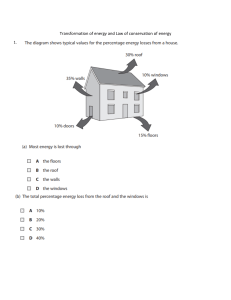
Rodrigo D. Palmero Memorial National High School Bannawag, Maria Aurora, Aurora ______________________________________________________________________________ GRADE 9 SCIENCE FOURTH QUARTER EXAMINATION 1. If a freely falling ball is somehow equipped with a speedometer, by how much would its speed reading increase for every second? a. 0 m/s b. 9.8 m/s c. 10 m/s d. 20 m/s 2. A sepaktakraw ball is hit vertically upward by a player. What is its acceleration after 1 second? b. 1 m/s2 a. 0 c. 9.8 m/s2 d. -9.8m/s2 3. A volleyball is tossed vertically upward, with an initial velocity of 5 m/s and caught back at the same level as when it was thrown. What is the velocity of the ball at that point? a. 0 m/s b. -5 m/s d. -9.8 m/s2 c. -9.8 m/s 4. The motion of an object with constant acceleration is also known as ________. a. Motion c. Constant Motion b. Uniform Motion d. Uniformly Accelerated Motion 5. Tiger Woods hits a 0.02 kg golf ball, giving it a speed of 25 m/s. What impulse does he impart to ball? a. 0.50 kg-m/s b. 5 m/s the d. 9.8 m/s2 c. 9.8 m/s 6. A ball is thrown vertically upward. What is its instantaneous speed at its maximum height? a. 0 b. 5 m/s d. 9.8 m/s2 c. 9.8 m/s 7. A ball is hit at an angle of 30o. At what point in its trajectory does this projectile have the least speed? a. Just after it was launched c. Just before it hits the ground b. At the highest point in its flight d. halfway between the ground and the highest point 8. Suppose a ping pong ball is tossed. When the ball reaches the highest point, which statement about the ball’s velocity and acceleration is true? a. Both its velocity and its acceleration are zero c. Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is zero. b. Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is not zero d. Neither its velocity nor its acceleration is zero. 9. At what angle should a water hose be aimed in order for the water to land with the greatest range? a. 0° b. 30° c. 45° horizontal d. 60° 10. A ball is hit at an angle of 30o and it reaches a distance of 50 m. Given the same initial velocity, at what other angle should a ball be hit to reach the same distance. a. 15° b. 45° c. 60° d. 75o. 11. Which has more momentum, a heavy truck moving at 30 km/h or a light truck moving at 30 km/h? a. heavy truck c. Both have the same momentum b. light truck d. Cannot be determined. 12. A moderate force will break an egg. However, an egg dropped on the road usually breaks, while one dropped on the grass usually doesn’t break. This is because for the egg dropped on the grass: a. The change in momentum is greater. c. The time interval for stopping is greater. b. The change in momentum is less. d. The time interval for stopping is less. 13. The impulse experienced by a body is equal to the change in its: A. Velocity B. Kinetic energy C. Momentum D. Potential energy 14. In certain martial arts, people practice breaking a piece of wood with the side of their bare hand. Use your understanding of impulse to explain how this can be done without injury to the hand. a. Given the same change in momentum, when the time interval is smaller the impact force is bigger. b. Given the same change in momentum, when the time interval is bigger the impact force is bigger. c. Given the same change in momentum, when the time interval is smaller the impact force is smaller. d. Given the same change in momentum, when the time interval is bigger the impact force is smaller. 15. A lady tennis player hits an approaching ball with a force of 750 N If she hits the ball in 0.002 s, how much impulse is imparted to the tennis ball? a. 0 N s b. 1.5 N s c. 3.0 N s d. 6.0 Ns 16. Which is a necessary condition for the total momentum of a system to be conserved? a. Kinetic energy must not change. c. An object must be at rest. b. No external force is present. d. Only the force of gravity acts on the system. 17. Two billiard balls approach each other at equal speed. If they collide in a perfectly elastic collision, what would be their velocities after collision? a. Zero c. Same in magnitude but opposite in direction b. Same in magnitude and direction d. Different in magnitude and opposite in direction 18. What is the energy of a motorcycle moving slowly at the top of a hill? a. entirely kinetic c. entirely gravitational b. entirely potential d. both kinetic and potential 19. Which event is explained in the sequence of energy changes shown in the diagram below? Chemical energy heat Mechanical energy (with wasted heat) a. a headlight is on c. electric current powers a flat iron b. a turbine spins d. gasoline burns to run a jeepney 20. In the Agus VI Hydroelectric Power (HEP) Plant, which energy transformation takes place? a. electrical energy mechanical energy b. gravitational potential energy c. heat kinetic energy mechanical energy d. nuclear energy electrical energy electrical energy. heat electrical energy. electrical energy 21. Which event does NOT describe potential energy being changed into kinetic energy? a. A box sliding down a ramp. c. A pen spring being compressed b. A mango falling from a crate.. d. A stretched rubber band got loosened. 22. Which event illustrates the direct transformation of potential to kinetic energy? c. Kathy’s arrow is released from its bow. a. A basketball player catches a flying ball. b. A Kalesa moves from rest. d. The spring mechanism of a toy is rotated until it locked. 23. Which sequence of energy transformation best describes what happens when you switch on your battery-run radio? a. Mechanical Energy Electrical Energy Sound Energy b. Mechanical Energy Chemical Energy c. Chemical Energy Electrical Energy d. Chemical Energy Sound Energy Sound Energy Mechanical Energy Sound Energy 24. Which among the forms of energy is considered a potential energy? a. chemical energy b. radiant energy c. sound energy d. thermal energy 25. Which of the following happens to the coconut that falls freely? a. Loses potential energy and gains kinetic energy. b. Loses both potential energy and kinetic energy. c. Gains potential energy and loses kinetic energy. d. Gains both potential energy and kinetic energy. 26. A torchlight fell from a watch tower. The potential energy of the torchlight at the highest point compared to its kinetic energy at the lowest point is _______ a. lesser. b. equal. c. greater. d. not related. 27. The potential energy of a 1-kg object on top of a hill is 18 J. What is its velocity in m/s just bottom of the hill? a. 36 28. b. 18 c. 6 before it hits the d. 3 The total mechanical energy of a swinging bungee jumper a. is equally divided between kinetic energy and potential energy. c. can never be negative. b. at any one instant, is either all kinetic energy or all potential energy. d. is constant, if only conservative forces act. 29. A bag drops some distance and gains 90 J of kinetic energy. Considering air resistance, how much gravitational potential energy did the bag lose? a. more than 90 J c. less than 90 J b. exactly 90 J d. cannot be determined from the information given 30. The wind-up toy that is fully wound and at rest possesses a. kinetic but no potential energy c. both potential and kinetic energy in equal amounts b. potential but no kinetic energy d. neither potential nor kinetic energy 31. In which case is there a decrease in gravitational potential energy? a. Amanda stretches horizontally a rubber band. c. Pamela’s puppy jumps down the chair. b. A car ascends a steep parking ramp. d. Water is forced upward through a pipe. 32. A picture frame falls off the wall. Considering the presence of air, how does the kinetic energy (K) just before striking the floor compare to the potential energy (P) at its hanging point? a. K is equal to P. b. K is greater than P. c. K is less than P. d. It is impossible to tell. (33-35 )Examine what happens to the mechanical energy of a roller coaster from the figure below. 33. If the cart moves from positions H to O, the potential energy _______since its height decreases. constant b. increases c. decreases 34. If the cart moves from positions O to P, the _______ increases a. potential energy b. kinetic energy c. decreases a. d. changeable since its height increases. d. changeable 35. The exchange of potential energy and kinetic energy on the cart is known as a.mechanical energy. b. chemical energy c. sound energy d. thermal energy 36. Francis stretched a rubber band five times. After that, he observed that the rubber band felt warmth. Did the rubber band gain heat? a. No, it is not evident. b. Yes, the rubber band felt warmth means it gained heat c. Yes, the rubber band felt warmth means it loss heat. d. No, temperature is not related to a gain or loss of heat. For nos.37-40 Beaker I, half-filled with water on hot plate for 2.5 minutes Beaker II, half-filled with water on hot plate for10minutes Beaker III, full of water on hot plate for 5 minutes Beaker IV, full of watero n hot plate for2.5 minutes Four identical beakers, I,II,III,IV are placed on a large electrical hotplate. I and II are half-full and III and IV are full of tap water at the same initial temperature. I and IV are placed on the hot plate for 2.5minutes, III is left on for 5minutes, and II is left on 10minutes. The water does not boil in any of the beakers. 37.Which one of the bakers of water will receive the most heat? B. a. I b. II c.III d.IV 38.Which one of the beakers of water will have the lowest temperature right after being heated? D a. I b.II c.III d.IV 39.Which two beakers of water will have almost the same final temperature after being heated? B a. I and II b. I and III c. I and IV d. II and III 40.What is commonly used as refrigerant for most of the refrigerators? a. Liquid that is easy to solidify. c. Gas that is easy to liquefy b. Liquid that is hard to solidify.. d. Gas that is hard to liquefy. 41.What is the efficiency of a gasoline engines that receives 192.75J of energy from combustion lose 125.25 J by heat to exhaust during one cycle? a. 36 % b. 18 % c. 6 % d. 30 % and 42. If 150J of energy is added to a system when no external work was done, by how much will the thermal energy of the system raised? a. 360 J b. 180J c. 60J d. 150 J 43.Mang Fermin, a carpenter, is planing a piece of wood with his planar. After how many minutes, he observed that it is hot. What is the evidence that there is heat transfer? A. It is not evident. B. Hotness means there is an increase in thetemperature. C. Yes, hotness means there is a decrease in the temperature D. No, hotness is not related to a change in temperature 44. How does can water from the deep well move upward? A. It occurs naturally. C. It is a spontaneous process B.It uses waterheat pump. . D.It flows from higher temperature to cooler temperature. 45. Given the following mechanisms, which best describes correct sequence of the refrigeration cycle? 1. compression 2. condensation 3.expansion 4. Evaporation a. 1,2,3,4 b. 2,3,4,1 c. 3,4,1,2 d.4, 3,1,2 46.Who among the following scientists discovered the relationship between electricity and magnetism? a. Andrei Marie Ampere b. Michael Faraday c. Hans Christian Oersted d. Alessandro Volta 47.In which of the following units is electrical consumption measured by electric companies four our household consumption in our homes? a. kilowatt b. volt c. megawatt d. kilowatt hour 48. In power stations generating electricity, power is measured in _________. a. joule b. kilojoule c. kilowatt d. megawatt 49.. Why do power stations generate AC, and not DC? a. It is easier to generate, safer and more economical to transmit AC than DC. b. Transformers work with AC. c. AC is used in mobile devices and gadgets d. AC is more efficient and economical. 50. If a 100 W light bulb is lit for 8 hours each day for 20 days in a month. How many kilowatt-hours will the bulb consume? a. 16 KWH b. 160KWH c. 1600KWH d.16000 Prepared by: RHEA D. VILORIA Subj. tchr.