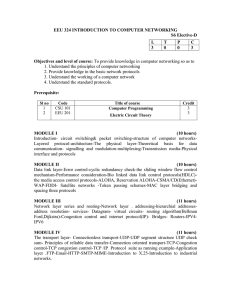
PLEASE SELECT PLEASE SELECT PLEASE SELECT COMPUTER NETWORKING TABLE OF CONTENTS 01 02 Introduction to Computer Networking Types of Networks 04 05 Networking Protocols Network Security 03 Network Topologies 06 Future of Computer Networking 01 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING A computer network is a group of interconnected devices that can communicate with each other. These devices can include computers, servers, printers, and routers. The purpose of a computer network is to share resources such as files, software, and hardware devices. Networks also allow for communication between users, whether it be through email or instant messaging. 02 TYPES OF NETWORKS TYPES OF NETWORKS There are several types of computer networks, including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and metropolitan area networks (MANs). LANs are typically used in small areas such as homes or offices, while WANs cover larger geographical areas such as cities or countries. MANs are somewhere in between, covering a larger area than a LAN but not as large as a WAN. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): A WLAN is a type of LAN that uses wireless technology, such as Wi-Fi, to connect devices. WLANs are often used in public spaces like airports, coffee shops, and libraries to provide internet access to users. Storage Area Network (SAN): A SAN is a specialized network that is used to provide block-level access to data storage. SANs are commonly used in data centers and other environments where large amounts of data need to be stored and accessed quickly. Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN is a network that uses encryption and other security protocols to create a secure connection over a public network, such as the internet. VPNs are often used by remote workers to access corporate resources securely. 03 NETWORK TOPOLOGIES NETWORK TOPOLOGIES A network topology refers to the physical layout of a network. There are several different topologies, including bus, star, ring, and mesh. The bus topology involves all devices being connected to a single cable, while the star topology has all devices connected to a central hub. The ring topology connects devices in a circular pattern, and the mesh topology has every device connected to every other device. 04 NETWORKING PROTOCOLS NETWORKING PROTOCOLS Network protocols are a set of rules that govern how data is transmitted over a network. Some common protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP. TCP/IP is the most widely used protocol and is responsible for ensuring data is transmitted accurately and reliably. HTTP is used for transferring web pages, while FTP is used for file transfers between devices. 05 NETWORK SECURITY NETWORK SECURITY Network security is a critical aspect of computer networks, as it protects against unauthorized access and cyber attacks. There are several measures that can be taken to secure a network, including firewalls, encryption, and regular updates. Firewalls act as a barrier between a network and the internet, while encryption ensures that data cannot be read by unauthorized users. Regular updates help to patch any security vulnerabilities in the network's software. 06 FUTURE OF COMPUTER NETWORK FUTURE OF COMPUTER NETWORK As technology continues to advance, so too will computer networks. One emerging technology is the Internet of Things (IoT), which involves everyday devices such as appliances and cars being connected to the internet. Another trend is the move towards cloud computing, where data and applications are stored on remote servers rather than locally on individual devices. This allows for greater flexibility and scalability in network management. THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!! OMEGA OMEGA Matthew Andrei D. Jimenez IGN: 두 배 ‘Namoash OMEGA Jay Ryan L. Caluyo IGN: Jay. OMEGA Klent Luke U. Dagpin IGN: MORPHEUS OMEGA Geianmar G. Tarroza IGN: GIYU OMEGA Prince Cedric R. Kasim IGN:カラス Raven OMEGA Mark Dave E. Lismis IGN: MARKDAVE PRESENTORS: MEMBERS: Matthew Andrei D. Jimenez Jay Ryan L. Caluyo Klent Luke U. Dagpin Geianmar G. Tarroza Prince Cedric R. Kasim Mark Dave E. Lismis