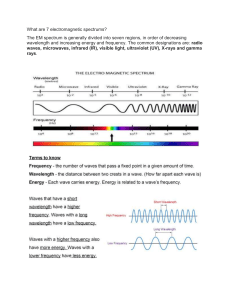
3.3 Electromagnetic spectrum Gamma rays Gamma rays (Topic 5.2) are more penetrating and dangerous than X-rays. They are used to both diagnose and treat cancer and also to kill harmful bacteria in food and on surgical instruments. They can also be used in engineering applications to detect flaws in metals. Dangers of electromagnetic radiation High exposures to electromagnetic radiation can cause harmful effects. wireless internet. Radio waves are weakened when passing through walls, but are suitable for shortrange applications such as Bluetooth. High-speed broadband internet and cable television signals are carried by optical fibres (Topic 3.2.2) because glass is transparent to visible light and some infrared. Visible light and shortwave infrared have higher frequencies than radio waves so can transmit data at a higher rate. Information is sent in digital form as a set of pulses, rather than in analogue form as a smoothly varying signal. Microwaves Analogue and digital signals Microwaves produce heat when they are absorbed by the water in living cells. This can damage or kill the cells. There is some debate at present as to whether their use in mobile phones is harmful; ‘hands-free’ mode, where separate earphones are used, may be safer. There are two main types of signals – analogue and digital. In analogue signals, voltages (and currents) can have any value within a certain range over which they can be varied smoothly and continuously, as shown in Figure 3.3.6a. Infrared a + Infrared radiation of high intensity can cause burns to the skin. voltage Ultraviolet Ultraviolet radiation absorbed in high doses can cause skin cancer and eye damage. Dark skin is able to absorb more UV in the surface layers than skin of a lighter colour, so reducing the amount reaching deeper tissues. Exposure to the harmful UV rays present in sunlight can be reduced by wearing protective clothing such as a hat or by using sunscreen lotion. X-rays and gamma rays cause mutation or damage to cells in the body which can lead to cancer. X-ray and gamma ray machines are shielded by lead to reduce unnecessary exposure. Communication systems Electromagnetic waves are the basis of many communication systems. Microwaves only need short aerials for transmission and reception of signals, and can penetrate the walls of most buildings, so are used for mobile phones and time – b + voltage X-rays and gamma rays 0 0 ‘high’ ‘low’ time – ▲ Figure 3.3.6 164 9781398310544.indb 164 19/02/21 8:16 PM Analogue and digital signals In digital signals, voltages have only one of two values, either ‘high’ (e.g. 5 V) or ‘low’ (e.g. near 0 V), as shown in Figure 3.3.6b. The advantages of using digital rather than analogue signals to transmit information are that they can be transmitted at a faster rate, can be sent over longer distances since they can be intermittently regenerated more accurately, and are less affected by noise. Analogue signals, such as sound waves, can be converted to digital signals electronically before transmission. Revision checklist After studying Topic 3.3 you should know and understand: ✓ that all electromagnetic waves travel with the same high speed in a vacuum ✓ that the speed of electromagnetic waves is 3 × 108 m/s in a vacuum and approximately the same in air ✓ the use of artificial satellites in communication systems Test yourself 3 Name one type of electromagnetic radiation which a causes sun tan b is used for satellite communication c is used to sterilise surgical instruments d is used in a TV remote control e is used to cook food f is used to detect a break in a bone. 4 Name one type of electromagnetic radiation which causes a damage to surface cells in the body b internal heating of body cells c burns to the skin d mutation or damage to cells in the body. 5 Name one type of electromagnetic radiation used for a wireless internet b Bluetooth c cable television d mobile phones. ✓ the use of specific types of electromagnetic waves for different communication applications. After studying Topic 3.3 you should be able to: ✓ describe the different types of electromagnetic radiation and distinguish between them in terms of their wavelengths, properties and uses ✓ describe the harmful effects of different types of electromagnetic radiation and how exposure to them can be reduced ✓ distinguish between analogue and digital signals and recall the benefits of digital signalling. 165 9781398310544.indb 165 19/02/21 8:16 PM