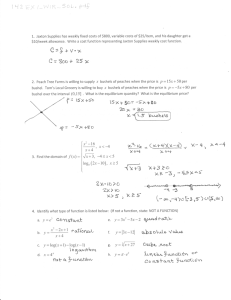
1) What has happened in the case under consideration? FTX Trading Ltd., commonly known as FTX (short for "Futures Exchange"), is a bankrupt company that formerly operated a cryptocurrency exchange and crypto hedge fund. The exchange was founded in 2019 by Sam Bankman-Fried and Gary Wang and, at its peak in July 2021, had over one million users and was the third-largest cryptocurrency exchange by volume. According to a complaint filed by the Securities and Exchanges Commission (SEC), Bankman-Fried used customer funds as a “personal piggy bank” to make private investments including real estate and political campaign donations. In August 2020, FTX acquired Blockfolio, a cryptocurrency portfolio tracking app, for $150 million.[27] In July 2021, the venture raised $900 million at an $18 billion valuation from over 60 investors, including Softbank, Sequoia Capital, and other firms.[28][29] Bankman-Fried bought out Zhao's stake for approximately $2 billion.[26] In September of that year, FTX moved its headquarters from Hong Kong to The Bahamas.[30] On January 14, 2022, FTX announced a $2 billion venture fund named FTX Ventures,[31] raising $400 million in Series C funding at a $32 billion valuation that month.[32] The FTX Ventures website went offline in November 2022.[33] On February 11, 2022, FTX.US announced that the company would soon begin offering stock trading to its US customers.[34] In February 2022, it was reported that FTX was creating a gaming division that would help developers add cryptocurrency, NFTs, and other blockchain-related assets into video games.[35] FTX, a major cryptocurrency exchange, and FTX.US, its U.S. branch, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy on Nov. 11, 2022. Former founder and CEO Sam Bankman-Fried was arrested on Dec. 12 in the Bahamas and was extradited to the U.S., where he later pleaded not guilty to eight criminal charges including wire fraud and conspiracy to defraud investors. According to a complaint filed by the Securities and Exchanges Commission (SEC), Bankman-Fried used customer funds as a “personal piggy bank” to make private investments including real estate and political campaign donations. On November 2, everything changed. The publication about cryptocurrencies CoinDesk published revealing material that the FTX exchange is provided only with tokens issued by its subsidiary. An FTX-affiliated company called Alameda Research had assets of $14.6 billion as of June 30. The problem was that most of these assets are FTT's own token, and not independent assets, as everyone thought. In simple terms, this means that the management attracted real money from large investors and creditors, including well-known and reputable funds Sino Global Capital, Tiger Global Management, Third Point Ventures, providing virtual obligations that have no real value as collateral. The CEO of rival exchange Binance, Changpeng Zhao, also known as CZ, tweeted on Nov. 6 that he was planning to sell off Binance’s stockpile of FTT because of “recent revelations that have came to light,” referring to the Nov. 2 CoinDesk report of FTX and Alameda’s blurred funds. 2) What wrong solutions and wrong activity did result in these exceptional losses? FTX and FTX.US crashed due to a lack of liquidity and mismanagement of funds, followed by a large volume of withdrawals from rattled investors. The value of FTT plummeted, taking other coins down with it including Ethereum and Bitcoin, which reached a two-year low as of Nov. 9. Other exchanges have been affected by the FTX collapse including BlockFi, which filed for bankruptcy on Nov. 28. The report emphasizes that these three people, who recently graduated from college and had no experience in risk management or business management, controlled almost all significant aspects of the FTX group of companies. In addition, the FTX group of companies stored almost all crypto assets in "hot" wallets, which exposed the funds to an increased risk of compromise, since the "hot" wallets are connected to the Internet, which makes their keys vulnerable to hacking, malware and other cybersecurity threats. The document notes that Bankman-Fried repeatedly falsely claimed that the exchange uses "cold" wallets (offline storage). 3) What should be done to prevent these losses? 4) Strong Financial Management: Ensuring that the company has competent and experienced financial executives and management that can manage its finances appropriately and avoid financial mismanagement. 5) Adequate Capitalization: A company must ensure that it has enough capital to support its operations and growth. A well-funded company is less likely to encounter financial difficulties. 6) Risk Management: Implementing effective risk management policies and procedures, such as diversifying investments and hedging against potential losses, can help minimize risk exposure. 7) Timely Financial Reporting: Regularly reviewing and analyzing financial statements can provide insight into the company's financial health, allowing management to make informed decisions based on accurate financial data. 8) Business Continuity Plan: Having a plan in place to manage unexpected events such as a pandemic, natural disaster, or economic downturn can mitigate the impact of such events on the company's financial health. 9) Vigilance Against Fraud: Enforcing strong internal controls and avoiding fraudulent activities can help prevent financial loss and maintain the company's financial stability. 10) What strategy could you recommend for avoiding such potentials in future?