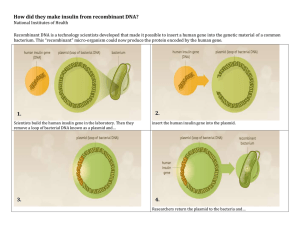
Recombinant DNA Abbey Taylor & Sacha Harrison Methodology of Recombinant DNA 1. Gene isolated from cell 2. Plasmid removed from bacteria 3. 2 pieces of DNA are ‘cut’ 4. Plasmid and DNA join together via bases 5. DNA ligase joins the strands 6. Recombined plasmid inserted into a bacterial cell Methodology of Recombinant DNA Biotechnology More than 20 million people in the world have Type 1 Diabetes Recombinant DNA technology produces artificially made insulin for individual diabetic patients whose pancreas does not produce insulin anymore due the absence of beta cells This procedure produces greater amounts of insulin with fewer side effects, making it more Sustainable and more accessible to patients in desperate need of insulin This method is not widely available to all nations as the price is extremely overpriced and is rarely subsidised by many countries' governments. DNA Replication - DNA exists in a double helix structure - When separating, DNA separates at the middle of 2 bases Insulin Production ● ● Higher quantity of insulin produced using recombinant technology as opposed to harvesting it from living sources Recombinant insulin is between $1 and 3$ more expensive to make than human insulin Ethics of Recombinant DNA - Recombinant insulin is more sustainable than harvesting human insulin - Saves more animal lives - Provides diabetic patients with a more stable source of external insulin - Technology is not as accessible worldwide