Annex 1c to DepEd Order No. 42 , s. 2016
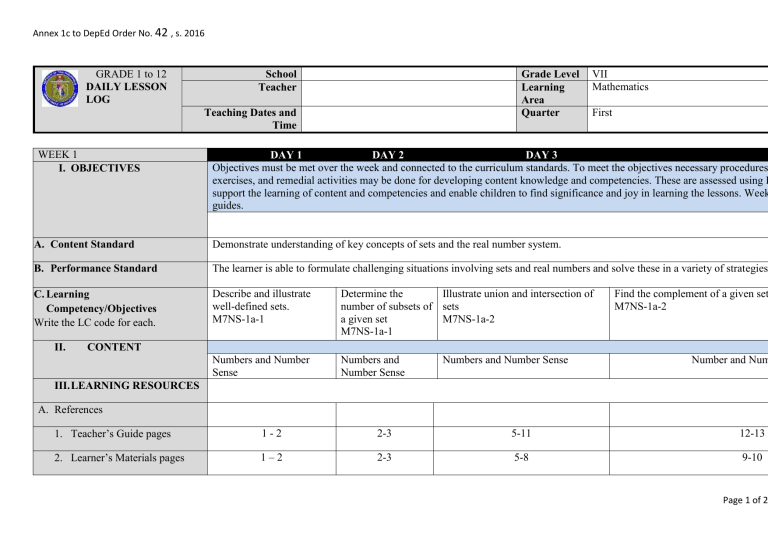
GRADE 1 to 12
DAILY LESSON
LOG
School
Teacher
Grade Level
Learning
Area
Quarter
Teaching Dates and
Time
WEEK 1
I. OBJECTIVES
VII
Mathematics
First
DAY 1
DAY 2
DAY 3
Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives necessary procedures
exercises, and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using F
support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Week
guides.
A. Content Standard
Demonstrate understanding of key concepts of sets and the real number system.
B. Performance Standard
The learner is able to formulate challenging situations involving sets and real numbers and solve these in a variety of strategies
C. Learning
Competency/Objectives
Write the LC code for each.
Describe and illustrate
well-defined sets.
M7NS-1a-1
Determine the
Illustrate union and intersection of
number of subsets of sets
a given set
M7NS-1a-2
M7NS-1a-1
Numbers and Number
Sense
Numbers and
Number Sense
II.
Find the complement of a given set
M7NS-1a-2
CONTENT
Numbers and Number Sense
Number and Num
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide pages
1-2
2-3
5-11
12-13
2. Learner’s Materials pages
1–2
2-3
5-8
9-10
Page 1 of 2
Annex 1c to DepEd Order No. 42 , s. 2016
3. Textbook pages
Understanding
Mathematics 7
Pages 3 - 7
Understanding
Mathematics,
pages 10 - 12
Understanding mathematicsGeometry Understanding Mathematics , pages
Pages 18 - 21
4. Additional Materials from
Learning Resource
(LR)portal
B. Other Learning Resource
IV.
PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson or
presenting the new lesson
DLP Learning Activity
sheet No. 1
DLP Learning
DLP Learning Activity Sheet No. 3
DLP Learning Activity Sheet No. 4
Activity Sheet No.
2
These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be g
you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to
learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge.
Look at the object below
Recall on sets
Observe the given illustrattion
and answer the question
below.
Recall sets, universal set, empty set
that follows.
sets, cardinality of sets.
How can you group the
objects given? Name each
groups.
How many groups can you
form?
Is there an object that
belongs to more than one
group? What are those
objects?
What do you call now
these groups of objects
you`ve formed?
How many elements are there in set A? Set
B?
How many elements are ther in set C? and
D?
How many elements are in the union
of A and B?
How many elements are there in the
union of C and D?
Page 2 of 2
Annex 1c to DepEd Order No. 42 , s. 2016
B. Establishing a purpose for the
lesson
What is a set? What do
you call each object in a
set? What is a welldefined set?
C. Presenting examples/Instances of
the new lesson
Example of well-defined
set
{a subject in math 7}
Reason: beacause it is
clear that the subject is
taught in grade 7
Example of not welldefined set
{aAgood
= {1,singer}
2, 3, 4} and
Which of the following shows the
intersection of set A and set B? How
many elements are there in the
intersection of A ?
Suppose A is a set Let us study another set, which is the
and B is a set that is union and intersections of sets
formed only the
elements of A (that
is B can be formed
entirely by
including
/excluding of A).
What can you say
about these two
sets? Can you find
any relationship
between sets A and
B?
Example:
Example . Let A = { a , b , c } and let
Let N = {Mae ,
B = { c , d , e}
Lars , Candy }
The union of set A and B, written in
List all the subsets
AUB={a,b,c, d,e}
of T.
The union of two sets is the sets
1.{ } – This set is
which consists of all elements that
known as the
belong to both.
empty set.
The intersection of A and B is c.
2.{Mae}
A ∩ B = {3 }
3.{Larry}
The intersection of two sets is the set
4.{Candy}
of elements which are in both sets.
We will tackle operation on sets an
complement of a set.
Examples:1. Let U = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4,
2, 4, 6, 8}.
Then the elements of A’ are the ele
found in A. Therefore, A’ = {1, 3
2. Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, A = {2, 4
B = {1, 5}. Then, A’ = {1, 3, 5}
B’ = {2, 3, 4} A’ B’ = {1, 2, 3, 4
3. Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8},
B = {3, 4, 7, 8}.
Then, A’ = {5, 6, 7, 8} B’ = {1, 2,
Page 3 of 2
Annex 1c to DepEd Order No. 42 , s. 2016
Reason: some people may
consider a singer is good
while the others may not.
5.{Mae , Lars}
6.{Mae , Candy}
7.{Lars, Candy}
8.{Mae , Lars ,
Candy}
Teacher will give more examples for
further discussion.
A’∩B’ = {5, 6}
Let U = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, A = {5, 7, 9
Then A∩ B = {5, 7, 9} (A∩ B)’
D. Discussing new concepts and
practicing new skills # 1
What are different ways of
writing set?
How do you write
cardinality of a set?
How to find the union of a given pair
of sets
How to find the intersection of a
given pair of sets?
How to describe and define the com
it relates to the universal set, U and
E. Discussing new concepts and
practicing new skills # 2
Write the following in rule
method or set-builder
notation and find its
cardinality.
1. {1, 3, 5, . . . , 39}
2. the positive integers
greater than 8
Write the following in
roster method.
1. the five sense organs
of the body
How many subsets
in set N? How to
determine the
number of subsets?
Supposed A is a
subset of B , but A
is not equal to B.
Can you find any
relationship
between sets A and
B?
What is a proper
subset? improper
subset?
How do we denote
proper subset and
improper subset?
A moment ago, we
listed all the
subsets of the set {
Mae, Lars , Candy}
Ask.
Which of these are
also proper subsets
of {Mae , Lars ,
Candy}
Page 4 of 2
Annex 1c to DepEd Order No. 42 , s. 2016
F. Developing mastery
(leads to Formative Assessment
3)
2. {x/x is an integer , 5≤
x ≤ 12}
Let A = {x/x is a whole
number less than or equal
to 10}
Classify each statement as
TRUE or FALSE.
1. n(A) =10
2. 0 €A
3. 10 €A
4. 5 € A
5. -5 €A
Determine the
number of subsets
and list down all of
them.
1. {a , b , c }
2. {2 , 4 , 6 , 8
}
3. { 1 , 2 ,3 ,4 ,
5}
Given the following sets A = { 0 , 1 ,
2,3,4}
B={0,2,4,6,8}
Determine the elements of the
following:
1. AUB
2. A ∩ B
3. A U B U C
( A U B) ∩ C
G. Finding practical application of
concepts and skills in daily
living.
H. Making generalizations and
abstractions about the lesson
I. Evaluating learning
Can you cite example on
the usage of sets in your
daily life?
Example: our bag ,
notebooks are keep in a
partition and all text books
in another partition.
Why is it important to
identify and recognize the
related terms in set?
What is a well-defined
set? ways in writing set?
cardinality of set?
Can you give a
pattern on how to
find the number of
subsets in a given
set?
Differentiate proper
subset and
improper subset.
Compare and contrast union and
intersection of sets
How to find the complement of a se
How to determine the elements that
belong to the union and intersection
of sets.?
Refer to Learning Activity Sheet N
J. Additional activities for
application or remediation
Page 5 of 2
Annex 1c to DepEd Order No. 42 , s. 2016
V.
REMARKS
VI.
REFLECTION
Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What el
help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions.
A. No. of learners who earned 80%
in the evaluation
B. No. of learners who require
additional activities for
remediation who scored below
80%
C. Did the remedial lessons work?
No. of learners who have caught
up with the lesson
D. No. of learners who continue to
require remediation
E. Which of my teaching strategies
worked well? Why did these
work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter
which my principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G. What innovation or localized
materials did I use/discover
which I wish to share with other
teachers?
Page 6 of 2






