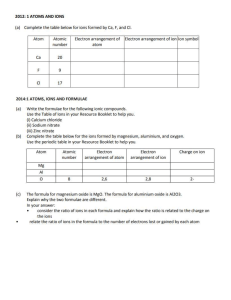
Classification: General Business Use Fertilizer Ca(NO3)2 CaSO4*2H2O All P Fertilizers Lime CaO, Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 CaMg(CO3)2 Calcium Cycle Other Shells Slag Marl Animals Decomposition of Plant and Animal Residues Ca2+ removed As plant matter 4x in leaves vs. grain OFF Moisture ON OFF Plants pH of Soil Dissolution Uptake decreases with Presence of high Al3+ ON Temporarily held on exchange sites, but tightly held on charged soils Mining Major Form Click on ON or OFF To see how the cycle Is effected by moisture Main Cycle Higher availability of Ca2+ Improves uptake of NH3 More Info Calcium Minerals Lime, Calcite, Dolomite, Gypsum, Florapatite, Plagioclases, Gabbro, Basalts Leaching CaCl2, CaSO4 Soil Microbes OFF Moisture Weathering (dissolution) ON Authers:Jason Warren, James Johnson, Derrel White, Lori Gallimore and Micah Deleon Classification: General Business Use Fertilizer Ca(NO3)2 CaSO4*2H2O All P Fertilizers Lime CaO, Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 CaMg(CO3)2 Other Shells Slag Marl Animals Decomposition of Plant and Animal Residues OFF Moisture ON Ca2+ removed As plant matter 4x in leaves vs. grain OFF Plants pH of Soil Dissolution ON Temporarily held on exchange sites, but tightly held on charged soils Mining Calcium Minerals Lime, Calcite, Dolomite, Gypsum, Florapatite, Plagioclases, Gabbro, Basalts Movement of calcium In the presents of moisture Main Cycle More Info Leaching CaCl2, CaSO4 Uptake decreases with Presence of high Al3+ Higher availability of Ca2+ Improves uptake of NH3 Major Form OFF Moisture Weathering (dissolution) ON Soil Microbes Classification: General Business Use Fertilizer Ca(NO3)2 CaSO4*2H2O All P Fertilizers Lime CaO, Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 CaMg(CO3)2 Other Shells Slag Marl Dissolution of Fertilizer,Lime and Other sources of Ca2+ can not occur Animals Decomposition of Plant and Animal Residues OFF Moisture ON Ca2+ removed As plant matter 4x in leaves vs. grain OFF Plants pH of Soil Dissolution ON Temporarily held on exchange sites, but tightly held on charged soils Mining Calcium Minerals Lime, Calcite, Dolomite, Gypsum, Florapatite, Plagioclases, Gabbro, Basalts Leaching CaCl2, CaSO4 Main Cycle More Info Uptake decreases with Presence of high Al3+ Higher availability of Ca2+ Improves uptake of NH3 Major Form OFF Moisture Weathering (dissolution) ON Soil Microbes Classification: General Business Use More Information on Calcium Form taken up by plants: Deficiency symptoms: Mobility in soil: Effect of pH on availability: Mobility in plant: Sources of Calcium: Role of nutrient in plant growth: Mayo Clinic about Calcium and Osteoporosis Role in microbial growth: Interactions with other nutrients: References: Concentration in plants: Content present in soils: Main Cycle More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. on Calcium • Form taken up by plants Ca+2 • Mobility in Soil No, slight mobility in soil solution • Mobility in plant Movement occurs in xylem to the leaves (one way ticket) Main Cycle More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. on Calcium • Role of nutrient in plant growth: Required for cell wall rigidity, cell division of meristems and root tips, normal mitosis, membrane function, acts as a secondary messenger, aids in storage of phosphates in vacuoles, actively involved in photosynthesis and found in the endoplasmic reticulum • Role in microbial growth: Needed for Rhizobium and Azotobacter Main Cycle More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. on Calcium • Interactions with other nutrients: – Since Ca+2 is so directly related to pH in solution, it effects all of the other nutrients. When NO3-N is applied to soil, Ca+2 absorption increases in the plant. Increases in Ca+2 in soil decreases Al+3 in acid soils, as well as decreasing Na+ in sodic soils. Increases in Ca+2 taken up by plants cause deficiencies of Mg+2 and K+. MoO4-2 and H2PO4availability increases with increases in Ca+2 concentrations. Main Cycle More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. on Calcium • Concentration in plants: – Fresh weight of plants typically contains 0.1-5.0%, can contain up to 10% dry weight in leaves before plant experiences toxicity • Deficiency symptoms: – First seen in the younger leaves of plants, loss in plant structure, under extreme deficiencies gel-like conditions, root development no longer takes place, stunted plant growth Main Cycle More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. on Calcium • Content present in soils: – – – – Main Cycle Tropical soils: 0.1-0.3% Temperate soils: 0.7-1.5% Calcareous soils: >3.0% Largely dependent on parent material of soil and rainfall More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. on Calcium • Effect of pH on availability: Depends on mineral • Sources of Calcium: – Lime (CaO) (Ca(OH)2), Calcite (CaCO3), Dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2, Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O), any Phosphorus fertilizer, Anorthite (CaAl2Si2O3), biotite, apatite, augite & hornblende. Main Cycle More Info Classification: General Business Use More Info. On Calcium • References Amjad, Z. (ed.) 1998. Calcium Phosphates in Biological and Industrial Systems. Klower Academic Press. Boston, MA.Lindsay, W.L. 1979. Chemical Equilibria in Soils. John Wiley & Sons. New York, NY. pp. 86-102. Marschner, H. 1995. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press. New York, NY. pp. 285-298. Tisdale, S.L., Nelson, W.L., Beaton, J.D. and Havlin, J.L. 1993. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers. Macmillan Publishing Company. pp. 289-296. Main Cycle More Info