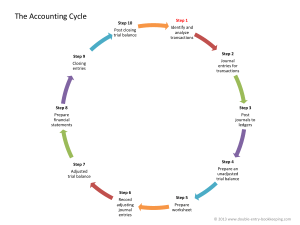
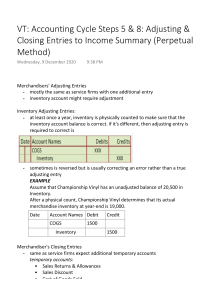
ACCT-2090 Principles of Financial Accounting Final Exam Study Guide (over principles, not problems) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Know the Accounting Equation and definitions for the elements thereof. Know which types of accounts increase or decrease with debits or credits. Know the Accounting Cycle and the order of the steps therein. Know the Journal Entry when the owner first contributes cash to his/her company. Know the difference between the Cash Basis and the Accrual Basis of accounting. Know which accounting method is GAAP and that which gives rise to Adjusting Journal Entries. 7. Know the difference types of Adjusting Journal Entries. 8. Know the difference between temporary accounts and permanent accounts for Closing Journal Entry purposes. 9. Know the different Closing Journal Entries. 10. Know the four different financial statements, their basic formats, and the order of preparation. 11. Know what “contra” means and be able to properly name specific types of “contra” accounts. 12. Know the word that means “to make an asset.” 13. Know the purchasing transactions for Merchandise Inventory purchased. 14. Know the definitions of and difference between the four types of inventory valuation methods. 15. Know the difference between adjusting for Bad Debts when calculating using a % of Sales and a % of Accounts Receivable. 16. Know the formula for calculating Accounts Receivable Turnover. 17. Know the basis over which a lumpsum Fixed Asset purchase is allocated. 18. Know the different depreciation methods, how to calculate each, and the differences between them. 19. Know how to account for gains/losses on sales of assets. 20. Know the different terms for allocating the cost of natural resources and intangible assets over their estimated useful lives. 21. Know the order of and different categories of a company’s cash flows. 22. Know at what value different types of stock are issued. 23. Know why Preferred Stock is preferred. 24. Know the mechanics of how to calculate the different types of cash flows in the Statement of Cash Flows. Jeopardy: Journal entries are posted to this book of record: general ledger Financial statements are created after this step in accounting cycle: Adjusted Trial Balance At period end this is the first step before recording adjusting journal entries: unadjusted trial balance This is the last step in the accounting cycle: Post Closing Trial Balance In an environment of ever-increasing merchandise costs, this inventory valuation method maximizes profit: FIFO This term is used to describe the allocation of costs over the estimated useful life of natural resources: Depletion This method of account is consistent with GAAP and creates the need for adjusting journal entries at period end: Accrual based accounting When selling a fixed asset for less then its book value this is generated as a debit: Loss on sale Using the indirect method of preparing the statement of cash flows this type of cash flow always begins with net income: Cash flow from operations Purchases of fixed assets are considered this type of cash flow in the statement of cash flow: Cash flow from investing When estimating bad debts based upon this this is your target balance in your allowance for doubtful accounts: Accounts receivable The financial statements basic format is assets= liabilities + equity= Balance sheet Estimates of bad debts are credited to this account when using the accrual basis of accounting: Allowance for doubtful accounts This type of stock is recorded as a contra equity account as cost when purchased by the company: treasury stock Accounts like accumulated depreciation and the allowance for doubtful accounts are considered these types of accounts: Contra assets This is the second closing entry in the sequence and it closes these accounts to income summary: closing expenses This is the third financial statement in order of preparation at period end: balance sheet This basis of account recognizes revenues when cash in received and expenses when cash is disbursed: Cash basis accounting This depreciation method allocated the cost of a fixed asset over its estimated useful life using the number of units produces: Units of production This is used to allocate the purchase price of fixed assets in a lump sum purchase: Fair market value Cash received for services yet to be provided is an example if this kind of adjusting journal entry: Unearned revenue. This metric is calculated as cost of goods sold/ average inventory: Inventory turnover These typoes of accounts increase with debits and decrease with credits: Assets This type of stock is given priority in dividend distribution and in case of company liquidation: preferd stock You debit this account when you purchase merchandise for resale in a perpetual inventory system: Merchandise inventory This step is when the accounting cycle begins: Identify and analyze business transactions This type of accont is closed during the recording of closing journal entries: Temporary You credit this account when the owner first invests cash into his/ her corporation: Common stock This to make an asset: Capitalize