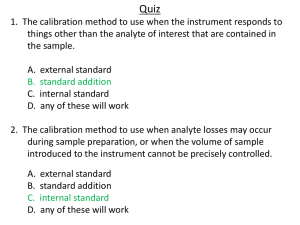
QUESTION In a standard addition method, you will prepare a series of solutions in which you add different increments of standard solutions to fixed aliquots of an unknown sample X i.e. 10.00 mL of X. All solutions were prepared using 50.00 mL volumetric flasks. Suppose that the analysis of standard solutions of X gave the following results: Solution Concentration of Added Standard, Absorbance ppm Standard 1 0.00 0.201 Standard 2 2.44 0.292 Standard 3 4.88 0.378 Standard 4 7.32 0.467 Standard 5 9.76 0.554 1. Plot the standard addition graph. (Graph below) 2. Determine the concentration of X (in ppm) in the unknown sample. CONCLUSION To summarize, we may draw the conclusion from this experiment that we learned more about the proper technique for operating a flame AAS instrument, which was necessary to follow to prevent the experiment from failing and harming the instrument. By getting the absorbance and the concentration of the solution that was utilised from the produced standard solutions of 1 ppm, 2 ppm, 3 ppm, 4 ppm, and 5 ppm, we can also plot a standard calibration curve for the determination of Ca in a sample. Finally, using the standard calibration curve that was plotted, the concentration of Ca in the sample was measured.