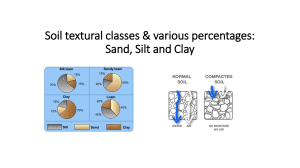
ABIOTIC AND BIOTIC COMPONENT Universal Solvent Inorganic substance which plays an important role in the ecosystem. It brings about changes in the life forms of plants and animals. Determines largely the character of vegetation and the types of animals. Types of Soil 1. Loam -Made up of particles of gravel sand and clay with the addition of organic materials 2. Sand -Inorganic soil particles those are larger than a clay or silt. 3. Silt -Made up of very fine particles of soil and clay, deposited as sediments. 4. Clay -Smallest inorganic particle of soil compared with silt and sand. It retains water before drying; it is sticky and not suitable for plant growth. Light is an important physical factor. Without light, life on earth would be impossible. The process of photosynthesis on which organisms depend on the manufacture of food, does not take place except in the presence of light. The character of the lightning of an area has a profound effect on animals and plants that live there. Certain plants will thrive in the shade, whereas others will not. This is likewise true of animals. Environmental temperature is an important factor because of its effect in metabolism. Temperatures in sunlight and in shade differ and influence animals in their selection of a habitat. The effect of temperature on the presence or absences of animals in different habitat are varied. Types of animals in different body temperature: Cold Blooded (fishes, amphibians, reptiles) and Warm Blooded (birds and mammals) Without oxygen, humans would not be able to live. Oxygen is produced by green plants through the process of photosynthesis and is therefore directly linked to sunlight. Tropophytes Mesophytes PLANTS Xerophytes Hydrophytes Halophytes These plants that can adapt it year after year where seasonal changes bring mark change in the amount of available water from the soil. Most of our plants bearing flowers and fruits are classified as mesophytes. They need a moderate supply of water for their subsistence. Plants that can tolerate where water supply is very scantly. HYDROPHYTES These plants thrive in places where the amount of water is abundant: usually fresh water plants are called hydrophytes. HALOPHYTES Plants thriving in a place where the water available contains much dissolved salts. The sea or oceans where plants inhabit have abundant supply of water, but due to its concentration, the plant absorbs it with difficulty. Carnivore ANIMALS Herbivore Omnivore Ectothermic animal with vertebrates that are characterized by scales, fins and pharyngeal gills. There are 3 main groups: jawless, cartilaginous and bony. Ex. Lamprey, dogfish shark, perch. AMPHIBIANS Ectothermic animal with vertebrates that are aquatic as larvae and terrestrial as adults. They breathe with lungs as adults, have a moist skin with glands and lack scales and claws. Ex. Frog, salamander, newt. Ectothermic animal with vertebrates that have lungs, scaly skin and a special type of egg (amniotic). They live entire life out of water. Ex. Snake, lizard, turtle. BIRDS Endothermic, reptile-like vertebrates with feathers, two legs used for walking and perching and wings that usually don ’ t have claws. Ex. Pigeon, hawk, eagle. Endothermic animals with fur or hair, and mammary glands that produce milk to nourish young. Almost all give birth to live young. Ex. Human, whale, fetal pig.