Module on Self, Materialism, Religion, and Filipino Identity
advertisement

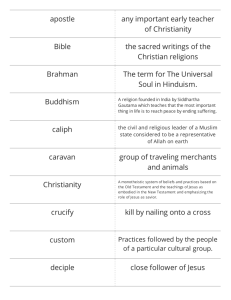
MODULE 2 Lesson I: Physical and Sexual Self In this lesson students may understand The physical self is our body that we use to interact with our environment and fellow beings. This is the concrete dimension and the tangible aspect of the person that can be directly observed and examined. On the other hand, our sexual self is defined as an individual’s evaluation of his/her sexual feelings and actions. These may include positive and negative concepts and feelings. in this lesson student are able to At the end of the lesson the students are able to: Recognize the importance of the beautiful self with the face t of the reproductive system. That may iclude the 5 sign of being beautiful person. Discuss the development aspect of the reproductive system; may identify the parts of men and woman. Describe the erogenous zones; mostly happens for young adulthood what may be the developemet in their body. Characterize the diversity of sexual behavior; which incude the different genders today. Describe sexually transmitted diseases STD that may cause of sexueal itercausen and lastly Differentiate natural, artificial methods of contraception and In Vitro Fertilizaion a little background for this we will know how is the proper way of giving birth ,the use of contraceptives and womens calendar and more process of the different methods . LESSON II:To Buy or Not To Buy? That is the Question! its learning outcomes are: At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to: Discover the signs of a materialistic person; 5 Signs Materialism Is Taking Over Your Life (And How To Take The Power Back) and the 11 ways on REDUCING MATERIALSM. Ending materialism doesn’t mean forsaking all your possessions. Ridding yourself of everything you own would only prove you are still too preoccupied with possessions themselves. Someone who has developed a healthy inner world would see possessions as neutral. This shift is more about attitude than specific actions.According to Russel Belk (1988) posits that ‘… we regard our possessions as part of ourselves. We are what we have and what we possess.” The identification of the self to things started in our infancy stage when we make a distinction among self and environment and others who may desire our possessions. Evaluate the statement “ I shop, therefore , I am” LESSON III Supernaturals: Believe it or Not! At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to: Describe some common religious practices related to your beliefs; Some World Religious Beliefs and Practices Buddhism Christianity Hinduism Muslim Judaism Integrate the self value with your religious beliefs; and Buddhism is a philosophy of life stated by Gautama Buddha means the "enlightened one", who lived and taught in northern India in the 6th century B.C. The Basic Teachings of Buddha which are core to Buddhism are: • The Three Universal Truths; • The Four Noble Truths; and • The Noble Eightfold Path. CHRISTIANITY Beliefs Christians are monotheistic, they believe there’s only one God, and he created the heavens and the earth. This divine Godhead consists of three parts: the father (God himself), the son (Jesus Christ) and the Holy Spirit. The essence of Christianity revolves around the life, death and Christian beliefs on the resurrection of Jesus. Christians believe God sent his son Jesus, the messiah, to save the world. They believe Jesus was crucified on a cross to offer the forgiveness of sins and was resurrected three days after his death before arise to heaven. o Christians contend that Jesus will return to earth again in what’s known as the Second Coming. o The Holy Bible includes important scriptures that outline Jesus’s teachings, the lives and teachings of Major Prophets and disciples, and offer instructions for how Christians should live. o Both Christians and Jews follow the Old Testament of the Bible, but Christians also embrace the New Testament. o The cross is a symbol of Christianity. o The most important Christian holidays are Christmas (which celebrates the birth of Jesus) and Easter (which commemorates the resurrection of Jesus). HINDUISM Beliefs Some basic Hindu concepts include: • Hinduism holds many religious ideas. For this reason, it’s sometimes referred to as a “way of life” or a “family of religions,” as opposed to a single, organized religion. • Most forms of Hinduism are henotheistic, which means they worship a single divinity, known as “Brahman,” but still recognize other gods and goddesses. Followers believe there are multiple paths to reaching their god. • Hindus believe in the doctrines of samsara (the continuous cycle of life, death, and reincarnation) and karma (the universal law of cause and effect). • One of the key thoughts of Hinduism is “atman,” or the belief in soul. This philosophy holds that living creatures have a soul, and they’re all part of the supreme soul. The goal is to achieve “moksha,” or salvation, which ends the cycle of rebirths to become part of the absolute soul. • One fundamental principle of the religion is the idea that people’s actions and thoughts directly determine their current life and future lives. • Hindus strive to achieve dharma, which is a code of living that emphasizes good conduct and morality. • Hindus revere all living creatures and consider the cow a sacred animal. • Food is an important part of life for Hindus. Most don’t eat beef or pork, and many are vegetarians. • Hinduism is closely related to other Indian religions, including Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. Islam Facts • The word “Islam” means “submission to the will of God.” • Followers of Islam are called Muslims. • Muslims are monotheistic and worship one, all-knowing God, who in Arabic is known as Allah. • Followers of Islam aim to live a life of complete submission to Allah. They believe that nothing can happen without Allah’s permission, but humans have free will. • Islam teaches that Allah’s word was revealed to the prophet Muhammad through the angel Gabriel. • Muslims believe several prophets were sent to teach Allah’s law. They respect some of the same prophets as Jews and Christians, including Abraham, Moses, Noah and Jesus. Muslims contend that Muhammad was the final prophet. • Mosques are places where Muslims worship. • Some important Islamic holy places include the Kaaba shrine in Mecca, the Al-Aqsa mosque in Jerusalem, and the Prophet Muhammad’s mosque in Medina. • The Quran (or Koran) is the major holy text of Islam. The Hadith is another important book. Muslims also revere some material found in the Judeo-Christian Bible. • Followers worship Allah by praying and reciting the Quran. They believe there will be a Day of Judgment, and life after death. • A central idea in Islam is “jihad,” which means “struggle.” While the term has been used negatively in mainstream culture, Muslims believe it refers to internal and external efforts to defend their faith. Although rare, this can include military jihad if a “just war” is needed. Judaism Beliefs • Jewish people believe there’s only one God who has established a covenant or special agreement with them. Their God communicates to believers through prophets and rewards good deeds while also punishing evil. • Most Jews (with the exception of a few groups) believe that their Messiah hasn’t yet come—but will one day. Elaborate ways of seeking the meaning of life According to Gomez, 2012 these are the tips on how to find meaning of life 1. Stop Playing by the rules Some people find that the meaning of life is to have a career, get married, and raise a family. However, that doesn't mean that everyone is meant to do that in their lives. 2. Step out of your comfort zone The term comfort zone is code for a place you live in yourself without fear. 3. Find your joy This step again relies on a solid grounding in making adventurous activities that you may just find bring you an incredible amount of freedom and happiness. When you know what truly makes you happy and joyful in life, then you will find a sense of purpose to your life. 4. Listen to your intuition Your intuition is connected to your inner-self. Finding the real person inside yourself is not easy but will definitely help you see what is really important in your life. 5. Appreciate the individual moments Don’t let the fast-paced superficial world take over your life. LESSON IV The Political Self and Being Filipino At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to: Identify Filipino values and traits , which you arre goimg to answer the values/t Appreciate the identity of being a Filipino through a creative illustration Build up Filipino feeling of patriotism. To participate in community outreach, and following the rules of grovernmemt. To conclude MODULE 2 with Iwiith IV lessons we are able to where we will learn the process of different methods, how to survive from being materialistic person ,also we have learn the different facts of religions, lastly on how we will describe oursel as a filipino and their values and traits.