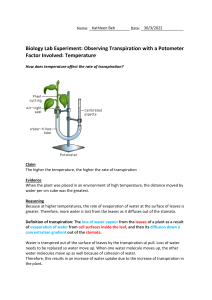
5.0 Conclusion Plants are called C3 plants because the first organic product of carbon fixation is a three-carbon compound which is 3-phosphoglycerate (Neil A Campbell, 2017). On arid, dry days, C3 plants produce less sugar because it close their stomata to prevent water less. This cause oxygen to build up O2 and CO2 will compete for the same active site on rubisco. O2 is a competitive inhibitor so when O2 concentration is higher than CO2, enzyme rubisco will fix oxygen to RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) instead of fixing CO2. This process is called photorespiration because it occurs in light and consumes O2 while producing CO2. In normal reaction, CO2 will combine with 5 carbon sugar named RuBP and form 2 molecule of 3phosphoglycerate but in photorespiration, O2 replace CO2 in non-productive wasteful reaction. Photorespiration produce no ATP in fact it consumes ATP. It does not produce sugar or organic molecule but decrease photosynthetic output by using organic material for Calvin Cycle. C3 plants have high rate photosynthesis compared to C4 and CAM plants. It also involved in transpiration which is the evaporation of water from plant leaves. There are several conditions that affect the rate of transpiration in C3 plants. Firstly, the temperature of the surrounding. If the temperature goes up, transpiration rates also goes up because the water can evaporates rapidly. Besides, the humidity. In a condition where humidity is high, the diffusion of water will decrease and causing the rate of transpiration also decreasing. Transpiration also can be increases by the presence of sunlight or in a light condition. The presence of sunlight can triggered the stomata to open and CO2 will then be used for lightdependent reaction of photosynthesis. Last but not least, the presence of wind also affect the rates of transpiration. When there is the presence of wind, the air surrounding the leaves will become dry and the transpiration rates will increasing. C3 plants have certain characteristics that helps it adapted to dry and hot condition. A deep root system and thick leaves able to make it more tolerate with heat. They also rolled their leaves and cause the stomata trapped inside the leaves and prevent water loss. The example of C3 plants are rice, wheat and soy beans (Neil A Campbell, 2017).