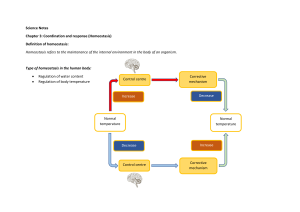
Science Notes Chapter 3: Coordination and response (Homeostasis) Definition of homeostasis: Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of the internal environment in the body of an organism. Type of homeostasis in the human body: • • Regulation of water content Regulation of body temperature Control centre Increase Corrective mechanism Decrease Normal temperature Normal temperature Decrease Control centre Increase Corrective mechanism Regulation of water content Regulation of body temperature High surrounding temperature (Hot) - Sweat glands produce more sweat to cool the skin when sweat is evaporated. - Hairs lie flat to reduce air trapped on the skin so that heat can be released easily. - Blood vessels dilate to let more blood flow to close to the skin increase heat loss Lower surrounding temperature (Cold) - Erect hairs trap a layer of air that acts as a heat insulator. - Blood vessels constrict to let more blood flow away from the skin to reduce heat loss. Homeostasis in Animals Examples of animals Cat Dog Lizard Snail Bee Ways of homeostasis Lick fur to reduce body temperature Hang the tongue to reduce body temperature Cold surrounding • Body activities become slower • Muscles function more slowly • Movements become slower • Metabolism rate decreases • Body temperature decreases Hot surrounding • The heart beats faster • Movements become faster • Metabolism rate increases • Body temperature increases Produces fluid and looks for humid places to reduce water loss Closes spiracles between two breathing movements to reduce water loss. Homeostasis in Plant Definition: Transpiration is the evaporation of water from leaves in the form of water vapour to the surrounding through stoma. • • Transpiration helps plants to absorb and carry water and minerals from the soil to all parts of the plant. Evaporation of water from the leaves cools the plant during the days. Stomata The small openings on the underside of leaves are called stomata During the day: Stoma opens to enable more water to be evaporated from the leaves through transpiration. During high temperature: Stoma closes to reduce water evaporated from the leaves through transpiration. The importance of homeostasis to humans and living things: • • Provide the optimum conditions in the body. The internal environment in the body is regulated and maintained in a balanced and stable condition.