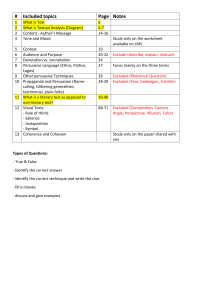
Words sounds images or objects, that serve as vehicles for the communication of meaning,…they represent meaning concepts, object people and things How do we understand signs? We draw on existing knowledge We apply on existing knowledge to new situations We do this both as audience and as creators We use codes: frameworks of meaning that define how we interpret a sign Examples: language, colour, style, genre, haircuts, clothing, rules, noise, beleifs, history Denotation - The first order of meaning – blatant, primary signification. Connotation – the second order of meaning – depend on more complex/specific cultural codes Representation – Signs are produced with intent to communicate This makes them re-representations Consider what is included and what’s excluded and who made these choices Word choices Framing choices Narrative choices What’s the story being told and what’s included/excluded in the story Week 3 readings: The flow of content across multiple media platforms, the cooperation between multiple media industries and the migratory behavior of media audiences who will go almost anywhere in search of the kinds of entertainment experiences they want. Convergence can be used to describe technological, cultural, social and industrial changes. Buzz = consumers talking about the media they consume Convergance – an old concept taking on a new meanings Remediation: Week 5: Hybrid economies: Many online contexts are far more complex than being commercial or noncommercial, they are often both Production Regimes Industrial Standardised, predictable, scheduled, contracted, financially motivated Social Passionate, unpredictable, fluid and unstable, non-contracted, coailly creative, motivated We need to reconsider our understanding of labour exploitation, rights and processes in online networked productions Key ideas: Participatory media Audience Content production Collective intelligence Branding through user generated content Labour and exploitation