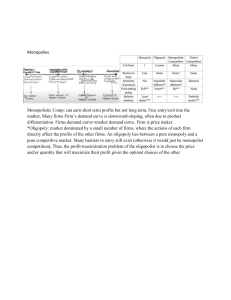
1.5.4: Monopolistic Competition (HL only) Definitions 1. Monopolistic competition is a market structure where there are many sellers producing differentiated products, with no barriers to entry or exit. 2. Product differentiation is a form of non-price competition where suppliers attempt to make their products different (or perceived to be different) from those of their competitors. Assumptions of the model ● ● ● ● Made up of large no. of small firms. All firms produce differentiated products. No barriers to entry and exit. Makes normal profits in the long run. Product differentiation ● Products are differentiated by brand name, color, appearance, packaging, design, quality of service, skill levels and other methods. ● Examples include salons, car mechanics and jewellers. ● Brand loyalty is important as firms takes risks, consumers still buy their products due to their image and reputation. ● Brand loyalty → Firms are independent for pricing decisions → Price takers. Movement from short run to long run in monopoly 1. Short term abnormal profit to normal profit ● When firms make short-run abnormal profits → Others firms will come into the industry → Takes the business activity away from existing firms → Shifts demand curve to the left → Price and cost stays the same → Normal profits. 2. Short term losses to abnormal profit. ● When firms make short-run losses → Firms in the industry starts to leave → Firms that remain will increase demand which should lead to increase in price, making price = cost → Normal profits for the firm. Productive and allocative efficiency ● Productive efficiency is where MC = AC. ● Allocative efficiency is where MC = AR. Advantages of monopolistic competition compared to perfect competition ● Monopolies have large economies of scale because of their size ● More variety of choice for consumers due to differentiated products. Disadvantages of monopolistic competition to perfect competition ● Productively and allocatively inefficient. ● Charge a higher price for lower level of output.