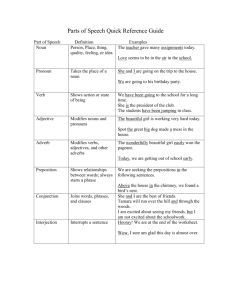
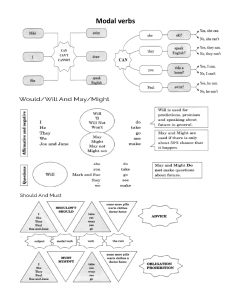
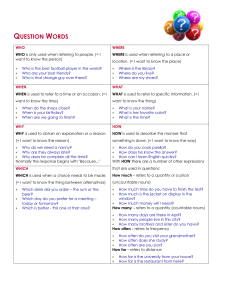
ELS 106: English Syntax Rachel Paquibot BAELANG 2A September 24, 2022 DEFINITION OF TERMS: verb, but is acts like a noun. Ex. Baking is one of her skills. 1. 2. Noun- a word that name something such as a IMPORTANT NOTE: All gerunds end in -ing, person, place, thing, or idea. but not all words ending in -ing that are Ex. Person, Place, Thing. formed from verbs are gerunds. Pronoun- a type of word that replaces a noun. 11. Determiners- a word that comes before a Ex. I, She, He, You, We. 3. noun to show how the noun is being used. Verb- a word used to describe an action, Articles: the, a, and an. state, or occurrence, and forming the main 4. part of the predicate of a sentence. refer to non-specific or Ex. Eat, Laugh, Write, Sing. general thing. Predicate- the part of a sentence or clause containing a verb and stating something Ex. Went home in, John went home. Subject- a person or thing that is being Demonstrative Determiners: this, that, those, and these Ex. Rachel is watching Netflix. Quantifiers: some, a few, many, a little, few, none and etc. Adjective- a word that modifies a noun or pronoun. 7. Possessive Determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, and their. discussed, describe, or dealt with. 6. Definite article (the) refers to a specific thing. about the subject. 5. Indefinite articles (a, an) Distributive Determiners: every, Ex. She is cheerful. each, either, neither, both, all, half, Adverb- a word modifies everything except and etc. nouns and pronouns. Ex. Runs slowly. 8. 12. Articles- the, a, and an. Prepositions- is a word used to link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a Indefinite articles (a, an) refer to non-specific or general thing. sentence. Ex. Go down the stairs and through the Definite article (the) refers to a specific thing door. 9. Conjunctions- words that link other words, WORLD CLASSESS NOUN phrases, or clauses together. Syntactic Roles of Nouns Phrases Coordinating: for, and, nor, but, or, Often called as Grammatical Relations yet, and so. because they define NPs in terms of their Correlative: both/and, either/or, relationships with the verb of which they are neither/nor, not only/but, an argument. whether/or. - Subordinating: after, although, as, Properties of Subjects in English - whenever, whereas, only, and etc. 10. Gerund- is a form of a verb that ends in -ing agreement) - that is used as a noun. A gerund is like a blend of verbs and nouns. It looks like a Subjects control the verbs (subject-verbSubjects precede the verb in English (normal position) - Pronominal Subjects (subjects that are ELS 106: English Syntax Rachel Paquibot BAELANG 2A September 24, 2022 pronouns) have a special subject form prepositional phrases. known as nominative case. TYPES OF PREPOSITIONS Number of Singularity and Plurality of the Subjects - Consider count and mass nouns. before, and after. POSITIONS AND FUNCTIONS OF ADJECTIVES Prepositions of Place- on, in, at, under, over, inside, outside, above, Attributive- directly modifying a noun, and and below. normally have fixed position. Prepositions of Time- at, on, in, Prepositions of Movement- to, Ex. The red car. across, off, down, into, up, past, Predicative- function as predicates around, and through. Ex. She felt very sad. Intensifiers- preceding the adjective; they VERBS modify, as in very. The main function of verbs is to express what is known as predication. (a predicate expresses and ‘event’ Adjectives and their grammatical categories; which may be quite literally an event but also includes Two ways: actions, processes, situations, states, and so on.) Morphological (straight- SYNTACTIC SUB-CLASSES OF VERBS straighter-straightest) 1. Sub-class of intransitive verbs Addition of a functional Ex. John sneezed. element (more/most) (participant is the argument of the verb) Three questions adjective answer about a noun or Verbs with only one participant or argument pronoun. are called INTRANSITIVE VERBS. - Which one? 2. Sub-class of transitive verbs - What kind of? Ex. Bella rejected my generous assistance. - How many? /How much? Verbs with two participants or arguments are called TRANSITIVE VERBS. ADVERBS 3. Third sub-class of a verb has three Some irregular English adverbs have the same form arguments. as the adjectives. Ex. Georgie handed the document # to Liza. Ex. She works fast/hard. Verbs with three participants or arguments NOTE: and are either considering transitive or Adjectives modify noun as in sad song. Adverbs modify adjective as in strangely sad ditransitive as its verb. song and other adverbs such as, she spoke DITRANSITIVE VERBS strangely lucidly. Ditransitive verbs are action verbs that are followed Adverbs also modify verbs as in, she spoke by two objects: the direct object and the indirect strangely. object. The indirect object comes right after the ditransitive verb and just before the direct object. PREPOSITION Ex. Prepositions combined with a noun phrase to for My mother taught me how to cook. ELS 106: English Syntax Rachel Paquibot BAELANG 2A September 24, 2022 I got the kids their favorite toys. NOTE: Ask WHAT to find out the direct object and WHOM to find out the indirect object. GRAMMATICAL CATEGORIES OF VERBS Tense and Aspect- Present, Past and Future. (simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive) Mood- grammatical category which marks properties such as possibility, probability, and certainty. Ex. Aleena goes to Denmark tomorrow. Aleena would go to Denmark tomorrow if she were wealthy enough. (the mood used for actual events is termed as INDICATIVE) The Indicative Mood- states a fact or asks a question. Ex. This broom is fast. Do you want a go? The Imperative Mood- expresses an order. Ex. Keep away from the sunlight. The Subjunctive Mood- shows a wish, a suggestion, or possible condition. Ex. If I were alive, I’d demand that I be at the party. GRAMMATICAL CATEGORIES OF VERBS Valency-changing Processes- passive is best know of the valency-changing processes in verbs. Agreement- verbs agreeing with their arguments.