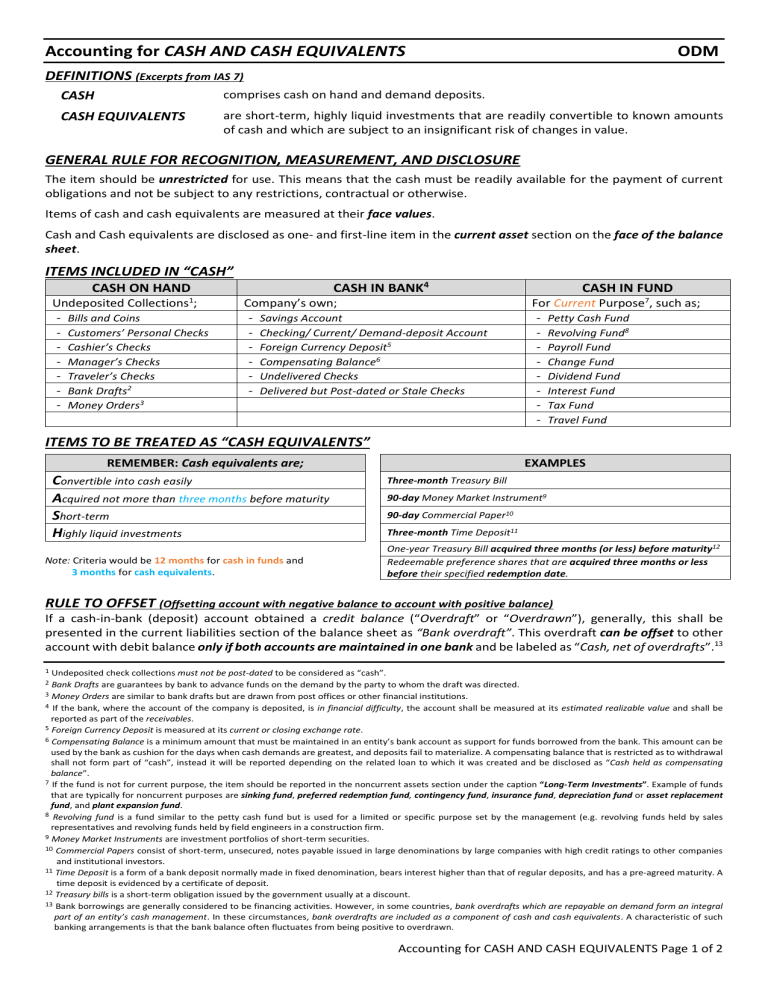
Accounting for CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ODM DEFINITIONS (Excerpts from IAS 7) CASH comprises cash on hand and demand deposits. CASH EQUIVALENTS are short-term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value. GENERAL RULE FOR RECOGNITION, MEASUREMENT, AND DISCLOSURE The item should be unrestricted for use. This means that the cash must be readily available for the payment of current obligations and not be subject to any restrictions, contractual or otherwise. Items of cash and cash equivalents are measured at their face values. Cash and Cash equivalents are disclosed as one- and first-line item in the current asset section on the face of the balance sheet. ITEMS INCLUDED IN “CASH” CASH IN BANK4 CASH ON HAND 1 Undeposited Collections ; - Bills and Coins - Customers’ Personal Checks - Cashier’s Checks - Manager’s Checks - Traveler’s Checks - Bank Drafts2 - Money Orders3 Company’s own; - Savings Account - Checking/ Current/ Demand-deposit Account - Foreign Currency Deposit5 - Compensating Balance6 - Undelivered Checks - Delivered but Post-dated or Stale Checks CASH IN FUND For Current Purpose7, such as; - Petty Cash Fund - Revolving Fund8 - Payroll Fund - Change Fund - Dividend Fund - Interest Fund - Tax Fund - Travel Fund ITEMS TO BE TREATED AS “CASH EQUIVALENTS” REMEMBER: Cash equivalents are; Convertible into cash easily Acquired not more than three months before maturity Short-term Highly liquid investments Note: Criteria would be 12 months for cash in funds and 3 months for cash equivalents. EXAMPLES Three-month Treasury Bill 90-day Money Market Instrument9 90-day Commercial Paper10 Three-month Time Deposit11 One-year Treasury Bill acquired three months (or less) before maturity12 Redeemable preference shares that are acquired three months or less before their specified redemption date. RULE TO OFFSET (Offsetting account with negative balance to account with positive balance) If a cash-in-bank (deposit) account obtained a credit balance (“Overdraft” or “Overdrawn”), generally, this shall be presented in the current liabilities section of the balance sheet as “Bank overdraft”. This overdraft can be offset to other account with debit balance only if both accounts are maintained in one bank and be labeled as “Cash, net of overdrafts”.13 1 Undeposited check collections must not be post-dated to be considered as “cash”. Bank Drafts are guarantees by bank to advance funds on the demand by the party to whom the draft was directed. 3 Money Orders are similar to bank drafts but are drawn from post offices or other financial institutions. 4 If the bank, where the account of the company is deposited, is in financial difficulty, the account shall be measured at its estimated realizable value and shall be reported as part of the receivables. 5 Foreign Currency Deposit is measured at its current or closing exchange rate. 6 Compensating Balance is a minimum amount that must be maintained in an entity’s bank account as support for funds borrowed from the bank. This amount can be used by the bank as cushion for the days when cash demands are greatest, and deposits fail to materialize. A compensating balance that is restricted as to withdrawal shall not form part of “cash”, instead it will be reported depending on the related loan to which it was created and be disclosed as “Cash held as compensating balance”. 7 If the fund is not for current purpose, the item should be reported in the noncurrent assets section under the caption “Long-Term Investments”. Example of funds that are typically for noncurrent purposes are sinking fund, preferred redemption fund, contingency fund, insurance fund, depreciation fund or asset replacement fund, and plant expansion fund. 8 Revolving fund is a fund similar to the petty cash fund but is used for a limited or specific purpose set by the management (e.g. revolving funds held by sales representatives and revolving funds held by field engineers in a construction firm. 9 Money Market Instruments are investment portfolios of short-term securities. 10 Commercial Papers consist of short-term, unsecured, notes payable issued in large denominations by large companies with high credit ratings to other companies and institutional investors. 11 Time Deposit is a form of a bank deposit normally made in fixed denomination, bears interest higher than that of regular deposits, and has a pre-agreed maturity. A time deposit is evidenced by a certificate of deposit. 12 Treasury bills is a short-term obligation issued by the government usually at a discount. 13 Bank borrowings are generally considered to be financing activities. However, in some countries, bank overdrafts which are repayable on demand form an integral part of an entity’s cash management. In these circumstances, bank overdrafts are included as a component of cash and cash equivalents. A characteristic of such banking arrangements is that the bank balance often fluctuates from being positive to overdrawn. 2 Accounting for CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS Page 1 of 2 ACCOUNTING FOR PETTY CASH FUND IMPREST FUND SYSTEM Petty Cash Fund Cash in bank xxx xxx <-Disbursements-> xxx xxx <-Replenishment-> (Equal to Petty Cash Disbursements) Various Expenses Petty Cash Fund - Fund level is fluctuating - Perpetual <-Establishment of the fund-> Memo in Petty Cash Journal Various Expenses Cash in bank FLUCTUATING FUND SYSTEM FUND OPERATIONS (STAGES) - Fund level is maintained - Periodic xxx xxx Petty Cash Fund Cash in bank xxx xxx Various Expenses Petty Cash Fund xxx xxx Petty Cash Fund Cash in bank xxx xxx (May not be equal to Petty Cash Disbursements) <-End of the period-> Without adjusting entry (With adjusting entry subject to reversal) BANK RECONCILIATION A bank reconciliation is a process which brings into agreement the cash balance per book and cash balance per bank. A bank reconciliation statement is usually prepared monthly because the bank provides the depositor with the bank statement as at the end of every month. RECONCILING ITEMS Credit memos Book reconciling items Debit memos Receivable collected by the bank Proceeds of loan directly credited by the bank Matured time deposit transferred to current account NSF / DAIF Checks Technically defective checks Bank service charges Automatic debit of loan payment Book errors Deposit in transit Outstanding checks Bank errors Bank reconciling items RECONCILIATION METHODS BOOK ADD: DEDUCT: ADD/DEDUCT: Unadjusted Balance Credit Memos Debit Memos Book Errors Adjusted Balance ADJUSTED BALANCE METHOD BOOK-TO-BANK METHOD BANK-TO-BOOK METHOD BANK ADD: DEDUCT: ADD/DEDUCT: Unadjusted Balance Deposit in Transit Outstanding Checks Bank Errors Adjusted Balance The unadjusted cash balance per ledger and the unadjusted bank statement balance are simultaneously adjusted. UNADJ BOOK + CM – DM ± BOOK ERRORS = UNADJ BANK + DIT – OC ± BANK ERRORS The reconciliation starts with the unadjusted cash balance per ledger, take effect the appropriate adjustments for the book and from the adjusted balance, work back the unadjusted bank balance that is reflected in the bank statement. UNADJ BOOK + CM – DM ± BOOK ERRORS ± BANK ERRORS + OC - DIT = UNADJ BANK The reconciliation starts with the unadjusted cash balance per bank statement, take effect the appropriate adjustments for the bank and from the adjusted balance, work back the unadjusted book balance that is reflected in the company’s ledger. UNADJ BANK + DIT – OC ± BANK ERRORS ± BOOK ERRORS + DM - CM = UNADJ BOOK PROOF OF CASH A Proof of cash statement is a four-column expanded, two-period bank reconciliation. Its purpose is to discover possible discrepancies in cash. “A wise person should have money in their head, but not in their heart. ” -Jonathan Swift Accounting for CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS Page 2 of 2




