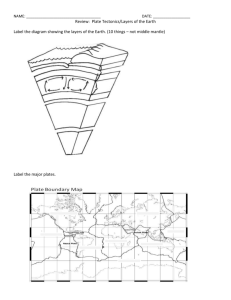
Geography Plate Tectonics: ➔ Layers of the Earth: - - Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust The plates below the land are called Continental Plates The plates below the ocean are called Oceanic Plates ➔ Type of Crust: ◆ Continental Crust: ○ ○ Thick Granite Low in density so it floats on the mantle ◆ Oceanic Crust: ● ● ○ Basalt Rock ○ High in density ○ Very Thin(1-3 miles) The granite is slightly lighter in density than mantle so Continental crust floats on the mantle The basalt is denser than the mantle so the the Oceanic crust kinda sinks into the mantle; leaving the Oceanic goes below the Continental ➔ Convectional: - The movement of the mantle denotes the position of the plates The flow of the mantle simultaneously also moves the plates ➔ Types of Plates Boundaries: ◆ Divergent: ○ 2 plates move away from each other ◆ Transform: ○ ○ 2 Plates move horizontally past each other Cause of Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruption ◆ Convergent: ○ ○ 2 Plates colliding Formation of mountains ◆ Subduction: ○ ○ When a Oceanic and Continental collide and the oceanic goes below and continental above - due to density - and the oceanic to goes as deep as the core where there is Magma Creation of Volcano and eruptions ➔ Types of Volcanoes: ◆ Active ◆ Dormant ◆ Extinct ➔ Types of Volcanic Eruptions: ◆ Ash Volcanoes ○ ○ ○ Eruption is usually in ashes Has steep-sides and large craters Example: Paricutin, Mexico ◆ Lava/Strato/Composite/Cone Volcanoes ○ Eruption in thick, slow-flowing lava ○ ○ Has steep-sided Example: Cotopaxi, Ecuador ◆ Lava/Dome/Shield Volcanoes ○ Eruption in runny, fast-flowing lava ○ ○ Has gentle slopes Example: Mauna Loa, HawaiI ➔ Features of Volcano: ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ Crater Ash Cloud/Volcanic Bombs Fallen Ashes Lava Flow Layers of ash and lava Conduit/Main Vent Magma Chamber ➔ ‘Three Ps’ Policy: ◆ Predict ○ ○ ○ Earthquakes most likely happen after a long period without any plate movement There will be many small small foreshocks before the main one. These can be measured by a Seismograph Animals often act strange before a earthquake ◆ Protect ○ In a building: - Cross-bracings allow the building to twist - Large concrete weight on the top controlled by a computer to move in opposite direction to the earthquake’s forces - Large rubber shock-absorbers at the bottom Strengthen existing roads, buildings and bridges ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Disaster plans and regular practices Train emergence forces(police, fire and ambulance) Have hospitals and evacuation center at safe places Educate people on what to except and what will happen Emergency supplies Earthquake warning and info systems ○ ◆ Prepare China - The emerging nation: ➔ Physical Features: ◆ North-west ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Rainfall is light and evenly spread throughout the year Extreme cold with high wind in winter, warm summer Lack of vegetation due to climate Mainly desert and mountains Hazards: Dust-storms and annual drought ◆ South-west ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Winter are very cold & dry and Summer are warm & wet Large range in annual temperature Limited vegetation Himalayas and the Tibet Plateau Hazards: Snow and high winter winds ◆ North-east, ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Very dry and cold cold winter and warm and wet summers Large annual range in temperature Forest near coast and grassland inland North China plains, Valley of the Huang He and Yellow River Hazards: Cold winter with humidity, soil erosion, river flooding and occasional drought ◆ South-east ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Warm and dry winter and hot wet summers Low annual range of temperature Tropical rainforest Mainly low mountains Hazards: Typhoons and high humidity in summers ➔ One-child Policy: ◆ In 1979, the ‘One-child Policy’ was established for stabilizing the population ◆ There was a minimum age for marriage and couples had to apply for it, same for having a baby ○ For those who failed to conform were deprived of benefits, had to pay a fine and were forced for abortion ○ There were exception for having a second child to families having a disabled child, belonging to an ethnic minority group or living in a remote place ◆ The 4-2-1 structure was a family structure, when an ‘one-only’ child started to work- they had to take care of ‘1’- themselves; ‘2’- their parents; ‘4’- their grandparents ➔ Shikumen Housing: ◆ Means ‘stone-framed door’ ◆ Are 2 or 3 storey buildings on narrow lanes; are made of wood; house lacks running water and electricity - everyday a cart collect sewage and waste ◆ Faced problems are: ○ ○ ○ Overcrowding Air pollution Traffic congestion ➔ Pudong: ◆ In 1989, Government decided a new settlement in Pudong which was a rice field- when work started from 1993 to 2000 ◆ Today is a major center for commerce and finance ◆ Rural-to-urban migration brought many farmers to mainland China ➔ Traffic: ◆ First attempt on traffic solution was in Shanghai by a 47 km ring road ◆ Took less than 3 years ◆ People were forced to leave their Shikumen housing - they were happy for the modern amenities but not for how far they were from their work ➔ Sichuan: ◆ There are still many farmers in China who don’t get enough money or food, they live at a subsistence level ○ ‘Subsistence farming’ is when they farm for the families needs only and the extra cultivation will be sold ◆ Many of them are now move to the cities and leaving their houses behind ➔ Shenzhen: ◆ When the chinese government made Shenzhen a Special Economic Zone to begin with trading ◆ The stages: ○ ○ ○ Attracted industries in Hong Kong by cheap labor and land Arrival of well-known global firms Rapid growth in high-tech industries ◆ Shenzhen-based companies all provided goods to Wal-Mart Stores Inc. ◆ Shenzhen became the’power-house’ of China ◆ Problems: ○ ○ ○ ○ Expense increased More work hours due to low wages Less attention to health and safety Growth no spread equally throughout the county International Development ➔ Overpopulation: ◆ Is when the resources of an area can’t support the population living there ➔ Employment Structure: ◆ The proportion of the population working in each sector(Primary, Secondary, Tertiary) ◆ Primary: ○ Production of raw materials ◆ Secondary: ○ Manufacturing goods ○ Services to the people ◆ Tertiary: ➔ Trade: ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ Trade is the exchange of goods Goods sold to other countries is Export Buying goods from other countries is Import Raw and Low value products are Primary goods ◆ Manufactured and high value products are Manufactured goods ◆ The many LEDCs only export one major product so their income is dependent on that one product ○ ○ - If there is a situation where they can’t export that good their economy will fall This is the reason why poor countries stay poor A way to measure a country’s wealth is by the country’s GNP(Gross National Product)