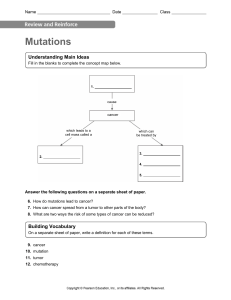
Name ______________________ Grade __________ Date __________ Summative assessment for the unit “11.4A Regularities and variabilities” Unit Learning objectives 11.4A Regularities and variabilities 11.2.4.9 classify types of variability; 11.2.4.10 explain the causes and formation of modificational variability; 11.2.4.11 investigate the patterns of modification variability 11.2.4.12 describe the mechanism of the formation of chromosome and genetic mutations; 11.2.4.13. Study the theory of Hugo de Vries mutation and the causes of mutagenesis; The learner Assessment criteria defines independent, dependent and control variables calculates the results of measurements plots graphs using data from table interprets the graph detect a pattern of correlation between some characteristics Level of Application of knowledge thinking skills Time 40 minutes Safety: Safe experiment ruler Apparatus and materials: scales for weighing Genetics is concerned with explaining how some characteristics are passed from generation Introduction to generation, i.e. heredity, or inheritance. Like most living organisms, humans show variation. If you consider almost any characteristic, you will find differences between various people (or other animals or plants) in a population. There are two forms of variation: continuous and discontinuous variation. Below is a list of characteristics which can be easily noted or measured. This includes a range of continuously variable and discontinuously variable characteristics, as well as features which are likely to be acquired rather than inherited. Carry out a survey of the class to gauge the extent of variation in these characteristics. As this is recorded in a grid format, you should be able to detect a pattern of correlation between some characteristics. Class survey CONTINUOUS DISCONTINUOUS ACQUIRED VARIATION Name/ initials Height /cm . . Armspan /cm . . . . . . . . . Height Weight / Tongue kg roller? (Y/N) . . Ear lobe? (free/ joined) . Scars? (Y/N) Fillings? (Y/N) . . . . . . . . . . Tongue roller Dental fillings Procedure: 1. Start by deciding on 3 pieces of continuous and 2 pieces of discontinuous data that you could collect. You should aim to sample at least 20 people in your study. More is better. 2. Record results in table. 3. You will now use excel to graph this data or plot the graph by hand. 4. You will draw one graph for each characteristics/ variable. 5. You need to decide on a suitable way of representing this data in a graph. Don’t forget titles, axes labels, units ets. [2] 6. (i) List the independent variables. ………………….……………………………………………………………….. [0.5] (ii) List the dependent variable. ……………………………………………………………………………………[0.5] 7. You can look at the graphs and make some comments on their shape. (i) Are there any similarities or differences between them? ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………….[1] (ii) Can you explain the shape of the graph? ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………[2] (iii) Do you think genetics or environmental factors play a greater or lesser part in determining continuous and discontinuous variation? ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………..[1] (iv) Why is it possible to calculate mean values for the first 3 characteristics from the table, but not the others? ……………………………………………………………………………………[1] 8. Using data from 2nd column of table, calculate (i) mean ……………………………………………………………………………………[1] (ii) standard deviation …………………………………………………………………………………… [1] The theoretical part of the questions 1. The given diagram represents phenotypic plasticity. (a) State what is shown on the given diagram with horizontal and slanted lines. (i) Horizontal line ______________________________________________ (ii) Slanted line _________________________________________________ (iii) Define phenotypic plasticity. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ [1,5] 2. Mutation is an alteration in the genetic material. There are chromosome mutations and gene mutations. (i) State two causes of chromosome mutation 1 ___________________________________________________________ 2 ___________________________________________________________ [1] (ii) Define any two types of gene mutations 1 ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 2________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ [1] (iii) Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disease that affects hemoglobin, the oxygen transport molecule in the blood. Explain with references to this disease how a mutation in gene can lead to the formation of an altered polypeptide. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ [1] 3. Hugo De Vries carried out the experiments with Evening primerose (Oenothera lamarckiana) and came up with some results. Name one feature from Hugo De Vries’s mutation theory _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ [0,5] [Total: 15] Assessment criteria Plots graph using data from table Defines independent, dependent variables Interprets the graph Detect a pattern of correlation between some characteristics Calculates the results of measurements Task Descriptor A learner x-axis appropriate labelled and units y-axis appropriate labelled and units all plots correct plotted points/ bars to cover at least half the width and height of the printed grid sensible and linear scale smooth unbroken curve/ bar chart defines independent variables defines dependent variables defines similarities or differences between the graphs explains the shape of the graphs defines factors determining continuous and discontinuous variation explains the possibility of calculation of mean values for continuous variation calculates the mean calculates the difference between each observation and the mean calculates the square of each difference calculates the sum of the square of each difference calculates the dividing the sum of the squares by n-1 calculates the standard deviation 10 Answers theoretical questions on learning objectives Total 15 5