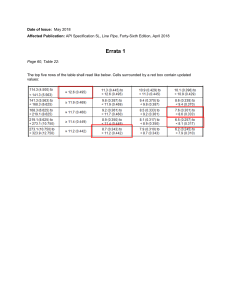
Siemens Building Technologies Fire Safety System – Basics 07th February 2018 Page 1 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Agenda Day 1 10.00 AM 10.15 AM Introduction 10.15 AM 11:30 AM Fire Detection Concept & Briefing of Basic Design ~11:30 AM 11:45 AM Coffee Break 11.45 AM 12.45 PM Knowing the Fire Alarm System Components 12.45 PM 01.00 PM Question and Answer ~1:00 PM 1:30 PM Lunch break 02.00 PM 02.30 PM Basics of Fire Protection System. ( Active & Passive ) PPT 02.30 PM 04.30 PM Basics of Gas based Fire Suppression System PPT 04.30 PM 05.00 PM Fire Graphics Video and FSS Video PPT 05.00 PM 05.15 PM Question and Answer 05.15 PM Page 2 PPT PPT Open Open End of the Session Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Basics of Fire Detection & Alarm System Page 3 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP What is Fire ? 3 Elements of Fire Oxygen Heat Fuel Page 4 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Classification of Fires & Flooding Media Suitable Media Water Foam Gas DCP Wet Chemical Page 5 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Fire Protection Concept Detecting Page 6 Extinguishing Alarming Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Types of Fire Safety Systems Fire Safety System Fire Detection Fire Protection and System Alarm System Page 7 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Types of FAS Type of Fire Alarm Systems Conventional Page 8 Jan 2018 Addressable Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Conventional FAS In a typical Conventional Fire Alarm System will identify the fire by zone wise. Page 9 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Addressable FAS System in which signals from detectors, manual call points or any other devices are individually identified at the control panel. The Fire Control Panel 'communicates' with each detector individually and receives a status report, i.e. 'Healthy', 'In Alarm' or 'In Fault', etc. Page 10 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Definitions Addressable Device : A fire alarm system component with separate identification or that is used to individually control other functions. Detector : A device in the circuit that has sensor that responds to a physical stimulus such as smoke or heat or flame. Multi Criteria Detector: A detector that responds to more than one of the fire phenomena. For example smoke-cumheat and Rate-of-rise and fixed temperature heat detector. Fixed Temp. Detector: A device that responds when its operating element becomes heated to a predetermined level. Page 11 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Definitions… Rate-of Rise Detector: A device that responds when the temperature rises at a rate exceeding a predetermined value. Manual Call Point: A manually operated device used to initiate an alarm signal. It can be only manual alarm system or automatic alarm system. Fire Alarm Control Panel: Equipment through which fire detectors supplied with power and which: a. Is used to accept a detection signal and actuate a fire alarm b. Is used to monitor automatically the correct functioning of the system c. Is used to indicate or display the location of fire/alarm activation device Page 12 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Definitions… Detection Zone : 1. Area that has a group of fire detection devices for which there is a separate common display in the fire alarm control panel. 2. The floor area of a single zone shall not exceed 2000m2. 3. Size of the conventional panels is normally referred by number of zones. 4. Each zone can be connected with the conventional detectors not exceeding 20. 5. The search distance shall not exceed 30m. 6. If the manual call points are located on the landings of an enclosed staircase shall be connected to the adjacent zones. Page 13 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Definitions… Addressable Panel: size of the analog addressable panel is normally referred by number of loops. Loop shall be of Class A wiring. Class A wiring will be return loop. Loop: 1. Length of the loop shall not exceed more than 3000m, where the size of the cable shall not be less than 1.5 mm2 2. Number of addressable detectors manufacturer’s recommendation. and devices per loop shall be as per 3. It is recommended that number of detectors per loop may not be exceeding 90 % of the full capacity. 4. Fault isolator modules shall be employed for every 20-30 devices. Page 14 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Definitions Sounders: 1. The sounders should be electronic hooters/horns 2. A minimum sound level of either 65dB or 5 dB above the ambient level 3. Sound level exceeding 120 dB in areas which are occupied may produce hearing damage. Page 15 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Choice of Detector • Computer / EDP centre / other electronic equipment which have high a value should be protected by smoke detectors or combination of smoke and heat detectors (multi criteria). • Heat detectors are suitable in areas where heat producing equipment like kitchen, pantry etc., • Flammable liquid storage area, where chances of rapid heat build- up exists like garages, repair shops, battery rooms etc., heat or Flame detector should be used. Page 16 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Sitting and Spacing of Detectors 1. Under flat ceilings, the horizontal distance between any point in a protected area and the detector shall not exceed 7.5 m in case of smoke detector and 5.3m in case of heat detector. 2. Detectors shall not be mounted within 500 mm of any walls, partitions or obstructions to flow of smoke, such as beams and duct work. 3. Ceiling obstructions like beams are deeper than 10 % of the overall ceiling height shall be considered as a wall. That is each bay shall be treated as a separate enclosure. 4. Detectors shall not be mounted within 1.0 m of any air inlet or forced ventilation system. Page 17 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Sitting and Spacing of Detectors 5. Voids as in false ceiling / flooring is more than 800 mm shall be protected with detectors with spacing like normal installation. 6. However the voids are less than 800 mm height no need for independent coverage unless the void is spread of fire products 7. Bathroom, lavatories, WC etc., need not be protected 8. For irregular shaped areas, the spacing between the detectors and any point of the area is not greater than 0.7 times the determined spacing Page 18 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Standards for FAS IS:2189 : Indian Standard for Selection, installation and Maintenance of Automatic Fire Detection And Alarm System – Code of Practice NFPA :72 : National Fire Alarm Code, USA BS: 5839-1 : Fire detection and alarm systems for buildings —Part 1 Page 19 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Selection & Design as per IS:2189 Page 20 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing’s at Different Ceiling Height Page 21 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Modified Spacing for High Air Movement Areas Page 22 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Height Limits 1. Smoke detectors can be used height upto 10.0 m 2. Beyond 7.0 m height Heat detectors are not allowed 3. Beyond 10.0 m height – Only Beam detectors or Aspirating type detectors shall be used. 4. Optical Beam detector shall be installed at every 15.0 m. Page 23 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing for Manual Call Point 1. Manual call points shall be located that, no person in the premises has to travel distances of more than 30 m to reach them. 2. Manual call points shall be located preferably near entry to staircases at every level. 3. When manual call points are also installed external to the building, the travel distance shall be 45 m. 4. Where necessary, the travel distance may require to be reduced to less than 30 m, where there is difficulty in free access or potentially dangerous risks. 5. Call points shall be fixed at a height of 1.4 m above the surrounding floor level. Page 24 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing & Design as per NFPA 72 Page 25 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per NFPA 72 1. On smooth ceiling, spacing of spot-type smoke detectors shall be 9.1m (30ft) 2. Listed spacing for Heat detectors shall also be 9.1 m 3. For smooth ceiling, all point on the ceiling shall have a detector within a distance equal to 0.7 times the selected spacing 4. Where the beams project more than 460mm below the ceiling and are more than 2.4m on center, each bay formed by the beams shall be treated as a separate area. Page 26 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per NFPA 72 Page 27 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per NFPA 72 Page 28 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per NFPA 72 Page 29 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing in Sloped Ceiling Page 30 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per NFPA 72 Page 31 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Location of Duct Detector Page 32 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Orientation of Duct Detector Page 33 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per BS:5839 Page 34 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per BS:5839 1. Under flat ceiling, the horizontal distance between any point in protected area and the detector nearest to that point should not exceed: • 7.5 m if the nearest detector is a smoke detector • 5.3 m if the nearest detector is a heat detector 2. Corridor not exceeding 2 m width: • 15.0 m for Smoke detector • 10.6 m for Heat detector Page 35 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Spacing as per BS: 5839 3. Ceiling obstructions, such as structural beams, greater than 150 mm in depth and deeper than 10 % of the overall ceiling height should be treated as walls Page 36 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Presented By… Kalidasan S Solutions Architect – Fire Safety Systems Siemens Ltd Building Technologies Seethakathi Business Centre 272/688, 8th Floor, Anna Salai Chennai – 600 006 Tel: + 91 44 3342 6062 Fax: + 91 44 3342 6002 HP: + 91 96000 48776 Email : kalidasan.s@siemens.com Page 37 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP Thank you for your Attention Page 38 Jan 2018 Kalidasan S IN BT SSP-OP