly for the environment. Every single year, 1.5 billion toothpaste tubes end up in landfills and the plastic in those tubes needs 500 years to degrade. Important Characteristics: 1. Should be light 2. Should no leak/ crack during pressing/ folding 3. Should be easily recyclable after disposal Improvement Ideas: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Wooden Bottle with toothpaste dispenser mechanism Tube with refilling mechanism Aluminium tube which can be used after disposal Paper laminated tube Shifting to mouthwash instead to toothpaste Step 3: Environmental and social issues Environmental Impacts: Impact Area Pollution of air Pollution of water Pollution of land Other Impacts Acidification and smog Toxic contamination Solid waste Noise Related Product Source Energy use, from fossil fuels Water use chemicals Material waste Product manufacturing operation Social Impacts: Impact Area Labour Issues Considerations Health and Safety Sources Manufacturing & Distribution Step 4: List of D4S approaches Product Charactristics Plastic Tubes Lamination Strategic Focus Information on product Introduce better The standard recyclable material plastic will take many years to recyclable Introduce easily The lamination on removable the plastic is not material which can easy to separate be easily recycled. D4S Approach Notes on Envr and Social Effects Substitute the Material to be existing material used which can be easily recycled. Substitute the Using material existing material that will be eco friendly and can be easily recycled. Step 5: Impact Profile Product Life cycle: Petrochemical Extraction Processing to produce plastic Tube Manufacturing Toothpaste filling and crimping/ packaging Tube Disposal Sale to customer and usage Transport to convenience stores Transport to distribution centre Knowledge Focus 1. Material Used for making the tube Most Relevant D4S responses Meet user needs with a different product NA Material Used for making the tube NA Meet user needs with a different product Material choices to reduce impacts Selection of low impact materials Impact Profile: Product Type/ Characteristics Passive Product Stationary Product Non consumable product Short life product Typical Impact Profile Key impact areas 1. Plastic Extraction 2. Disposal of toothpaste tubes after usage NA Key impact areas 3. Plastic Extraction Disposal of toothpaste tubes after usage Emphasis on beginning and end of life Materials Recovery Step 6: Product’s improvement targets and design approaches 1. Main social and environmental issues in market • Plastic Extraction from fossil fuels is a polluting process both in terms of air and land. • This also leads to resource depletion in terms of fossil fuels 2. Most significant life-cycle stages in the life-cycle diagram Petrochemical Extraction Processing to produce plastic Tube Manufacturing Toothpaste filling and crimping/ packaging Tube Disposal Sale to customer and usage Transport to convenience stores Transport to distribution centre 3. List of highlighted D4S approaches from the analysis • Substitute the existing material with one that is more easily recyclable 4. Development of improvement targets and design approaches • Double the content of recyclable material in the toothpaste tube • Ensure 50% reduction of greenhouse gases during product manufacturing operation Step 7: Redesign Concepts Selected life stages → Selected D4S responses ↓ 1 Meet user needs with different product 2 Selection of low impact materials 3 Material Recovery 1. Processing produce plastic to 2. Tube Disposal Shifting to mouthwash instead to toothpaste Wooden Bottle with toothpaste dispenser mechanism Paper laminated tube Tube with refilling mechanism Aluminium tube which can be used after disposal Step 8: Prioritising Ideas 1 (High Gains/ High Cost) 1. Wooden Bottle with toothpaste dispenser mechanism 2. Tube with refilling mechanism 3 (Low Gains/ Low Cost) 1. Paper laminated tube 2 (High Gains/ Low Cost) 1. Aluminium tube which can be used after disposal (specific disposal points) 4 (Low Gains/ High Cost) 1. Shifting to mouthwash instead toothpaste to Step 9: Business Case Aim: To redesign toothpaste tubes based on the D4S approach to reduce environmental and social impacts. Target: • Double the content of recyclable material in the toothpaste tube • Ensure 50% reduction of greenhouse gases during product manufacturing operation Report: The current generation toothpaste tubes are made from a mix of plastics inserted around a thin layer of aluminium which are difficult to separate at the end of the lifecycle, and hence serious threats to the environment. The team brainstormed on steps 1-8 and inferred that the plastic production process and tube disposal process were the 2 significant stages in the product life cycle. We tried to use alternate material with easier recyclability and came up with a list of options, which upon prioritizing was shortlisted to the following solution1. Use of Aluminium material for the tubes. This would eliminate the need to separate materials at the time of recycling. 2. Setting up specific disposal points at convenience stores, where the customer would dispose off the used tube. 3. Setting up a circular material flow for the tube, where in the disposed tube could be sent to aluminium dealers who in turn could extract the aluminium from the tubes and use the same for their own purposes going forward. 4. The customer would be offered a benefit on disposing the tube at these designated points. Financial Gains: 1. Cost reduction due to avoidance of material mixing in tubes. 2. Improved marketing as product can now be marketed as one having environmental value. 3. Improved awareness in society regarding D4S approaches.